
Angkor, also known as Yasodharapura, was the capital city of the Khmer Empire, located in present-day Cambodia. The city and empire flourished from approximately the 9th to the 15th centuries. The city houses the Angkor Wat, one of Cambodia's most popular tourist attractions.
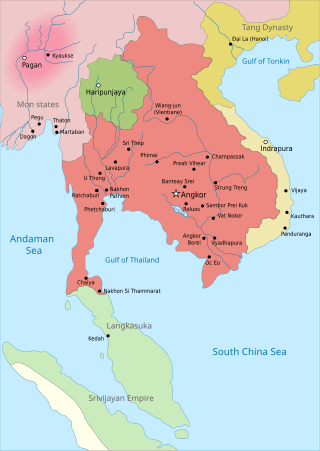
The Khmer Empire was a Hindu-Buddhist empire in Southeast Asia, centered around hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilisation of Chenla and lasted from 802 to 1431. Historians call this period of Cambodian history the Angkor period, after the empire's most well-known capital, Angkor. The Khmer Empire ruled or vassalised most of mainland Southeast Asia and stretched as far north as southern China. At its peak, the Empire was larger than the Byzantine Empire, which existed around the same time.

Phimeanakas or Vimeanakas at Angkor, Cambodia, is a Hindu temple in the Khleang style, built at the end of the 10th century, during the reign of Rajendravarman, then completed by Suryavarman I in the shape of a three tier pyramid as a Hindu temple. On top of the pyramid there was a tower, while on the edge of top platform there are galleries. Phimeanakas is located inside the walled enclosure of the Royal Palace of Angkor Thom north of Baphuon.
Somdet Phra Ramesuan, son of king Ramathibodi I, reigned as the second and fifth king of the kingdom of Ayutthaya. When King Ramathibodi ascended to the throne of Ayuthaya, he sent King Ramesuan to reign in Lavo. Upon King Ramathibodi's death in 1369, King Ramesuan traveled to Ayutthaya to assume the throne, but held it for less than a year before being deposed by his uncle, King Borommaracha I, the ruler of Suphanburi. Sources differ over the nature of their conflict; official chronicles state that the older Boromaracha ruled with the willing consent of his nephew, while Jeremias van Vliet's Short History of Thailand indicated that Boromaracha's ascension came only after a bloody conflict bordering on civil war.

Udayadityavarman II ruled the Angkor Kingdom from 1050 to 1066 A.D. He was the successor of Suryavarman I but not his son; he descended from Yasovarman I's spouse.

Suryavarman I was king of the Khmer Empire from 1006 to 1050. Suryavarman usurped King Udayadityavarman I, defeating his armies in approximately 1002. After a protracted war with Udayadityavarman's would-be successor, Jayavirahvarman, Suryavarman I claimed the throne in 1010. Suryavarman was a Mahayana Buddhist who was also tolerant of the growing Theravada Buddhist presence in the Khmer kingdom.

Banteay Samré is a temple at Angkor, Cambodia, located 400 metres to the east of the East Baray. Built during the reign of Suryavarman II and Yasovarman II in the early 12th century, it is a Hindu temple in the Angkor Wat style.

Tambralinga was an Indianised kingdom located on the Malay Peninsula, existing at least from the 2nd to 13th centuries CE. It was under the influence of Srivijaya for some time, but later became independent from it. The name had been forgotten until scholars recognized Tambralinga as Nakhon Si Thammarat. In Sanskrit and Prakrit, tām(b)ra means "copper", "copper-coloured" or "red" and linga means "symbol" or "creation", typically representing the divine energy of Shiva.
Jayavarman VI was king of the Khmer Empire from about 1080 to 1107 AD.
Jayavarman V was a ruler of the Khmer Empire from his state temple, Jayendranagari, at Jayendrapura. During his reign, the Khmer Empire had 20 cities or pura.
Dharanindravarman I was a king of the Khmer Empire, reigning from 1107 AD to 1113 AD. He ascended to the throne following the death of his younger brother, Jayavarman VI. He was married to Queen Vijayendralakshmi, former wife of Jayavarman VI. He was murdered in battle by his great-nephew, Suryavarman II. The event is supported by the Ban That inscription.
Indravarman III, also titled Srindravarman was a ruler of the Khmer Empire from 1295 to 1308. He rose to power after the abdication of his father in law Jayavarman VIII, whose eldest daughter, Srindrabhupesvarachuda, he had married. Indravarman III was a follower of Theravada Buddhism and upon his ascension to power he made it the state religion.

Very little is known about Jayavarman II's son and successor, Jayavarman III, or Vishnuloka, the second ruler of Angkor. The future Khmer king, Yasovarman I, claimed to be related to the brother of Jayavarman III's grandmother, Rudravarman. An inscription from Prasat Sak describes: "When he failed to capture a wild elephant while hunting, a divinity promised that he would secure the animal if he built a sanctuary." There are some temples dated to his reign though none said that they belonged to him. He may have begun a small construction project which was overshadowed by his more ambitious successor and builder, Indravarman I. He died in 877 probably from chasing a wild elephant.

Ak Yum is an ancient temple in the Angkor region of Cambodia. Helen Jessup dates the temple to the 8th century, and states it is the oldest known example of "temple mountain" in Southeast Asia.
Rajendravarman II was the king of the Khmer Empire, from 944 to 968 AD.
The Battle of Pinhoe took place between the Danes and the men of Devon and Somerset at Pinhoe, Devon.
Jeyavarman IV was an Angkorian king who ruled from 928 to 941 CE. Many early historians thought that he was a usurper. However, recent evidence shows that he had a legitimate claim to the throne. During his reign, the nation had 12 cities or pura.
Harshavarman III was a king of Khmer who ruled from 1066 to about 1080 AD. He succeeded his elder brother Udayadityavarman II and his capital was the so-called Second Yasodharapura, which had its center in Baphuon, built by his brother, and West Baray as its principal bàrày. He was married to queen Kambujarajalakshmi.
Jayaviravarman is a king who reigned over the Khmer Empire from 1002 to 1011 AD.








