
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers.

Db2 is a family of data management products, including database servers, developed by IBM. It initially supported the relational model, but was extended to support object–relational features and non-relational structures like JSON and XML. The brand name was originally styled as DB2 until 2017, when it changed to its present form.

UNIVAC was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company and successor organizations.

The UNIVAC 1100/2200 series is a series of compatible 36-bit computer systems, beginning with the UNIVAC 1107 in 1962, initially made by Sperry Rand. The series continues to be supported today by Unisys Corporation as the ClearPath Dorado Series. The solid-state 1107 model number was in the same sequence as the earlier vacuum-tube computers, but the early computers were not compatible with their solid-state successors.
A database transaction symbolizes a unit of work, performed within a database management system against a database, that is treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions. A transaction generally represents any change in a database. Transactions in a database environment have two main purposes:
- To provide reliable units of work that allow correct recovery from failures and keep a database consistent even in cases of system failure. For example: when execution prematurely and unexpectedly stops in which case many operations upon a database remain uncompleted, with unclear status.
- To provide isolation between programs accessing a database concurrently. If this isolation is not provided, the programs' outcomes are possibly erroneous.
SAP ASE (Adaptive Server Enterprise), originally known as Sybase SQL Server, and also commonly known as Sybase DB or Sybase ASE, is a relational model database server developed by Sybase Corporation, which later became part of SAP SE. ASE was developed for the Unix operating system, and is also available for Microsoft Windows.
Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database is an in-memory, relational database management system with persistence and high availability. Originally designed and implemented at Hewlett-Packard labs in Palo Alto, California, TimesTen spun out into a separate startup in 1996 and was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2005.
The MCP is the operating system of the Burroughs B5000/B5500/B5700 and the B6500 and successors, including the Unisys Clearpath/MCP systems.
A transaction processing system (TPS) is a software system, or software/hardware combination, that supports transaction processing.
LINC is a fourth-generation programming language, used mostly on Unisys computer systems.
Kernel Transaction Manager (KTM) is a component of the Windows operating system kernel in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 that enables applications to use atomic transactions on resources by making them available as kernel objects.
The software which Oracle Corporation markets as Oracle Data Guard forms an extension to the Oracle relational database management system (RDBMS). It aids in establishing and maintaining secondary standby databases as alternative/supplementary repositories to production primary databases.
The Unisys Data Management System II (DMSII) is a database system originally created by the Burroughs Corporation in 1972. It was available on the Burroughs (later Unisys) Small (B1000), Medium (4000, V Series) and Large System (5000, 6000, 7000) product lines. The later, A Series, Clearpath, Libra product lines support it and in recent releases of Unisys Clearpath software it has been renamed as the Enterprise Database Server for ClearPath MCP. The original DMS II used a network model.
OS 2200 is the operating system for the Unisys ClearPath Dorado family of mainframe systems. The operating system kernel of OS 2200 is a lineal descendant of Exec 8 for the UNIVAC 1108 and was previously known as OS 1100. Documentation and other information on current and past Unisys systems can be found on the Unisys public support website.
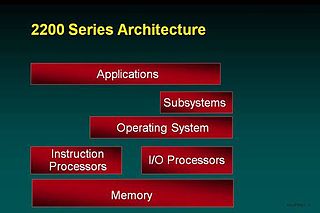
The figure shows a high-level architecture of the OS 2200 system identifying major hardware and software components. The majority of the Unisys software is included in the subsystems and applications area of the model. For example, the database managers are subsystems and the compilers are applications.

The OS 2200 communications management system includes CPComm and MCB along with many programs that provide communications related functions such as file transfer, e-mail, and distributed transaction processing protocols.

OS 2200 supports all commonly used, and many not so commonly used, distributed processing protocols, APIs, and development technology.
OS 2200 has had several generations of compilers and linkers in its history supporting a wide variety of programming languages. In the first releases, the Exec II assembler (SLEUTH) and compilers were used. The assembler was quickly replaced with an updated version (ASM) designed specifically for the 1108 computer and Exec 8 but the early compilers continued in use for quite some time.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to MySQL:
Oracle TopLink is a mapping and persistence framework for Java developers. TopLink is produced by Oracle and is a part of Oracle's OracleAS, WebLogic, and OC4J servers. It is an object-persistence and object-transformation framework. TopLink provides development tools and run-time functionalities that ease the development process and help increase functionality. Persistent object-oriented data is stored in relational databases which helps build high-performance applications. Storing data in either XML or relational databases is made possible by transforming it from object-oriented data.






