A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
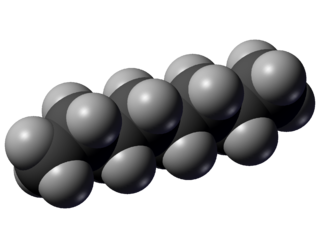
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane) is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
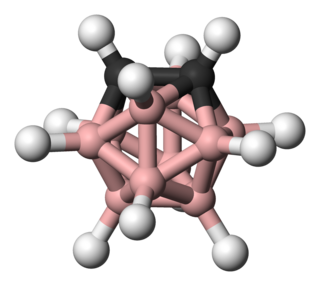
Carboranes are electron-delocalized clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms. Like many of the related boron hydrides, these clusters are polyhedra or fragments of polyhedra. Carboranes are one class of heteroboranes.
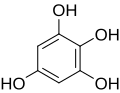
Dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three isomer: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
Trimethoxyamphetamines (TMAs) are a family of isomeric psychedelic hallucinogenic drugs. There exist six different TMAs that differ only in the position of the three methoxy groups: TMA, TMA-2, TMA-3, TMA-4, TMA-5, and TMA-6. The TMAs are analogs of the phenethylamine cactus alkaloid mescaline. The TMAs are substituted amphetamines, however, their action does not resemble that of the unsubstituted compound amphetamine, which is a stimulant and not a psychedelic. It is reported that some TMAs elicit a range of emotions ranging from sadness to empathy and euphoria. TMA was first synthesized by Hey, in 1947. Synthesis data as well as human activity data has been published in the book PiHKAL.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.

Dinitrophenols are chemical compounds which are nitro derivatives of phenol.
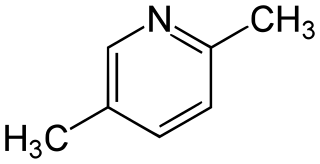
Lutidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are dimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Lutidine comes in several isomers:
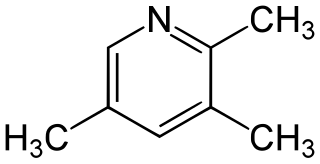
Collidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are trimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Collidine comes in several isomers:
Pyridinecarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are monocarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinecarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:
1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.
The molecular formula C6H6O4 (molar mass : 142.10 g/mol, exact mass : 142.026608 u) may refer to:
Mononitrotoluene, or methylnitrobenzene or nitrotoluene (MNT or NT), is a group of three organic compounds, a nitro derivative of toluene (or alternatively a methyl derivative of nitrobenzene). Its chemical formula is C6H4(CH3)(NO2).
A trichlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains three covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Trichlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine. Different isomers of trichlorophenol exist according to which ring positions on the phenol contain chlorine atoms. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, for example, has two chlorine atoms in the ortho positions and one chlorine atom in the para position.
Dichlorophenols (DCPs) are any of several chemical compounds which are derivatives of phenol containing two chlorine atoms. There are six isomers:

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae — that is, same number of atoms of each element — but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
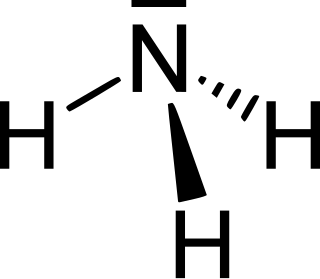
Azanes are acyclic, saturated hydronitrogens, which means that they consist only of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms and all bonds are single bonds. They are therefore pnictogen hydrides. Because cyclic hydronitrogens are excluded by definition, the azanes comprise a homologous series of inorganic compounds with the general chemical formula N
nH
n+2.

Benzenedicarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenedicarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

Pyridinedicarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinedicarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:
Pyridinetricarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinetricarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.