In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.

A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.

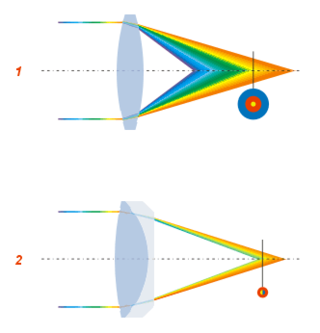
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion and spherochromatism, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image.

A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes.

A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.
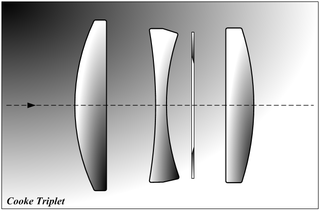
The Cooke triplet is a photographic lens designed and patented in 1893 by Dennis Taylor who was employed as chief engineer by T. Cooke & Sons of York. It was the first lens system that allowed elimination of most of the optical distortion or aberration at the outer edge of the image.
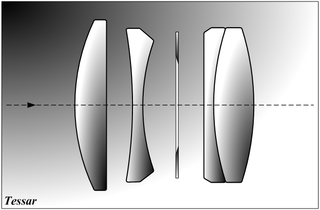
The Tessar is a photographic lens design conceived by the German physicist Dr. Paul Rudolph in 1902 while he worked at the Zeiss optical company and patented by Zeiss in Germany; the lens type is usually known as the ZeissTessar. Since its introduction, millions of Tessar and Tessar-derived lenses have been manufactured by Zeiss and other manufacturers, and are still produced as excellent intermediate aperture lenses.

A refracting telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image. The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece.

A zoom lens is a system of camera lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed-focal-length (FFL) lens.

In optical engineering, an objective is an optical element that gathers light from an object being observed and focuses the light rays from it to produce a real image of the object. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses.

An optical system with astigmatism is one where rays that propagate in two perpendicular planes have different foci. If an optical system with astigmatism is used to form an image of a cross, the vertical and horizontal lines will be in sharp focus at two different distances. The term comes from the Greek α- (a-) meaning "without" and στίγμα (stigma), "a mark, spot, puncture".

A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle. A magnifying glass can be used to focus light, such as to concentrate the Sun's radiation to create a hot spot at the focus for fire starting.

An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens that has better correction of chromatic and spherical aberration than the much more common achromat lenses.

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through an optical device to observe an object or sample. The objective lens or mirror collects light from an object or sample and brings it to focus creating an image of the object. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image to the eyes. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.

A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors.

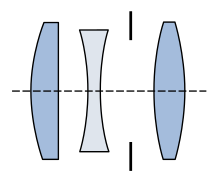
In optics, a doublet is a type of lens made up of two simple lenses paired together. Such an arrangement allows more optical surfaces, thicknesses, and formulations, especially as the space between lenses may be considered an "element". With additional degrees of freedom, optical designers have more latitude to correct more optical aberrations more thoroughly.

In photography, purple fringing is the term for an unfocused purple or magenta "ghost" image on a photograph. This optical aberration is generally most visible as a coloring and lightening of dark edges adjacent to bright areas of broad-spectrum illumination, such as daylight or various types of gas-discharge lamps.

An anastigmat or anastigmatic lens is a photographic lens completely corrected for the three main optical aberrations: spherical aberration, coma, and astigmatism. Early lenses often included the word Anastigmat in their name to advertise this new feature.
The design of photographic lenses for use in still or cine cameras is intended to produce a lens that yields the most acceptable rendition of the subject being photographed within a range of constraints that include cost, weight and materials. For many other optical devices such as telescopes, microscopes and theodolites where the visual image is observed but often not recorded the design can often be significantly simpler than is the case in a camera where every image is captured on film or image sensor and can be subject to detailed scrutiny at a later stage. Photographic lenses also include those used in enlargers and projectors.

The invention of the camera in the early 19th century led to an array of lens designs intended for photography. The problems of photographic lens design, creating a lens for a task that would cover a large, flat image plane, were well known even before the invention of photography due to the development of lenses to work with the focal plane of the camera obscura.