Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6H2(OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates".
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.

Catechol, also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(OH)2. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances.
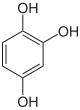
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols.
The chlorobenzenes are a family of covalent compounds consisting of one or more chlorine atoms as substituents on a benzene core. Depending on the number of chlorine substituents, there may be several constitutional isomers possible.

Durene, or 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H2(CH3)4. It is a colourless solid with a sweet odor. The compound is classified as an alkylbenzene. It is one of three isomers of tetramethylbenzene, the other two being prehnitene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) and isodurene (1,2,3,5-tetramethylbenzene). Durene has an unusually high melting point (79.2 °C), reflecting its high molecular symmetry.
In enzymology, a cholestanetetraol 26-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.161) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrogallol hydroxytransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cholestanetriol 26-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydroxyquinol 1,2-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.37) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrogallol 1,2-oxygenase (EC 1.13.11.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a petromyzonol sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Damascenones are a series of closely related chemical compounds that are components of a variety of essential oils. The damascenones belong to a family of chemicals known as rose ketones, which also includes damascones and ionones. beta-Damascenone is a major contributor to the aroma of roses, despite its very low concentration, and is an important fragrance chemical used in perfumery.

Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Pelobacter acidigallici is the type species in the bacterial genus Pelobacter.
Norbert Pfennig was a German microbiologist.

1,2,3,5-Tetrahydroxybenzene is a benzenetetrol.

Tetrahydroxybenzenes or Benzenetetrols are a group of organic compounds which are tetrahydroxy derivatives of benzene. Tetrahydroxybenzene comes in three isomers:
Pelobacter propionicus is a species of bacteria that ferments 2,3-butanediol and acetoin. It is Gram-negative, strictly anaerobic and non-spore-forming. Ott Bd 1 is the type strain.

1,2,3,4-Cyclohexanetetrol (also named cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetrol, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroxycyclohexane, or ortho-cyclohexanetetrol) is an organic compound whose molecule can be described as a cyclohexane with four hydroxyl (OH) groups substituted for hydrogen atoms on four consecutive carbon atoms. Its formula can be written C
6H
12O
4, C
6H
8(OH)
4, or (–CH(OH)–)4(–CH
2–)2.