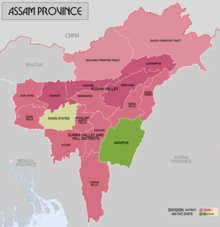
Meghalaya is a state in northeast India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills and (b) the Garo Hills. The population of Meghalaya as of 2014 is estimated to be 3,211,474. Meghalaya covers an area of approximately 22,429 square kilometres, with a length-to-breadth ratio of about 3:1.

The North-West Frontier Province was a province of British India from 1901 to 1947, of the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955, and of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan from 1970 to 2010. It was established on 9 November 1901 from the north-western districts of the British Punjab, during the British Raj. Following the referendum in 1947 to join either Pakistan or India, the province voted hugely in favour of joining Pakistan and it acceded accordingly on 14th August, 1947. It was dissolved to form a unified province of West Pakistan in 1955 upon promulgation of One Unit Scheme and was re-established in 1970. It was known by this name until 19 April 2010, when it was dissolved and redesignated as the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa following the passing of the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan, by erstwhile President Asif Ali Zardari.

Northeast India, officially known as the North Eastern Region(NER) is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim.

Ri Bhoi is an administrative district in the state of Meghalaya in India. The district headquarters are located at Nongpoh. The district occupies an area of 2378 km² and has a population of 258,840. As of 2011 it is the second least populous district of Meghalaya, after South Garo Hills.

West Garo Hills is an administrative district in Garo Hills of the state of Meghalaya in India. Tura town is the administrative headquarters of the district. The district occupies an area of 3714 km². In 2011 its population was 643,291. As of 2011 it is the second most populous district of Meghalaya, after East Khasi Hills.

Cachardistrict is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. After independence, the pre-existing undivided Cachar district was split into four districts: Dima Hasao, Hailakandi, Karimganj, and the current Cachar district. Silchar is Cachar district's center of government.

Kokrajhar district is an administrative district in Bodoland Territorial Region of Assam. It is predominantly inhabited by the Boro tribe. The district has its headquarters located at Kokrajhar Town and occupies an area of 3,169.22 km2 (1,223.64 sq mi). It has two civil sub-divisions namely Parbatjhora and Gossaigaon and five revenue circles namely Kokrajhar, Dotma, Bhaoraguri, Gossaigaon and Bagribarilll

Kamrup Rural district, or simply Kamrup district, is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India formed by dividing the old Kamrup district into two in the year 2003; other being Kamrup Metropolitan district, named after the region it constitutes. This district, along with Nalbari, Barpeta, Kamrup Metropolitan, Bajali and Baksa districts has been created from the Undivided Kamrup district. Rangia is the plantation valley city of Assam located at Kamrup District.

Dima Hasao district, is an administrative district in the state of Assam, India. As of 2011, it is the least populous district of Assam.

The Kuki people are an ethnic group in the Northeastern Indian states of Manipur, Nagaland, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram, as well as the neighbouring countries of Bangladesh and Myanmar. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh.

The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods:

The Barak River flows 900 kilometres (560 mi) through the states of Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram and Assam in India. Further it enters Bangladesh where it bifurcates into the Surma river and the Kushiyara river which converge again to become the Meghna river before forming the Ganges Delta with the Ganga and the Brahmaputra rivers and flowing into the Bay of Bengal. Of its total length, 524 km (326 mi) is in India, 31 km (19 mi) on the Indo–Bangladesh border and the rest in Bangladesh. The upper part of its navigable part is in India — 121 km (75 mi) between Lakhipur and Bhanga, declared as National Waterway 6, (NW-6) since the year 2016. It drains a basin of 52,000 km2 (20,000 sq mi), of which 41,723 km2 (16,109 sq mi) lies in India, 1.38% (rounded) of the country. The water and banks host or are visited by a wide variety of flora and fauna.

Eastern Bengal and Assam was a province of India between 1905 and 1912. Headquartered in the city of Dacca, it covered territories in what are now Bangladesh, Northeast India and Northern West Bengal.

Colonial Assam (1826–1947) refers to the period in the history of Assam between the signing of the Treaty of Yandabo and the Independence of India when Assam was under British colonial rule. The political institutions and social relations that were established or severed during this period continue to have a direct effect on contemporary events. The legislature and political alignments that evolved by the end of the British rule continued in the post Independence period. The immigration of farmers from East Bengal and tea plantation workers from Central India continue to affect contemporary politics, most notably that which led to the Assam Movement and its aftermath.
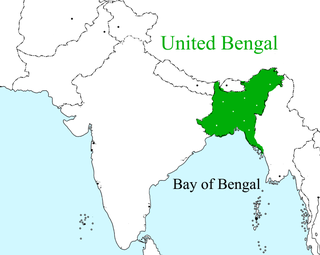
Greater Bangladesh, or Greater Bengal, represents the ideological assertion that Bangladesh will inevitably expand its sphere of influence to include the Indian states that currently has, or historically had, large populations of ethnic Bengali people. These include West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, and Jharkand to the west, Sikkim to the north, and the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, and Nagaland to the east. The first and only real attempt at forming such an entity was made in 1943 by the Indische Legion under Bengali Nationalist Subhas Chandra Bose, de facto leader of the Azad Hind movement. Such endeavors, however, failed to ultimately materialize due to Germany and Japan’s loss in World War II.

Assam Province was a province of British India, created in 1912 by the partition of the Eastern Bengal and Assam Province. Its capital was in Shillong.

Northeast India consists of the eight states Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. Tourism in this area is based around the unique Himalayan landscape and culture distinct from the rest of India.
South Salmara-Mankachar is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. The district headquarter is located at Hatsingimari village which is situated at about 245 km from Guwahati. It was earlier a sub-division of the Dhubri District.
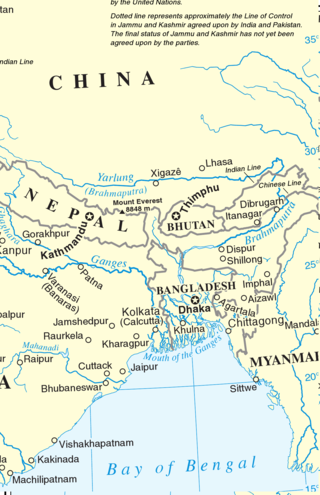
Eastern South Asia is a geographical area in the Southern Asian subregion, precisely the eastern region of the subcontinent. It includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal and India. Geographically, it lies between the Eastern Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal. Two of the world's largest rivers, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, flow into the sea through the Bengal region. The region includes the world's highest mountainous terrain and the world's largest delta, and has a climate ranging from alpine and subalpine to subtropical and tropical. Since Nepal, Bhutan, and northeast India are landlocked, the coastlines of Bangladesh and East India serve as the principal gateways to the region.

The hill tribes of Northeast India are hill people, mostly classified as Scheduled Tribes (STs), who live in the Northeast India region. This region has the largest proportion of scheduled tribes in the country.