
In geology, a boulder is a rock fragment with size greater than 25.6 cm (10.1 in) in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive. In common usage, a boulder is too large for a person to move. Smaller boulders are usually just called rocks or stones.

Chatfield Hollow State Park is a public recreation area occupying 412 acres (167 ha) that lie adjacent to Cockaponset State Forest in the town of Killingworth, Connecticut. The state park offers hiking trails, a swimming beach, trout fishing, mountain biking, rock climbing, and picnicking areas. Park attractions include 6.67-acre (2.70 ha) Schreeder Pond, Indian caves, historic sites, a restored water wheel, and a reproduction covered bridge. The park is managed by the Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection.

A glacial erratic is a glacially deposited rock differing from the type of rock native to the area in which it rests. Erratics, which take their name from the Latin word errare, are carried by glacial ice, often over distances of hundreds of kilometres. Erratics can range in size from pebbles to large boulders such as Big Rock in Alberta.

Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have extensive occurrences of glacial landforms; other areas, such as the Sahara, display rare and very old fossil glacial landforms.

Ringing rocks, also known as sonorous rocks or lithophonic rocks, are rocks that resonate like a bell when struck. Examples include the Musical Stones of Skiddaw in the English Lake District; the stones in Ringing Rocks Park, in Upper Black Eddy, Bucks County, Pennsylvania; the Ringing Rocks of Kiandra, New South Wales; and the Bell Rock Range of Western Australia. Ringing rocks are used in idiophonic musical instruments called lithophones.

Okotoks Erratic is a 16,500-tonne (18,200-ton) boulder that lies on the otherwise flat, relatively featureless, surface of the Canadian Prairies in Alberta. It is part of the 930-kilometre-long (580 mi) Foothills Erratics Train of typically angular boulders of distinctive quartzite and pebbly quartzite.

The Midstate Trail is a scenic footpath which runs 92 miles (148 km) through Worcester County, Massachusetts, from the Rhode Island border to the New Hampshire border, approximately 45 miles (72 km) west of Boston. The trail is considered highly accessible, scenic, and remarkably rural despite its proximity to urban Boston. The trail includes the summits of Mount Wachusett and Mount Watatic, as well as many interesting geologic, historic, and natural features.

Hickory Run State Park is a 15,990-acre (6,471 ha) Pennsylvania state park in Kidder and Penn Forest Townships in Carbon County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is spread across the Pocono Mountains. The park is easily accessible from Interstate 476 and Interstate 80.

Rocking stones are large stones that are so finely balanced that the application of just a small force causes them to rock. Typically, rocking stones are residual corestones formed initially by spheroidal weathering and have later been exposed by erosion or glacial erratics left by retreating glaciers. Natural rocking stones are found throughout the world. A few rocking stones might be man-made megaliths.

Bear Mountain is one of the best-known peaks of New York's Hudson Highlands. Located partially in Orange County in the town of Highlands and partially in Rockland County in the town of Stony Point, it lends its name to the nearby Bear Mountain Bridge and Bear Mountain State Park that contains it.
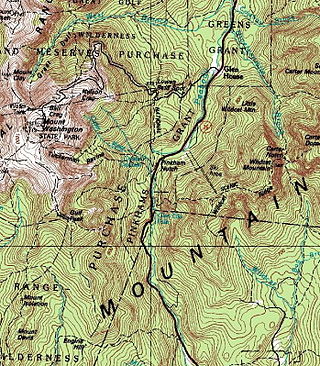
Pinkham Notch is a mountain pass in the White Mountains of north-central New Hampshire, United States. The notch is a result of extensive erosion by the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the Wisconsinian ice age. Pinkham Notch was eroded into a glacial U-shaped valley whose walls are formed by the Presidential, Wildcat, and Carter-Moriah ranges. Due to the volatility of the area's climate and rugged character of the terrain, a number of rare or endemic ecosystems have developed throughout the notch.

The Monoliths, also known as Agassiz Rock, is a 116-acre (47 ha) park in Manchester-by-the-Sea, Massachusetts, owned and maintained by The Trustees of Reservations. The park's name is from two examples of large glacial erratic boulders plucked from bedrock. As glaciers scoured this landscape, the mass of bedrock forming the hill proved more resistant than the surrounding soil, forcing the bottom of the glacier up and over the hill. The north side was smoothed and the south side left steep and rugged as the glacier broke off chunks of rock as it passed.

The Foothills Erratics Train is a 580 miles (930 km) long, narrow, linear scatter of thousands of typically angular boulders of distinctive quartzite and pebbly quartzite that lie on the surface of a generally north-south strip of the Canadian Prairies. These boulders, which are between 1 foot (0.30 m) and 135 feet (41 m) in length, are glacial erratics that lie upon a surficial blanket of Late Wisconsin glacial till. The largest glacial erratic within the Foothills Erratics Train is Big Rock.

Boulder Park National Natural Landmark, of Douglas County, Washington, along with the nearby McNeil Canyon Haystack Rocks and Sims Corner Eskers and Kames natural landmarks, illustrate well-preserved examples of classic Pleistocene ice stagnation landforms that are found in Washington. These landforms include numerous glacial erratics and haystack rocks that occur near and on the Withrow Moraine, which is the terminal moraine of the Okanogan ice lobe.

The Ice Age Floods National Geologic Trail is a network of routes connecting natural sites and facilities that provide interpretation of the geological consequences of the Glacial Lake Missoula floods of the last glacial period that occurred about 18,000 to 15,000 years ago. It includes sites in Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana. It was designated as the first National Geologic Trail in the United States in 2009.

A balancing rock, also called a balanced rock or precarious boulder, is a naturally occurring geological formation featuring a large rock or boulder, sometimes of substantial size, resting on other rocks, bedrock, or on glacial till. Some formations known by this name only appear to be balancing, but are in fact firmly connected to a base rock by a pedestal or stem.

Goffle Hill, also referred to as Goffle Mountain and historically known as Totoway Mountain and Wagaraw Mountain, is a range of the trap rock Watchung Mountains on the western edge of the Newark Basin in northern New Jersey. The hill straddles part of the border of Bergen County and Passaic County, underlying a mostly suburban setting. While hosting patches of woodlands, perched wetlands, and traprock glades, the hill is largely unprotected from development. Extensive quarrying for trap rock has obliterated large tracts of the hill in North Haledon, and Prospect Park. Conservation efforts seeking to preserve undeveloped land, such as the local Save the Woods initiative (2007–present), are ongoing.

Bear Peak is a mountain summit in the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The 8,459-foot (2,578 m) peak is located in Boulder Mountain Park, 5.2 miles (8.3 km) south-southwest of downtown Boulder in Boulder County, Colorado, United States.

Glacial erratic boulders of King County are large glacial erratic boulders of rock which were moved into King County, Washington by glacial action during previous ice ages.

The Glen Rock is a 570-ton boulder located in Glen Rock, New Jersey, United States. The boulder, which is the namesake of the town in which it is located, is the largest glacial erratic found atop Triassic bedrock in the state of New Jersey. The exact origin of the rock is uncertain, though studies alternatively place its origin in New York State's Hudson Highlands and the New Jersey Highlands. The Glen Rock, which is composed of gneiss, is located in the center of a former glacial lake.




















