
Year 623 (DCXXIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 623 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
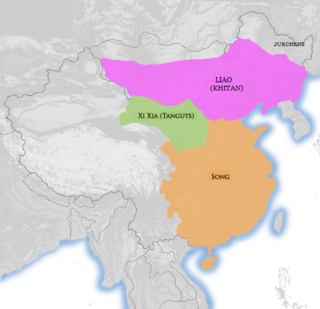
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (Chinese: 西夏; pinyin: Xī Xià; Wade–Giles: Hsi1 Hsia4), officially the Great Xia (大夏; Dà Xià; Ta4 Hsia4), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as Mi-nyak to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China that existed from 1038 to 1227. At its peak, the dynasty ruled over the modern-day northwestern Chinese provinces of Ningxia, Gansu, eastern Qinghai, northern Shaanxi, northeastern Xinjiang, and southwest Inner Mongolia, and southernmost Outer Mongolia, measuring about 800,000 square kilometres (310,000 square miles).

The Tangut people were a Sino-Tibetan people that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted to the Tang dynasty. After the collapse of Tang dynasty, the Tanguts established the Western Xia. They spoke the Tangut language, which was previously believed to be one of the Qiangic languages or Yi languages which belong to the Tibeto-Burman family." Phylogenetic and historical linguistic accounts, however, reveal that Tangut belonged instead to the Gyalrongic branch of Tibeto-Burman. Western Xia was annihilated by the Mongol Empire in 1227, most of its written records and architecture were destroyed. Today the Tangut language and its unique script are extinct, only fragments of Tangut literature remain.

Emperor Taizong of Tang, previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty for his role in encouraging his father Li Yuan to rebel against the Sui dynasty at Jinyang in 617. Taizong subsequently played a pivotal role in defeating several of the dynasty's most dangerous opponents and solidifying its rule over China proper.

The Battle of Hulao, or Battle of Sishui, was a decisive Tang victory over the rival Zheng and Hebei-based Xia polities during the transition from Sui to Tang. The battle took place during the Luoyang–Hulao campaign on 28 May 621 when a Xia army – led by Dou Jiande, ruler of Xia – was defeated attacking a smaller Tang army – led by Prince Li Shimin – entrenched at the strategic Hulao Pass.

Princess Pingyang (Chinese: 平陽公主; pinyin: Píngyáng Gōngzhǔ, formally Princess Zhao of Pingyang was a Chinese princess and general.
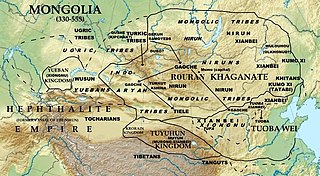
Tuyuhun, also known as Henan and Azha, was a dynastic monarchy established by the nomadic peoples related to the Xianbei in the Qilian Mountains and upper Yellow River valley, in modern Qinghai, China.

Emperor Taizong of Tang, the second emperor of the Tang dynasty faced challenges throughout his reign from Tang's western neighbor, the state of Tuyuhun, whose Busabuo Khan Murong Fuyun constantly challenged Tang authority in the border regions. In 634, Emperor Taizong launched a major attack, commanded by the major general Li Jing, against Tuyuhun, dealing Tuyuhun forces heavy defeats and causing Murong Fuyun's subordinates to assassinate him in 635. Tuyuhun, thus weakened, no longer remained a major power in the region, and while Tang, ironically, played the role of protector for Murong Fuyun's son, the Gandou Khan Murong Shun, and grandson, the Ledou Khan Murong Nuohebo, Tuyuhun was never able to recover, particularly with its southwestern neighbor, the Tibetan Empire, constantly attacking it. By 672, during the reign of Emperor Taizong's son Emperor Gaozong of Tang, Tang was forced to move Tuyuhun remnants into its own territory, ending Tuyuhun.
This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs from the Northern and Southern dynasties period to the collapse of the Southern Song dynasty.

During Tang dynasty rule in China (618–907), a complex relationship between imperial China and Tibet regime was developed. During this period Chinese and Tibetan forces had many battles since both parties were military powers, but there were also years of peace and friendly relations.
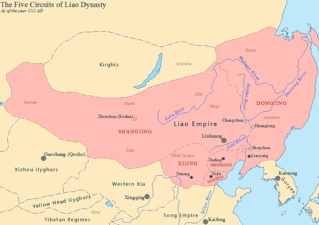
The Liao dynasty, also known as the Khitan Empire, officially the Great Liao, was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü clan of the Khitan people. Founded around the time of the collapse of the Tang dynasty, at its greatest extent it ruled over Northeast China, the Mongolian Plateau, the northern part of the Korean Peninsula, southern portions of the Russian Far East, and the northern tip of the North China Plain.

Chai Shao (588–638), courtesy name Sichang, posthumously known as Duke Xiang of Qiao, was a Chinese general who served under the emperors Gaozu and Taizong in the early Tang dynasty.
The Battle of Huoyi was fought in China on 8 September 617, between the forces of the rebel Duke of Tang, Li Yuan, and the army of the ruling Sui dynasty. Li Yuan, with an army of around 25,000, was advancing south along the Fen River towards the imperial capital, Daxingcheng. His advance was stalled for two weeks due to heavy rainfall and he was met at the town of Huoyi by an elite Sui army of 20,000 men. Li Yuan's cavalry, under the command of his two eldest sons, lured the Sui out of the protection of the city walls, but in the first clash between the two main armies, Li Yuan's forces were initially driven back. At that point, possibly due to a stratagem on Li Yuan's behalf, the arrival of the rest of the rebel army, or to the flanking maneuver of Li Yuan's cavalry, which had gotten behind the Sui army, the Sui troops collapsed and routed, fleeing back towards Huoyi. Li Yuan's cavalry, however, cut off their retreat. The battle was followed by the capture of weakly-defended Huoyi, and the advance on Daxingcheng, which fell to the rebels in November. In the next year, Li Yuan deposed the Sui and proclaimed himself emperor, beginning the Tang dynasty.

The conquest of the Western Turks, known as the Western Tujue in Chinese sources, was a military campaign in 655–657 led by the Tang dynasty generals Su Dingfang and Cheng Zhijie against the Western Turkic Khaganate ruled by Ashina Helu. The Tang campaigns against the Western Turks began in 640 with the annexation of the Tarim Basin oasis state Gaochang, an ally of the Western Turks. Several of the oasis states had once been vassals of the Tang dynasty, but switched their allegiance to the Western Turks when they grew suspicious of the military ambitions of the Tang. Tang expansion into Central Asia continued with the conquest of Karasahr in 644 and Kucha in 648. Cheng Zhijie commanded the first foray against the West Tujue, and in 657 Su Dingfang commanded the main army dispatched against the Western Turks, while the Turkic generals Ashina Mishe and Ashina Buzhen led the side divisions. The Tang troops were reinforced by cavalry supplied by the Uyghurs, a tribe that had been allied with the Tang since their support for the Uyghur revolt against the Xueyantuo. Su Dingfang's army defeated Helu at the battle of Irtysh River.

The military of the Tang dynasty was staffed with a large population of Turkic soldiers, referred to as Tujue (突厥) in Chinese sources. Tang elites in northern China were familiar with Turkic culture, a factor that contributed to the Tang acceptance of Turkic recruits. The Tang emperor Taizong adopted the title of "Heavenly Kaghan" and promoted a cosmopolitan empire. Turkic soldiers that served under the Tang dynasty originated from the Eastern Turkic Khaganate. It began with Tang dynasty Emperor Taizong who sent his general Li Jing, eventually ended in defeating the Eastern Turks and capturing their leader Jiali Khan.

The Battle of Yanshi was fought on 5–6 October 618 between the armies of Wang Shichong and Li Mi, rival contenders for the succession of the Sui dynasty. Wang, who was still ostensibly a Sui loyalist and had been blockaded in Luoyang for months by Li, gambled on a decisive battle and led his troops out to attack the besieging army. Li assembled his forces on a naturally defensible position north of Yanshi town, but Wang managed to surprise Li's forces and approach their camp before they could react. Aided by a secondary cavalry attack from the rear, Wang secured a decisive victory over Li's forces. Although Li managed to escape with part of his army, his authority was shattered, and his followers joined Wang. While Li sought refuge in the rival Tang court, Wang consolidated his control over Henan and eventually deposed the Sui puppet ruler Yang Tong and declared himself as emperor of the new Zheng dynasty. Wang's power lasted until his surrender to the Tang prince Li Shimin in 621, and Li Mi was captured and executed by Sheng Yanshi.

The Battle of Yinshan was fought in 630 CE near the Yin mountain range close to the city of Dingxiang. Emperor Taizong (598-649) commissioned the famed Tang military officer Li Jing, along with Li Shiji, Wei Xiaojie, Li Daozong, Chai Shao (柴紹), and Xue Wanche (薛萬徹) to attack forces under the command of Illig Qaghan, leader of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples based in Inner Asia. The battle ended in defeat for the Göktürks and resulted in the dissolution of the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, which was eventually replaced by the Protectorate General to Pacify the North, otherwise known as the Anbei Protectorate (安北都護府) in 647 CE after the Tang dynasty definitively conquered the Xueyantuo.
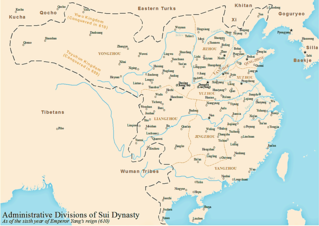
The military history of the Sui and Tang dynasties encompasses the period of Chinese military activity from 581 to 907. Although the Sui dynasty (581–618) preceded the Tang (618–907), it was extremely short lived, ending in 618. The two dynasties share many similar trends and behaviors in terms of military tactics, strategy, and technology. It can therefore be viewed that the Tang continued the Sui tradition, or that the Sui set the precedent for the Tang dynasty.
Ma Sanbao was a Chinese general during the Tang dynasty. He played an important role in the establishment of the Tang dynasty.
The Song–Xia wars were a series of military conflicts fought by the Northern Song dynasty, Western Xia dynasty, and Liao dynasty from the late 10th century to early 12th century. Although sporadic conflicts would continue, the Northern Song lost their land border with the Western Xia after the Jin–Song Wars and the Jingkang Incident of 1127 which saw the fall of their capital, Kaifeng, to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty.
















