
In the theory of computation, a branch of theoretical computer science, a pushdown automaton (PDA) is a type of automaton that employs a stack.
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, a type theory is the formal presentation of a specific type system. Type theory is the academic study of type systems.
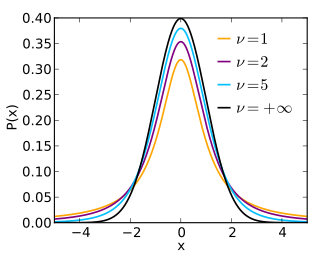
In probability theory and statistics, Student's t distribution is a continuous probability distribution that generalizes the standard normal distribution. Like the latter, it is symmetric around zero and bell-shaped.

In mathematics, Stirling's approximation is an asymptotic approximation for factorials. It is a good approximation, leading to accurate results even for small values of . It is named after James Stirling, though a related but less precise result was first stated by Abraham de Moivre.
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a type to every term. Usually the terms are various language constructs of a computer program, such as variables, expressions, functions, or modules. A type system dictates the operations that can be performed on a term. For variables, the type system determines the allowed values of that term.
In type theory, a typing rule is an inference rule that describes how a type system assigns a type to a syntactic construction. These rules may be applied by the type system to determine if a program is well-typed and what type expressions have. A prototypical example of the use of typing rules is in defining type inference in the simply typed lambda calculus, which is the internal language of Cartesian closed categories.

In mathematics, Felix Klein's j-invariant or j function, regarded as a function of a complex variable τ, is a modular function of weight zero for special linear group SL(2, Z) defined on the upper half-plane of complex numbers. It is the unique such function that is holomorphic away from a simple pole at the cusp such that
In mathematical logic and computer science, the calculus of constructions (CoC) is a type theory created by Thierry Coquand. It can serve as both a typed programming language and as constructive foundation for mathematics. For this second reason, the CoC and its variants have been the basis for Coq and other proof assistants.
In physics, the Hamilton–Jacobi equation, named after William Rowan Hamilton and Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi, is an alternative formulation of classical mechanics, equivalent to other formulations such as Newton's laws of motion, Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics.
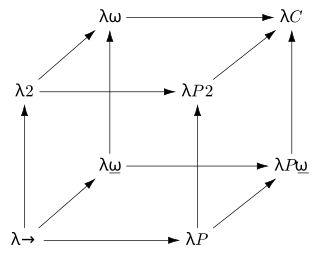
In mathematical logic and type theory, the λ-cube is a framework introduced by Henk Barendregt to investigate the different dimensions in which the calculus of constructions is a generalization of the simply typed λ-calculus. Each dimension of the cube corresponds to a new kind of dependency between terms and types. Here, "dependency" refers to the capacity of a term or type to bind a term or type. The respective dimensions of the λ-cube correspond to:
In logic, a rule of inference is admissible in a formal system if the set of theorems of the system does not change when that rule is added to the existing rules of the system. In other words, every formula that can be derived using that rule is already derivable without that rule, so, in a sense, it is redundant. The concept of an admissible rule was introduced by Paul Lorenzen (1955).
The simply typed lambda calculus, a form of type theory, is a typed interpretation of the lambda calculus with only one type constructor that builds function types. It is the canonical and simplest example of a typed lambda calculus. The simply typed lambda calculus was originally introduced by Alonzo Church in 1940 as an attempt to avoid paradoxical use of the untyped lambda calculus.
Information flow in an information theoretical context is the transfer of information from a variable to a variable in a given process. Not all flows may be desirable; for example, a system should not leak any confidential information to public observers—as it is a violation of privacy on an individual level, or might cause major loss on a corporate level.
In computer science, Programming Computable Functions (PCF) is a typed functional language introduced by Gordon Plotkin in 1977, based on previous unpublished material by Dana Scott. It can be considered to be an extended version of the typed lambda calculus or a simplified version of modern typed functional languages such as ML or Haskell.
In mathematics, the theory of optimal stopping or early stopping is concerned with the problem of choosing a time to take a particular action, in order to maximise an expected reward or minimise an expected cost. Optimal stopping problems can be found in areas of statistics, economics, and mathematical finance. A key example of an optimal stopping problem is the secretary problem. Optimal stopping problems can often be written in the form of a Bellman equation, and are therefore often solved using dynamic programming.
In programming language semantics, normalisation by evaluation (NBE) is a method of obtaining the normal form of terms in the λ-calculus by appealing to their denotational semantics. A term is first interpreted into a denotational model of the λ-term structure, and then a canonical (β-normal and η-long) representative is extracted by reifying the denotation. Such an essentially semantic, reduction-free, approach differs from the more traditional syntactic, reduction-based, description of normalisation as reductions in a term rewrite system where β-reductions are allowed deep inside λ-terms.
Minimalist grammars are a class of formal grammars that aim to provide a more rigorous, usually proof-theoretic, formalization of Chomskyan Minimalist program than is normally provided in the mainstream Minimalist literature. A variety of particular formalizations exist, most of them developed by Edward Stabler, Alain Lecomte, Christian Retoré, or combinations thereof.
A Hindley–Milner (HM) type system is a classical type system for the lambda calculus with parametric polymorphism. It is also known as Damas–Milner or Damas–Hindley–Milner. It was first described by J. Roger Hindley and later rediscovered by Robin Milner. Luis Damas contributed a close formal analysis and proof of the method in his PhD thesis.
In mathematical logic, category theory, and computer science, kappa calculus is a formal system for defining first-order functions.
In mathematical logic, the intersection type discipline is a branch of type theory encompassing type systems that use the intersection type constructor to assign multiple types to a single term. In particular, if a term can be assigned both the type and the type , then can be assigned the intersection type . Therefore, the intersection type constructor can be used to express finite heterogeneous ad hoc polymorphism . For example, the λ-term can be assigned the type in most intersection type systems, assuming for the term variable both the function type and the corresponding argument type .














