
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal management using methadone can be accomplished in less than a month, or it may be done gradually over a longer period of time, or simply maintained for the rest of the patient's life. While a single dose has a rapid effect, maximum effect can take up to five days of use. After long-term use, in people with normal liver function, effects last 8 to 36 hours. Methadone is usually taken by mouth and rarely by injection into a muscle or vein.

Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use and sexual activity without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others.
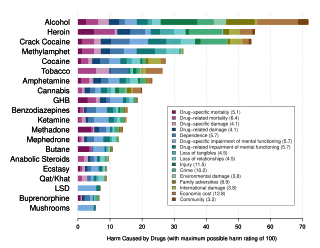
Drug rehabilitation is the process of medical or psychotherapeutic treatment for dependency on psychoactive substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, and street drugs such as cannabis, cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines. The general intent is to enable the patient to confront substance dependence, if present, and stop substance misuse to avoid the psychological, legal, financial, social, and medical consequences that can be caused.
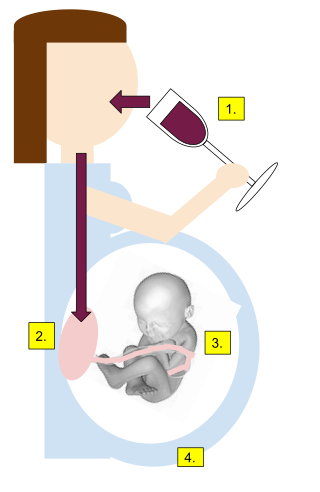
Alcohol dependence is a previous psychiatric diagnosis in which an individual is physically or psychologically dependent upon alcohol.

Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a substance use disorder characterized by cravings for opioids, continued use despite physical and/or psychological deterioration, increased tolerance with use, and withdrawal symptoms after discontinuing opioids. Opioid withdrawal symptoms include nausea, muscle aches, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, agitation, and a low mood. Addiction and dependence are important components of opioid use disorder.
A methadone clinic is a medical facility where medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) are dispensed-—historically and most commonly methadone, although buprenorphine is also increasingly prescribed. Medically assisted drug therapy treatment is indicated in patients who are opioid-dependent or have a history of opioid dependence. Methadone is a schedule II (USA) opioid analgesic, that is also prescribed for pain management. It is a long-acting opioid that can delay the opioid withdrawal symptoms that patients experience from taking short-acting opioids, like heroin, and allow time for withdrawal management. In the United States, by law, patients must receive methadone under the supervision of a physician, and dispensed through the Opioid Treatment Program (OTP) certified by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.

The Royal North Shore Hospital (RNSH) is a major public teaching hospital in Sydney, Australia, located in the suburb of St Leonards. It serves as a teaching hospital for Sydney Medical School at the University of Sydney, University of Technology Sydney and Australian Catholic University and has over 600 beds.
Motivational interviewing (MI) is a counseling approach developed in part by clinical psychologists William R. Miller and Stephen Rollnick. It is a directive, client-centered counseling style for eliciting behavior change by helping clients to explore and resolve ambivalence. Compared with non-directive counseling, it is more focused and goal-directed, and departs from traditional Rogerian client-centered therapy through this use of direction, in which therapists attempt to influence clients to consider making changes, rather than engaging in non-directive therapeutic exploration. The examination and resolution of ambivalence is a central purpose, and the counselor is intentionally directive in pursuing this goal. MI is most centrally defined not by technique but by its spirit as a facilitative style for interpersonal relationship.
Treatment Improvement Protocols (TIPs) are a series of best-practice manuals for the treatment of substance use and other related disorders. The TIP series is published by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), an operational division of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The Australian National Council on Drugs (ANCD) describes itself as "the principal advisory body to Government on drug policy and plays a critical role in ensuring the voice of the community is heard in relation to drug related policies and strategies." The Council occupies a unique position by virtue of its role in enhancing the partnership between the government and the community. It has pivotal advisory, advocacy and representative functions, with a significant role to provide government Ministers with independent, expert advice on matters related to licit and illicit drugs.
Illicit drug use in Australia is the recreational use of prohibited drugs in Australia. Illicit drugs include illegal drugs, pharmaceutical drugs when used for non-medical purposes, and other substances used inappropriately. According to government and community organisations, the use and abuse, and the illegality, of illicit drugs is a social, health and legal issue that creates an annual illegal market estimated to be worth A$6.7 billion. Estimates made in 2022 place the figure at A$11.3 billion per year.

Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include substance use problems and problematic drug or alcohol use.

The Ted Noffs Foundation is a charitable organisation located in Randwick, New South Wales, Australia. Founded as the Wayside Foundation in 1971 in Sydney by the Reverend Ted Noffs and his wife, Margaret, which provides drug and alcohol services for young people in Australia.

headspace, formally the headspace National Youth Mental Health Foundation, is an Australian non-profit organisation for youth mental health established by the Australian Government in 2006. The project is funded by the Department of Health and Aged Care under the Youth Mental Health Initiative Program, and indirectly supported through the Better Access Scheme.
Discrimination against people with substance use disorders is a form of discrimination against people with this disease. In the United States, people with substance use disorders are often blamed for their disease, which is often seen as a moral failing, due to a lack of public understanding about substance use disorders being diseases of the brain with 40-60% heritability. People with substance use disorders are likely to be stigmatized, whether in society or healthcare.
Anthony Trimingham is an English-born Australian public health activist. he worked as a relationship counsellor and a group leader for over 30 years. After his son died from a heroin drug overdose, Trimingham founded the Australian charity Family Drug Support in 1997 and named the Damien Trimingham Foundation for his son. Trimingham is also the vice president and co-founder of Harm Reduction Australia and is an advocate of drug law reform and harm reduction.
Narcology, from Russian нарко- + -логия is a subspecialty of psychiatry dealing with the prevention, treatment, diagnosis, social care and recovery of drug-dependent persons. The study and science of phenomena of "narcomania", "toxicomania", chronic alcoholism, and its ætiology, pathogenesis, and clinical aspects. The term for a practitioner of narcology is narcologist. In the United States, the comparable terms are "addiction medicine" and "addictionist".
Alcoholism in Ireland is a significant public health problem. In 2021, 70% of Irish men and 34% of Irish women aged 15+ were considered to be hazardous drinkers. In the same age group, there are over 150,000 Irish people who are classified as 'dependent drinkers'. According to Eurostat, 24% of Ireland's population engages in heavy episodic drinking at least once a month, compared to the European average of 19%.
The National Drug Strategy (NDS) is the national drug regulation organization which maintains drug policy of the Australian Government. It began with its first framework in 1998 and has regularly formulated the Australian approach to drug education, treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention of substance abuse. It is directed by the Ministerial Drug and Alcohol Forum (MDAF) who use the NDS to implement and monitor the effectiveness of Australian drug policy at all levels of government. The MDAF consists of various elected Commonwealth and State Ministers, as well as civil servants. The aim of the NDS is to minimise the harms associated with licit and illicit drugs by reducing demand, supply, and harm in a holistic approach to the social, individual, and economic problems created by drugs. Its main function is establishing a set of policies, implemented at state and local level, that promote research-based solutions to the complex issues presented by drug use in society. The NDS has been responsible for introduction of several harm minimisation programs specifically placed in areas with a demographic deemed high-risk. Through the various iterations of the NDS it has faced increasing scrutiny over its perceived divergence from its original purpose, as well as perpetuating policies which allocate resources inefficiently.










