
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat and quinoa, are pseudocereals. Most cereals are annuals, producing one crop from each planting, though rice is sometimes grown as a perennial. Winter varieties are hardy enough to be planted in the autumn, becoming dormant in the winter, and harvested in spring or early summer; spring varieties are planted in spring and harvested in late summer. The term cereal is derived from the name of the Roman goddess of grain crops and fertility, Ceres.

Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a staple food around the world. The many species of wheat together make up the genus Triticum ; the most widely grown is common wheat. The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BC. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a caryopsis, a type of fruit.

Fusarium ear blight (FEB), is a fungal disease of cereals, including wheat, barley, oats, rye and triticale. FEB is caused by a range of Fusarium fungi, which infects the heads of the crop, reducing grain yield. The disease is often associated with contamination by mycotoxins produced by the fungi already when the crop is growing in the field. The disease can cause severe economic losses as mycotoxin-contaminated grain cannot be sold for food or feed.

Wheat beer is a top-fermented beer which is brewed with a large proportion of wheat relative to the amount of malted barley. The two main varieties are German Weizenbier and Belgian witbier; other types include Lambic, Berliner Weisse, and Gose.

The Canadian Wheat Board was a marketing board for wheat and barley in Western Canada. Established by the Parliament of Canada on 5 July 1935, its operation was governed by the Canadian Wheat Board Act as a mandatory producer marketing system for wheat and barley in Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and a small part of British Columbia. It was illegal for any farmer in areas under the CWB's jurisdiction to sell their wheat and barley through any other channel than the CWB. Although often called a monopoly, it was actually a monopsony since it was the only buyer of wheat and barley. It was a marketing agency acting on behalf of Western Canadian farmers, passing all profits from its operation back to farmers. Its market power over wheat and barley marketing was referred to as the "Single Desk".
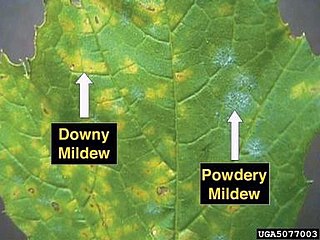
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as the signs of the causal pathogen are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. This mycelial layer may quickly spread to cover all of the leaves. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.

In brewing, adjuncts are unmalted grains or grain products used in brewing beer which supplement the main mash ingredient. This is often done with the intention of cutting costs, but sometimes also to create an additional feature, such as better foam retention, flavours or nutritional value or additives. Both solid and liquid adjuncts are commonly used.
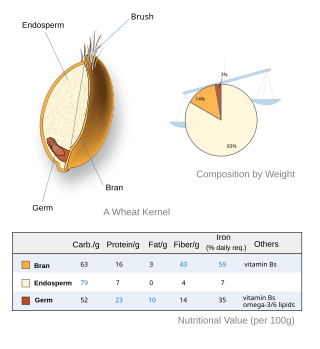
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.

A cereal coffee is a hot drink made from one or more cereal grains roasted and commercially processed into crystal or powder form to be reconstituted later in hot water. The product is often marketed as a caffeine-free alternative to coffee and tea, or in other cases where those drinks are scarce or expensive.
The cereal grain wheat is subject to numerous wheat diseases, including bacterial, viral and fungal diseases, as well as parasitic infestations.
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice, and other food grains. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other agricultural products. Healthy grain supply and trade is important to many societies, providing a caloric base for most food systems as well as important role in animal feed for animal agriculture.

Stem rust, also known as cereal rust, black rust, red rust or red dust, is caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis, which causes significant disease in cereal crops. Crop species that are affected by the disease include bread wheat, durum wheat, barley and triticale. These diseases have affected cereal farming throughout history. The annual recurrence of stem rust of wheat in North Indian plains was discovered by K.C. Mehta. Since the 1950s, wheat strains bred to be resistant to stem rust have become available. Fungicides effective against stem rust are available as well.
The Alaska Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station (AFES) was established in 1898 in Sitka, Alaska, also the site of the first agricultural experiment farm in what was then Alaska Territory. Today the station is administered by the University of Alaska Fairbanks through the School of Natural Resources and Agricultural Sciences. Facilities and programs include the Fairbanks Experiment Farm, the Georgeson Botanical Garden, the Palmer Research and Extension Center, the Matanuska Experiment Farm, and the Reindeer Research Program.

Agriculture in Kazakhstan remains a small scale sector of Kazakhstan's economy. Agriculture's contribution to the GDP is under 10% – it was recorded as 6.7%, and as occupying only 20% of labor. At the same time, more than 70% of its land is occupied in crops and animal husbandry. Compared to North America, a relatively small percentage of land is used for crops, with the percentage being higher in the north of the country. 70% of the agricultural land is permanent pastureland.

Gibberella zeae, also known by the name of its anamorph Fusarium graminearum, is a fungal plant pathogen which causes fusarium head blight (FHB), a devastating disease on wheat and barley. The pathogen is responsible for billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide each year. Infection causes shifts in the amino acid composition of wheat, resulting in shriveled kernels and contaminating the remaining grain with mycotoxins, mainly deoxynivalenol (DON), which inhibits protein biosynthesis; and zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin. These toxins cause vomiting, liver damage, and reproductive defects in livestock, and are harmful to humans through contaminated food. Despite great efforts to find resistance genes against F. graminearum, no completely resistant variety is currently available. Research on the biology of F. graminearum is directed towards gaining insight into more details about the infection process and reveal weak spots in the life cycle of this pathogen to develop fungicides that can protect wheat from scab infection.

Barley, a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikelets and making it much easier to harvest. Its use then spread throughout Eurasia by 2000 BC. Barley prefers relatively low temperatures and well-drained soil to grow. It is relatively tolerant of drought and soil salinity but is less winter-hardy than wheat or rye.
Harold Corby Kistler is an American Adjunct Professor of biology and plant pathology at the University of Minnesota and a fellow of the American Phytopathological Society and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Grain From Ukraine is a humanitarian food program that was launched on November 26, 2022, on the 90th anniversary of the beginning of the Holodomor of 1932–1933, by the President of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelenskyy, to supply grain to the poorest countries in Africa.
Ralph Merrill Caldwell was an American plant breeder, mycologist, and plant pathologist. Through his work with the U.S. Department of Agriculture and Purdue University, he developed disease-resistant cultivars for a wide variety of plants, including widely-grown wheat cultivars.












