Related Research Articles

Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5FeS4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic).

Hilgardite is a borate mineral with the chemical formula Ca2B5O9Cl·H2O. It is transparent and has vitreous luster. It is colorless to light pink with a white streak. It is rated 5 on the Mohs Scale. It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. Crystals occur as distorted tabular triangles and are hemimorphic, polytypes exist.

Hydrokenoelsmoreite is a hydrous tungsten oxide mineral with formula □2W2O6(H2O). Hydrokenoelsmoreite is a colorless to white, translucent isometric mineral. It has a Mohs hardness of 3, exhibits no cleavage and has a splintery fracture. It has a vitreous to adamantine luster. It is optically isotropic with an index of refraction of n = 2.24.
Schreyerite (V2Ti3O9), is a vanadium, titanium oxide mineral found in the Lasamba Hill, Kwale district in Coast Province, Kenya. It is polymorphous with kyzylkumite.

Penroseite is a rare selenide mineral with formula (Ni,Co,Cu)Se2. It has a gray-steel color and black streak with a hardness of 3. It is an isometric mineral, 2/m3. Penroseite was first discovered in 1925 in a Bolivian rhyolite. It was named for Richard Penrose (1863–1931), an economic geologist.
Mosesite is a very rare mineral found in few locations. It is a mercury mineral found as an accessory in deposits of mercury, often in conjunction with limestone. It is known to be found in the U.S. states of Texas and Nevada, and the Mexican states of Guerrero and Querétaro. It was named after Professor Alfred J. Moses (1859–1920) for his contributions to the field of mineralogy in discovering several minerals found alongside mosesite. The mineral itself is various shades of yellow and a high occurrence of spinel twinning. It becomes isotropic when heated to 186 °C (367 °F).
Athabascaite is a member of the copper selenide minerals, and forms with other copper selenides. It was first discovered by S. Kaiman in 1949 while he was researching radioactive materials around Lake Athabasca. Kaiman was conducting research near Uranium City, Saskatchewan where mass amounts of uranium mines were present.
Nabalamprophyllite has a general formula of Ba(Na,Ba){Na3Ti[Ti2O2Si4O14](OH,F)2}. The name is given for its composition and relation to other lamprophyllite-group minerals. Lamprophyllite is a rare Ti-bearing silicate mineral usually found in intrusive igneous rocks.

Marrite (mar'-ite) is a mineral with the chemical formula PbAgAsS3. It is the arsenic equivalent of freieslebenite (PbAgSbS3), but also displays close polyhedral characteristics with sicherite and diaphorite. Marrite was named in honor of geologist John Edward Marr (1857–1933) of Cambridge, England.
Suessite is a rare iron silicide mineral with chemical formula: Fe3Si. The mineral was named after Professor Hans E. Suess. It was discovered in 1982 during the chemical analysis of The North Haig olivine pigeonite achondrite (ureilite). It is a cream white color in reflected light, and ranges in size from 1 μm "blebs" to elongated grains that can reach up to 0.45 cm in length. This mineral belongs in the isometric crystal class. The isometric class has crystallographic axes that are all the same length and each of the three axes perpendicular to the other two. It is isotropic, has a structural type of DO3 and a crystal lattice of BiF3.

Leightonite is a rare sulfate mineral with formula of K2Ca2Cu(SO4)4•2H2O.
Jolliffeite is a rare selenide mineral with formula NiAsSe or (Ni,Co)AsSe. It is the selenium analogue of the sulfide mineral gersdorffite, NiAsS, with a common impurity of cobalt, CoAsSe. It is named for its discoverer, Alfred Jolliffe, (1907–1988), a Canadian geologist of Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario.
Babefphite is a rare phosphate mineral with the general formula BaBe(PO4)(F,OH). The name is given for its composition (Ba meaning barium, Be meaning beryllium, F meaning fluorine, and P for phosphorus).
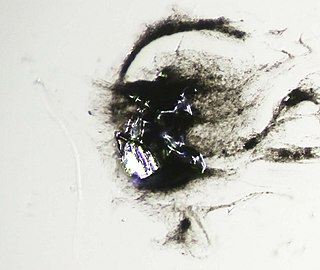
Gabrielite is a rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with a chemical formula of Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 or Tl2AgCu2As3S7.

Nambulite is a lithium bearing manganese silicate mineral with the chemical formula (Li,Na)Mn4Si5O14(OH). It is named after the mineralogist, Matsuo Nambu (born 1917) of Tohoko University, Japan, who is known for his research in manganese minerals. The mineral was first discovered in the Funakozawa Mine of northeastern Japan, a metasedimentary manganese ore.

Zorite is a silicate mineral with the chemical formula of Na2Ti(Si,Al)3O9·nH2O. It is named because of its pink color, after the Russian word "zoria" which refers to the rosy hue of the sky at dawn. It is primarily found in Mount Karnasurta, Lovozero Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. The Lovozero Massif is an area with an igneous mountain range, home to various types of minerals such as eudialyte, loparite, and natrosilitite.
Sewardite is a rare arsenate mineral with formula of CaFe2+3(AsO4)2(OH)2. Sewardite was discovered in 1982 and named for the mineralogist, Terry M. Seward (born 1940), a professor of geochemistry in Zürich, Switzerland.
Gananite (simplified Chinese: 赣南矿; traditional Chinese: 贛南礦; pinyin: gànnánkuàng) is a rare bismuth fluoride mineral form of bismuth trifluoride with a general formula of BiF3. Gananite is an isotropic mineral, it belongs to the space group P43m. This means that gananite does not show any colors in cross polarized light, because when polarized light passes through it, it does not split into two perpendicular rays. In other words, because gananite is an isometric mineral, it does not exhibit double refraction. Moreover, this tells us that this mineral is not birefringent. Its color in plane-polarized light is blackish-brown, and it does not show pleochroism.

Vladimirite is a rare calcium arsenate mineral with a formula of Ca5(HAsO4)2(AsO4)2·5H2O. It is named after the Vladimirovskoye deposit in Russia, where it was discovered in the 1950s.

Pearceite is one of the four so-called "ruby silvers", pearceite Cu(Ag,Cu)6Ag9As2S11, pyrargyrite Ag3SbS3, proustite Ag3AsS3 and miargyrite AgSbS2. It was discovered in 1896 and named after Dr Richard Pearce (1837–1927), a Cornish–American chemist and metallurgist from Denver, Colorado.
References
- ↑ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi: 10.1180/mgm.2021.43 . S2CID 235729616.
- ↑ Webmineral data
- 1 2 3 Handbook of Mineralogy
- 1 2 Mindat.org
- 1 2 3 Robinson, S.C. and Brooker, E.J. (1952) A cobalt-nickel-copper selenide from the Goldfields District, Saskatchewan. American Mineralogist, 37, 542-544.
- 1 2 3 Harris, D.C. (1970) New Data on Tyrrellite. The Canadian Mineralogist, 10, 731-735.
- ↑ Klein, C., Dutrow, B. (2007) The 23rd edition of the Manual of Mineral Science. John Wiley Publishers, p. 290