
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.

The Russian Federation continued to use the Soviet Union's seat, including its permanent membership on the Security Council in the United Nations after the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union, which originally co-founded the UN in 1945. The continuity was supported by the USSR's former members and was not objected to by the UN membership; Russia accounted for more than 75% of the Soviet Union's economy, the majority of its population and 75% of its land mass; in addition, the history of the Soviet Union began in Russia with the October Revolution in 1917 in Petrograd. If there was to be a continuator to the Soviet seat on the Security Council among the former Soviet republics, these factors made Russia seem a logical choice.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any decision other than a "procedural" decision.

The African Union-United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur was a joint African Union (AU) and United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission formally approved by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1769 on 31 July 2007, to bring stability to the war-torn Darfur region of Sudan while peace talks on a final settlement continue.

United Nations Security Council resolution 736, adopted without a vote on 29 January 1992, after examining the application of the Kyrgyz Republic for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Kyrgyzstan be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 737, adopted without a vote on 29 January 1992, recommended to the General Assembly that the Republic of Uzbekistan be admitted as a member. This recommendation followed an examination of Uzbekistan's application for membership in the United Nations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 738, adopted without a vote on 29 January 1992, after examining the application of the Republic of Tajikistan for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Tajikistan be admitted.
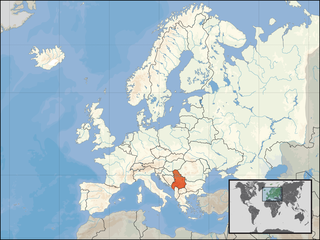
United Nations Security Council resolution 777, adopted unanimously on 19 September 1992, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1992) and all subsequent resolutions on the topic, the Council considered that, as the state known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) had ceased to exist, it noted that under Resolution 757 (1992), the claim by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to continue automatic membership in the United Nations was not widely accepted and so determined that membership of the SFRY in the United Nations could not continue. Therefore, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia cease participation in the General Assembly and apply for membership in the United Nations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 817, adopted unanimously on 7 April 1993, after examining the application of the Republic of Macedonia for membership in the United Nations, the council recommended to the General Assembly that Macedonia be admitted to membership in the United Nations, this State being provisionally referred to for all purposes within the United Nations as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" pending settlement of the difference that has arisen over the name of the State.

United Nations Security Council resolution 821, adopted on 28 April 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions, the council also recalled resolutions 757 (1992), 777 (1992) and General Assembly Resolution 47/1 (1992) which stated that the state formerly known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia had ceased to exist and that it should apply for membership in the United Nations and until then should not participate in the General Assembly.
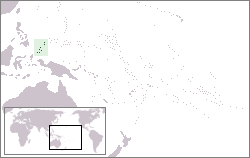
United Nations Security Council resolution 963, adopted unanimously on 29 November 1994, after examining the application of the Republic of Palau for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Palau be admitted.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1691, regarding the accession of Montenegro to the United Nations, was adopted without a vote on 22 June 2006. In the resolution, after examining the country's application for membership, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that it be admitted.
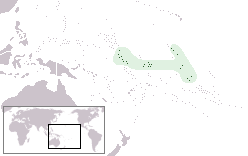
United Nations Security Council resolution 1248, adopted without a vote on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Kiribati for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Kiribati be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 186.
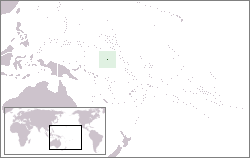
United Nations Security Council resolution 1249, adopted on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Nauru for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Nauru be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 187.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1326, adopted without a vote on 31 October 2000, after examining the application of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Yugoslavia be admitted.

The Republic of Korea and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea were simultaneously admitted to the United Nations (UN) in 1991. On 8 August 1991, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 702, recommending both states to the General Assembly for membership. On 17 September 1991, the General Assembly admitted both countries under Resolution 46/1.
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania joined the United Nations on 14 December 1955, and has participated in several UN peacekeeping operations. The current Representative of Albania in the UN is Mr. Ferit Hoxha. Albania is a non-permanent member of the 15-country UN Security Council for the two-year term (2022–2023).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2623 called for the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly on the subject of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Albania and the United States introduced the resolution before the United Nations Security Council, which adopted it on 27 February 2022. Russia voted against while China, India and the United Arab Emirates abstained. As this was a procedural resolution, no permanent member could exercise their veto power.















