Related Research Articles
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica.

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 64 km in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound.

The Fildes Peninsula is a 7 km (4.3 mi) long peninsula that forms the south-western end of King George Island in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was named from association with nearby Fildes Strait by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960; the strait was likely named for Robert Fildes, a British sealer of the 1800s.
Arthur Harbour is a small harbour entered between Bonaparte Point and Amsler Island on the south-west coast of Anvers Island in the Palmer Archipelago of Antarctica.
The Larsen Islands are a small group of islands north-west of Moreton Point, the western extremity of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. They were discovered by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer on the occasion of their joint cruise in December 1821. The islands were named on Petter Sørlle's chart, based upon his survey of the South Orkney Islands in 1912–1913, in honour of Carl Anton Larsen.
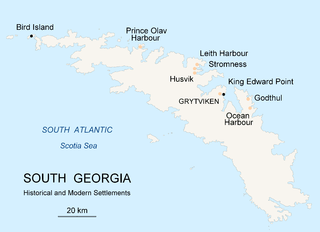
Prince Olav Harbour is a small harbour in the south west portion of Cook Bay, entered between Point Abrahamsen and Sheep Point, along the north coast of South Georgia.

Ezcurra Inlet is an inlet forming the western arm of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and named "Fiord Ezcurra" after Pedro de Ezcurra, an Argentine politician and Minister of Agriculture in 1908, who assisted the French expedition.
Ajax Icefall' is an icefall between Stenhouse Bluff and Ullmann Spur at the head of Visca Anchorage, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. Charted by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot in 1908–10. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for HMS Ajax, which assisted in the search for a boat crew from the Discovery II, missing on King George Island in January 1937.
Erratic Point is a small, moss-covered point at the head of South West Bay, 1.3 nautical miles (2.4 km) northeast of Cape Gazert, on the west side of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. The First German Antarctica Expedition in 1902 charted a cape in this vicinity, from the summit of Mount Drygalski, and applied the name "Kap Lerche." In November 1929 the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson charted a small point in this position and applied the name "Erratic Point" because of the large number of massive erratic boulders encountered there. The Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition was unable to find any significant feature in this immediate area during their 1948 survey of the island, hence the name Erratic Point was retained by them for this small point.
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. A large part of the valley has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of its pristine condition.
Cinder Spur is a small spur extending into Legru Bay, 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) west of Low Head on the south coast of King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 because the feature is composed mainly of volcanic cinders.
The Nash Range is a mainly ice-covered coastal range in the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica.
Derrick Peak is a prominent ice-free peak, 2,070 metres (6,790 ft) high, overlooking the south side of Hatherton Glacier, 3 nautical miles west of the north end of Johnstone Ridge.

Domeyko Glacier is a glacier flowing southeast into Mackellar Inlet, Admiralty Bay, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was named by the Polish Antarctic Expedition, 1980, after Ignacy Domeyko, a Polish-born explorer of the Andes and sometime Professor of Chemistry and Mineralogy, and Rector, of the University of Chile, Santiago.
Duclaux Point is a point extending into Bouquet Bay from the east side of Pasteur Peninsula, 3 nautical miles (6 km) southeast of Cape Cockburn on Brabant Island in the Palmer Archipelago. It was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for Pierre E. Duclaux, a French biochemist who was director of the Pasteur Institute in Paris in 1895.

Ecology Glacier is a glacier flowing northeast into Admiralty Bay, King George Island, north of Llano Point. It was named by the Polish Antarctic Expedition, 1980, after the Institute of Ecology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the sponsor of nearby Arctowski Station.

Goetel Glacier is a glacier flowing south between Ullmann Spur and the Precious Peaks into Martel Inlet, Admiralty Bay, on King George Island in the South Shetland Islands. It was named by the Polish Antarctic Expedition, 1980, after Professor Walery Goetel (1889–1972), a Polish geologist and conservationist.

Martel Inlet is an inlet forming the northeast head of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands off Antarctica. The inlet and most of its constituent features were charted in December 1909 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot and named "Fiord Martel" after J.L. Martel, a French politician. The mountain ridge Ullmann Spur is located at the head of the inlet.

Point Hennequin is a point forming the eastern side of the entrance to Martel Inlet and Mackellar Inlet, on the east side of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was named by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, who surveyed Admiralty Bay in 1909.
Bone Bay is a rectangular bay along the northwest coast of Trinity Peninsula. It is nearly 10 nautical miles wide at the entrance between Notter Point and Cape Roquemaurel. The bay and most of its constituent features were charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948, and later named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC). Bone Bay was named after Thomas M. Bone, midshipman on the brig Williams used in exploring the South Shetland Islands and Bransfield Strait in 1820.
References
- ↑ "Ullmann Spur". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ↑ "Ullmann Point". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2020-09-11.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey .
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey .