
Trigona is one of the largest genera of stingless bees, comprising about 32 species, exclusively occurring in the New World, and formerly including many more subgenera than the present assemblage; many of these former subgenera have been elevated to generic status.
Pahabengkakia piliceps is a species of true bug (harpactorinae) found in Thailand. This species is apparently a specialist predator of the stingless bee Trigona collina. Larval P. piliceps mimic the bees, and eggs are laid in the bees' hives. Nymphs of P. piliceps were found to occupy the nest entrance and kill returning foraging bees. The assassin bug does not seem to predate other Trigona species, even though they are also present in the area.

Tetragonula carbonaria is a stingless bee, endemic to the north-east coast of Australia. Its common name is sugarbag bee. They are also occasionally referred to as bush bees. The bee is known to pollinate orchid species, such as Dendrobium lichenastrum, D. toressae, and D. speciosum. It has been identified as an insect that collects pollen from the cycad Cycas media. They are also known for their small body size, reduced wing venation, and highly developed social structure comparable to honey bees.

Trigona spinipes is a species of stingless bee. It occurs in Brazil, where it is called arapuá, aripuá, irapuá, japurá or abelha-cachorro ("dog-bee"). The species name means "spiny feet" in Latin. Trigona spinipes builds its nest on trees, out of mud, resin, wax, and assorted debris, including dung. Therefore, its honey is not fit for consumption, even though it is reputed to be of good quality by itself, and is used in folk medicine. Colonies may have from 5,000 to over 100,000 workers.

Tetragonisca angustula is a small eusocial stingless bee found in México, Central and South America. It is known by a variety of names in different regions. A subspecies, Tetragonisca angustula fiebrigi, occupies different areas in South America and has a slightly different coloration.

The Indian stingless bee or dammar bee, Tetragonula iridipennis, is a species of bee belonging to the family Apidae, subfamily Apinae. It was first described by Frederick Smith in 1854 who found the species in what is now the island of Sri Lanka. Many older references erroneously placed this species in Melipona, an unrelated genus from the New World, and until recently it was placed in Trigona, therefore still often mistakenly referred to as Trigona iridipennis. For centuries, colonies of T. iridipennis have been kept in objects such as clay pots so that their highly prized medicinal honey can be utilized.

Trigona corvina is a species of stingless bee that lives primarily in Central and South America. In Panama, they are sometimes known as zagañas. They live in protective nests high in the trees, but they can be extremely aggressive and territorial over their resources. They use their pheromones to protect their food sources and to signal their location to nest mates. This black stingless bees of the tribe Meliponini can be parasitic toward citrus trees but also helpful for crop pollination.

Scaptotrigona postica is a species of stingless bee that lives mainly in Brazil. It is a eusocial bee in the tribe Meliponini. S. postica is one of 25 species in the genus Scaptotrigona and is a critical pollinator of the tropical rain forests of Brazil. They construct their nests in hollowed sections of tree trunks, allowing for effective guarding at the nest entrance. This species shows colony structure similar to most members of the Meliponini tribe with three roles within the colony: queen, worker, and male. S. postica individuals have different forms of communication from cuticular hydrocarbons to pheromones and scent trails. Communication is especially useful during worker foraging for nectar and pollen through the Brazilian tropical rain forests. S. postica is a very important pollinator of the Brazilian tropical rain forests and is widely appreciated for its honey. Stingless bees account for approximately 30% of all pollination of the Brazilian Caatinga and Pantanal ecosystems and up to 90% of the pollination for many species of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest and the Amazon.

Melipona quadrifasciata is a species of eusocial, stingless bee of the order Hymenoptera. It is native to the southeastern coastal states of Brazil, where it is more commonly known as mandaçaia, which means "beautiful guard," as there is always a bee at the narrow entrance of the nest. M. quadrifasciata constructs mud hives in the hollows of trees to create thin passages that only allow one bee to pass at a time. Because they are stingless bees, M. quadrifasciata is often used as pollinators in greenhouses, outperforming honey bees in efficiency and leading to overall larger yields of fruits that were heavier, larger, and contained more seeds.

Tetragonula is a genus of stingless bees. In 1961, Brazilian bee expert J.S. Moure first proposed the genus name Tetragonula to improve the classification system by dividing the large genus Trigona stingless bees into 9 smaller groups. About 30 stingless bee species formerly placed in the genus Trigona are now placed in the genus Tetragonula. These bees are found in Oceania, in countries such as Australia, Indonesia, New Guinea, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, India, Sri Lanka, and the Solomon Islands. The most recent tabulation of species listed 31 species.
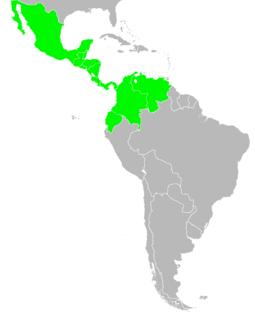
Trigona fuscipennis is a stingless bee species that originates in Mexico but is also found in Central and South America. They are an advanced eusocial group of bees and play a key role as pollinators in wet rainforests. The species has many common names, including "mapaitero", "sanharó", "abelha-brava", "xnuk", "k'uris-kab", "enreda", "corta-cabelo", "currunchos", "zagaño", and "enredapelos".

Trigona fulviventris, known by the common names "culo-de-vaca," "culo-de-señora," "mu'ul-kab," "culo-de-buey," and "culo-de-vieja," is a species of stingless bee found in neotropical regions of Central and South America. It is one of the largest and most widespread bees of its genus. They exhibit complex foraging behaviors by integrating spatio-temporal learning and flower scents. T. fulviventris has traditionally been observed to abstain from aggressive behavior with other species; however, more recent analyses have shown that T. fulviventris emit pheromones that act as attack signals particularly when related individuals are captured by predators.

Lestrimelitta limao is a neotropical eusocial bee species found in Brazil and Panama and is part of the Apidae family. It is a species of stingless bees that practices obligate nest robbing. They have never been spotted foraging from flowers, an observation that supports their raiding behavior. Because of their lack of hind corbiculae, they must raid to obtain enough protein in their diet in the form of pollen and nectar. Lestrimelitta limao secrete a lemon-scented alarm allomone, from which they receive their name, in order to conduct successful raids. L. limao are hypothesized to produce poisonous honey that is toxic if consumed by humans. Because robber bees are so rare and difficult to observe, there is a limited scope of information available.
Syntretus is a genus of parasitic wasps of adult bumblebees.
Trigona dimidiata is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini.
Trigona cilipes is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini.
Trigona amalthea, commonly known as jandaíra-preta or sanharão in Brazil, is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini.
Trigona branneri is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini.
Trigona chanchamayoensis is a species of eusocial stingless bee in the family Apidae and tribe Meliponini.

Tetragonula mellipes is a small eusocial stingless bee first described by Friese in 1898 and it is found in Northern Australia.











