
Angola was first settled by San hunter-gatherer societies before the northern domains came under the rule of Bantu states such as Kongo and Ndongo. In the 15th century, Portuguese colonists began trading, and a settlement was established at Luanda during the 16th century. Portugal annexed territories in the region which were ruled as a colony from 1655, and Angola was incorporated as an overseas province of Portugal in 1951. After the Angolan War of Independence, which ended in 1974 with an army mutiny and leftist coup in Lisbon, Angola achieved independence in 1975 through the Alvor Agreement. After independence, Angola entered a long period of civil war that lasted until 2002.
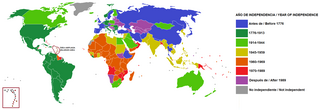
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence movements in the colonies and the collapse of global colonial empires.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and established the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). It followed an agreement by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milošević to terms proposed by President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari and former Prime Minister of Russia Viktor Chernomyrdin on 8 June, involving withdrawal of all Yugoslav state forces from Kosovo.

The United Nations Transition Assistance Group (UNTAG) was a United Nations (UN) peacekeeping force deployed from April 1989 to March 1990 in Namibia, known at the time as South West Africa, to monitor the peace process and elections there. Namibia had been occupied by South Africa since 1915, first under a League of Nations mandate and later illegally. Since 1966, South African forces had been combating an insurgency by the People's Liberation Army of Namibia (PLAN), the military wing of the Namibian-nationalist South West African People's Organization (SWAPO). The UN Security Council passed Resolution 435 in 1978, which set out a plan for elections administered by South Africa but under UN supervision and control after a ceasefire. However, only in 1988 were the two parties able to agree to a ceasefire. As UNTAG began to deploy peacekeepers, military observers, police, and political workers, hostilities were briefly renewed on the day the transition process was supposed to begin. After a new round of negotiations, a second date was set and the elections process began in earnest. Elections for the constitutional assembly took place in November 1989. They were peaceful and declared free and fair; SWAPO won a majority of the seats. The new constitution was adopted four months later and it was followed by Namibia's official independence and the successful conclusion of UNTAG.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 218, adopted on November 23, 1965, after recalling previous resolutions on the topic, and Portugal's failure to implement them, the Council again demanded that Portugal withdrawal its military presence from her colonies and enter negotiations with political parties there regarding independence.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 275, adopted on December 22, 1969, after a letter from the representative of Guinea and observing that these incidents by Portugal jeopardize international peace and security, the Council called upon Portugal to desist from violating the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Guinea. The Council deeply deplored the loss of life and heavy damage to several Guinean villages inflicted by the action from Guinea-Bissau, a territory under Portuguese administration, solemnly warning Portugal that if such acts were to be repeated in the future the Council would consider further steps to give effect to the resolution. It also called upon Portugal to release a motor barge by the name of Patrice Lumumba and all of its passengers.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 277, adopted on March 18, 1970, concerned the state of Southern Rhodesia, now known as Zimbabwe. The Council reaffirmed its previous resolutions and noted with grave concern that efforts thus far to bring the rebellion to the end had failed, some countries had not been obeying the Council's resolutions and that the situation in Southern Rhodesia continued to deteriorate as a result of the regime's new measures.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 290, adopted on December 8, 1970, after more invasions of the territory of the Republic of Guinea by naval and military units of Portugal on November 22/23 and 27/28, the Council reaffirmed its numerous previous resolutions on the topic, including the right of the peoples of Angola, Mozambique and Portuguese Guinea to be freed from the Portuguese Empire ruled by the Estado Novo regime. The Council endorsed the conclusions of the report by the Special Mission to the Republic of Guinea, strongly condemned the Portuguese Government, demanded that full compensation be paid to the Republic and declared that Portuguese colonialism was a serious threat to the peace and security of Africa.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 294, adopted on July 15, 1971, disturbed by the longstanding Portuguese violations of Senegalese territory and the recent laying of mines inside that nation which was giving shelter to independentist guerrillas of PAIGC, during the Portuguese Colonial War. The Council noted Portugal's failure to comply with previous resolutions and demanded that they immediately cease all acts of violence and destruction in Senegal and respect her territorial integrity. The Council included the usual condemnations and requested that the Secretary-General urgently send a special mission of members of the Council assisted by their military experts to carry out an inquiry into the facts of the situation and make recommendations.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 302, adopted on November 24, 1971, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic, the Council expressed its appreciation for the work accomplished by the Special Mission established in resolution 294. The Council deplored the lack of co-operation with the Special Mission by the Portuguese and called upon its government to take effective measures so that the territorial integrity of Senegal would be respected and to prevent acts of violence and destruction against the territory and its people.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 312, adopted on February 4, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic and deploring those who failed to conform to them the Council called upon Portugal to immediately recognize the right of the peoples of her colonies to self-determination, to cease all acts of repression against the peoples of Angola, Mozambique and Guinea (Bissau), to withdraw its armed forces from those areas, to promulgate an unconditional political amnesty and to transfer power to freely elected native representative institutions.

United Nations Security Council resolution 591, adopted unanimously on 28 November 1986, after recalling resolutions 418 (1977), 421 (1977), 473 (1980) and 558 (1984), the Council strengthened the mandatory arms embargo against apartheid South Africa imposed by Resolution 418, and made it more comprehensive. Resolution 591 sought to clarify vague terms from previous resolutions on the topic.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 321, adopted on October 23, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions, the Council expressed its concern that Portugal persistently refused to comply with them. The Council attacked the latest cross-border action by the Portuguese army against Senegalese territory and demanded that the Portuguese cease any further acts of violence. The Council went on to reaffirm their position that Portugal's continued holding of colonies in Africa was unjust and that the native peoples of those colonies should be allowed self-determination.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 322, adopted unanimously on November 22, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions and considering the Organisation of African Unity's recognition of the revolutionary movements of Angola, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde and Mozambique, the Council called on the government of Portugal to cease its military operations and all acts of repression against the people of those territories. The Resolution called on Portugal to enter negotiations with the parties concerned with a view to achieving a solution to the armed confrontations and permitting the peoples of those territories to exercise their right to self-determination and requested the Secretary-General to follow developments and report periodically to the Council.

Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held to be an illegal act. Annexation is a unilateral act where territory is seized and held by one state, as distinct from the complete conquest of another country, and differs from cession, in which territory is given or sold through treaty.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 384, adopted on December 22, 1975, noted statements from the representatives of Portugal, Indonesia and East Timor and recognized the right of the people of East Timor to self-determination and independence in accordance with the Charter. The Council expressed its grave concern with the deterioration of the situation in East Timor, deplored the intervention of the armed forces of Indonesia in that nation and expressed its regret that Portugal did not discharge fully its responsibilities as administering Power.
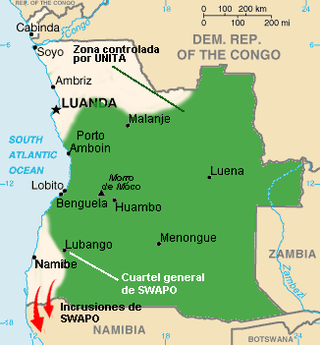
United Nations Security Council resolution 851, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993) and 834 (1993), the Council noted the continuing deterioration of the situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 15 September 1993, discussing further the peace process in the country.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1246, adopted unanimously on 11 June 1999, after recalling previous resolutions on East Timor, particularly Resolution 1236 (1999), the council established the United Nations Mission in East Timor (UNAMET) to organise and conduct the East Timor Special Autonomy Referendum on the future status of East Timor, scheduled for August 1999.

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, and United States.









