Ubangi (also spelled Ubangui, Ubanghi, or Oubangui) may refer to:
Ubangi (also spelled Ubangui, Ubanghi, or Oubangui) may refer to:
The history of the Central African Republic is roughly composed of four distinct periods. The earliest period of settlement began around 10,000 years ago when nomadic people first began to settle, farm and fish in the region. The next period began around 10,000 years prior.

Congo may refer to:

Lingala is a Bantu language spoken in the northwest of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the northern half of the Republic of the Congo, in their capitals, Kinshasa and Brazzaville, and to a lesser degree in Angola, the Central African Republic, Kenya and southern South Sudan. Lingala has 20 million native speakers and about another 20 million second-language speakers, for an approximate total of 40 million speakers.
The Adamawa–Ubangi languages are a geographic grouping and formerly postulated family of languages spoken in Nigeria, Chad, the Central African Republic, Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and South Sudan, by a total of about 12 million people.

The Ubangi River, also spelled Oubangui, is a river in Central Africa, and the largest right-bank tributary of the Congo River. It begins at the confluence of the Mbomou and Uele Rivers and flows west, forming the border between Central African Republic (CAR) and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Subsequently, the Ubangi bends to the southwest and passes through Bangui, the capital of the CAR, after which it flows south – forming the border between the DRC and the Republic of the Congo. The Ubangi finally joins the Congo River at Liranga.
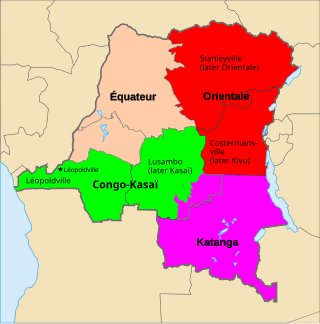
Équateur was a province in the northwest of Belgian Congo and the independent Republic of the Congo, now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had its origins in the Équateur District of the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. It was upgraded to the status of a province in 1917. Between 1933 and 1947 it was named Coquilhatville. In 1962 it was divided into three smaller provinces, but there were recombined in 1966. Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo until 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces.

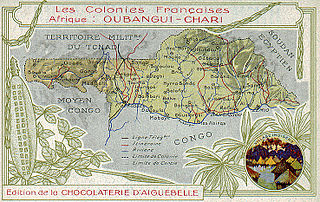
Ubangi-Shari was a French colony in central Africa, a part of French Equatorial Africa. It was named after the Ubangi and Chari rivers along which it was colonised. It was established on 29 December 1903, from the Upper Ubangi and Upper Shari territories of the French Congo; renamed the Central African Republic (CAR) on 1 December 1958; and received independence on 13 August 1960.

Ubangi-Shari was a French colony in central Africa which later became the independent country of the Central African Republic on August 13, 1960. It followed the establishment of the Bangui outpost in 1889, and was named in 1894.

Zongo is a city in Sud-Ubangi Province in the northwestern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo, lying on the south bank of the Ubangi River, across from Bangui in the Central African Republic. It is linked by ferry to Bangui but has declined in importance as a transport hub since much traffic moved east in the late 1980s.

The lip plate, also known as a lip plug, lip disc, or mouth plate, is a form of body modification. Increasingly large discs are inserted into a pierced hole in either the upper or lower lip, or both, thereby stretching it. The term labret denotes all kinds of pierced-lip ornaments, including plates and plugs.
Zongo may refer to:
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Molegbe is a suffragan Latin diocese in the ecclesiastical province of Mbandaka-Bikoro in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Pointe-Noire is an archdiocese located in the city of Pointe-Noire in the Republic of the Congo. This province has suffragan dioceses Dolisie and Nkayi.
The Lake Chad replenishment project is a proposed major water diversion scheme to divert water from the Congo River basin to Lake Chad to prevent it drying up. Various versions have been proposed. Most would involve damming some of the right tributaries of the Congo River and channeling some of the water to Lake Chad via a canal to the Chari River basin.

Tshuapa is one of the 21 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Tshuapa, Équateur, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi, and Sud-Ubangi provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Équateur province. Tshuapa was formed from the Tshuapa District whose town of Boende was elevated to capital city of the new province.
Yaka may refer to the following languages of Africa:

The Central African Republic–Chad border is 1,556 km (987 mi) in length and runs from the tripoint with Cameroon in the west, to the tripoint with Sudan in the east.

The Central African Republic–Republic of the Congo border is 487 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Cameroon in the west to the tripoint with the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the east.
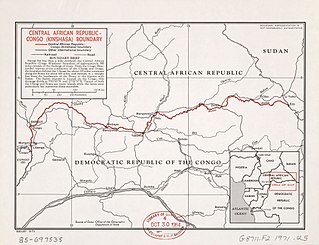
The Central African Republic–Democratic Republic of the Congo border is 1,747 km in length and runs from the tripoint with the Republic of the Congo in the west to the tripoint with South Sudan in the east.