Related Research Articles

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.
A borate is any of a range of boron oxyanions, anions containing boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate BO3−3, metaborate BO−2, or tetraborate B4O2−7; or any salt of such anions, such as sodium metaborate, Na+[BO2]− and borax (Na+)2[B4O7]2−. The name also refers to esters of such anions, such as trimethyl borate B(OCH3)3.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.

Trisodium phosphate (TSP) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na3PO4. It is a white, granular or crystalline solid, highly soluble in water, producing an alkaline solution. TSP is used as a cleaning agent, builder, lubricant, food additive, stain remover, and degreaser.
Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although the latter may not be a stable compound.

Sodium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and in alcohol. It is usually encountered as the monohydrate. The compound is noteworthy as the most water-soluble of the common perchlorate salts.
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written NaH2BO4, Na2H4B2O8, or, more properly, [Na+]2[B2O4(OH)4]2−. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS.

Sodium permanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaMnO4. It is closely related to the more commonly encountered potassium permanganate, but it is generally less desirable, because it is more expensive to produce. It is mainly available as the monohydrate. This salt absorbs water from the atmosphere and has a low melting point. Being about 15 times more soluble than KMnO4, sodium permanganate finds some applications where very high concentrations of MnO4− are sought.

Sodium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3AsO4. Related salts are also called sodium arsenate, including Na2HAsO4 (disodium hydrogen arsenate) and NaH2AsO4 (sodium dihydrogen arsenate). The trisodium salt is a white or colourless solid that is highly toxic. It is usually handled as the dodecahydrate Na3AsO4.12H2O.

Disodium octaborate is a borate of sodium, a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen — a salt with elemental formula Na2B8O13 or (Na+)2[B8O13]2−, also written as Na2O·4B2O3. It is a colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water.
Sborgite is a sodium borate mineral with formula Na[B5O6(OH)4]·3H2O. The formula can be written as the oxide formulation, Na2O.5B2O3.10H2O. Sometimes called sodium pentaborate pentahydrate it contains the pentaborate anion, (B5O6(OH)4)−.

Sodium monothiophosphate, or sodium phosphorothioate, is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Na3PO3S(H2O)x. All are white solids. The anhydrous material (x = 0) decomposes without melting at 120-125 °C. More common is the dodecahydrate. A nonahydrate is also known.
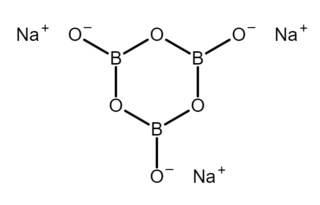
Sodium metaborate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with formula NaBO2. However, the metaborate ion is trimeric in the anhydrous solid, therefore a more correct formula is Na3B3O6 or (Na+)3[B3O6]3−. The formula can be written also as Na2O·B2O3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron. The name is also applied to several hydrates whose formulas can be written NaBO2·nH2O for various values of n.

Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.

Sodium hydrogenoxalate is salt of formula NaHC
2O
4, consisting of sodium cations Na+
and hydrogenoxalate anions HC
2O−
4 or HO(O=)C-C(=O)O−
. The anion can be described as the result of removing one hydrogen ion H+
from oxalic acid H
2C
2O
4, or adding one to the oxalate anion C
2O2−
4.

Sodium acetylacetonate is an organic compound with the nominal formula Na[CH(C(O)CH3)2]. This white, water-soluble solid is the conjugate base of acetylacetone.
Disodium enneaborate is the traditional name for a salt of sodium, boron, oxygen, and hydrogen, with elemental formula Na2B9H22O20 or Na2B9O9·11H2O. It is the sodium borate with the highest boron/sodium ratio.
Sodium pentaborate, more properly disodium decaborate, is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen; a salt with elemental formula NaB5O8, Na2B10O16, or Na2O·5B2O3. It is a colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water.
Trisodium borate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen, with formula Na3BO3, or (Na+)3[BO3]3−. It is a sodium salt of the orthoboric acid B(OH)3.

Sodium tetrahydroxyborate is a salt of with chemical formula NaH4BO4 or Na+[B(OH)4]−. It is one of several sodium borates. At room temperature it is a colorless crystalline solid.
References
- 1 2 3 Silvio Menchetti and Cesare Sabelli (1977): "The crystal structure of synthetic sodium pentaborate monohydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B, volume B33, pages 3730-3733. doi : 10.1107/S0567740877011959