Related Research Articles

Mesoamerican languages are the languages indigenous to the Mesoamerican cultural area, which covers southern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize and parts of Honduras and El Salvador and Nicaragua. The area is characterized by extensive linguistic diversity containing several hundred different languages and seven major language families. Mesoamerica is also an area of high linguistic diffusion in that long-term interaction among speakers of different languages through several millennia has resulted in the convergence of certain linguistic traits across disparate language families. The Mesoamerican sprachbund is commonly referred to as the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area.
The Popolocan languages are a subfamily of the Oto-Manguean language family of Mexico, spoken mainly in the state of Puebla.

Arbouet-Sussaute is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine of south-western France.

Uhart-Mixe is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in south-western France.

The Mixe are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the eastern highlands of the state of Oaxaca. They speak the Mixe languages, which are classified in the Mixe–Zoque family, and are more culturally conservative than other indigenous groups of the region, maintaining their language to this day. A population figure of 90,000 speakers of Mixe were estimated by SIL international in 1993. The Mixe name for themselves is ayuujkjä'äy meaning "people who speak the mountain language" The word "Mixe" itself is probably derived from the Nahuatl word for cloud: mīxtli.
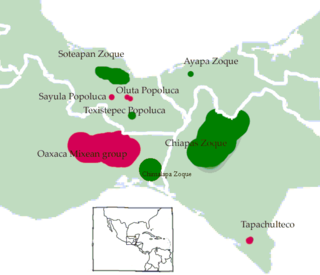
The Mixe–Zoque languages are a language family whose living members are spoken in and around the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico. The Mexican government recognizes three distinct Mixe–Zoquean languages as official: Mixe or ayook with 188,000 speakers, Zoque or o'de püt with 88,000 speakers, and the Popoluca languages of which some are Mixean and some Zoquean with 69,000 speakers. However the internal diversity in each of these groups is great and the Ethnologue counts 17 different languages, and the current classification of Mixe–Zoquean languages by Wichmann (1995) counts 12 languages and 11 dialects. Extinct languages classified as Mixe–Zoquean include Tapachultec, formerly spoken on Tapachula, along the southeast coast of Chiapas.

Totontepec Villa de Morelos is a small village and municipality, in the Sierra Mixe district of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is located some 1840 metres above sea level and some 326 km from the state capital, Oaxaca de Juárez. In spite of the Mixe influence, the toponym is Nahuatl in origin, meaning "hot hill".
Popoluca is a Nahuatl term for various indigenous peoples of southeastern Veracruz and Oaxaca. Many of them speak languages of the Mixe–Zoque family. Others speak the unrelated Mazatecan languages, in which case the name in English and Spanish is generally spelled Popoloca.

The Mixe languages are languages of the Mixean branch of the Mixe–Zoquean language family indigenous to southern Mexico. According to a 1995 classification, there are seven of them. The four that are spoken in Oaxaca are commonly called Mixe while their two relatives spoken in Veracruz are commonly called "Popoluca", but sometimes also Mixe. This article is about the Oaxaca Mixe languages, which their speakers call Ayuujk, Ayüük or Ayuhk.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a mountain range in southern Mexico. It is primarily in the state of Oaxaca, and extends north into the states of Puebla and Veracruz.

The Sierra Mixe or Mixes District is a district in the east of the Sierra Norte Region of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It comprises 17 municipalities and covers 4,930 km2 at an average elevation of 1,200 meters above sea level. As of 2005 the district had a total population of 96,920. The main food crops are maize and beans, while permanent crops include coffee, lemon and oranges.

Lit-et-Mixe is a commune in the Landes department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in south-western France.
Isthmus Mixe, called Lowland Mixe in Wichmann (1995), is a Mixe language spoken in Mexico. It is spoken in the villages of Coatlán San José el Paraíso, Mazatlán, Guichicovi, and Camotlán, Oaxaca.
Totontepec Mixe, called North Highland Mixe in Wichmann (1995), is a Mixe language spoken in Mexico, in the town of Totontepec Villa de Morelos, Oaxaca.
Tlahuitoltepec Mixe, called South Highland Mixe in Wichmann (1995), is a Mixe language spoken in Mexico.
Midland a.k.a. Central Mixe is a Mixe language spoken in Mexico. According to Wichmann (1995), there are two groups of dialects:

San Juan Cotzocon is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. It is part of the Sierra Mixe district within the Sierra Norte de Oaxaca Region.

Totozoquean is a proposed language family of Mesoamerica, originally consisting of two well-established genetic groupings, Totonacan and Mixe–Zoque. The erstwhile isolate Chitimacha was later proposed to be a member. The closest relatives of Totozoquean may be the Huavean languages.
Isabel Marant is a French fashion house founded in 1994 by designer Isabel Marant. Originally consisting only of a line of jerseys and knitwear, the brand is now best known for its shoes, which have been worn by celebrities including Kate Bosworth, Katie Holmes, Anne Hathaway and Hilary Duff.
XHJP-FM is a community radio station on 107.9 FM in Santa María Tlahuitoltepec, Oaxaca. It is known as Jën Poj and is operated by Kukoj, A.C.
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Ulterior-Mixe". Glottolog 3.0 . Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
| This article related to indigenous languages of the Americas is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |