
The Gulf of Tonkin incident was an international confrontation that led to the United States engaging more directly in the Vietnam War. It consisted of a confrontation on 2 August 1964, when United States forces were carrying out covert amphibious operations close to North Vietnamese territorial waters, which triggered a response from North Vietnamese forces. The United States government falsely claimed that a second incident occurred on 4 August, between North Vietnamese and United States ships in the waters of the Gulf of Tonkin. Originally, US military claims blamed North Vietnam for the confrontation and the ostensible, but in fact imaginary, incident on 4 August. Later investigation revealed that the second attack never happened. The National Security Agency, an agency of the US Defense Department, had deliberately skewed intelligence to create the impression that an attack had been carried out.
United Nations Security Council resolution 668, adopted unanimously on 20 September 1990, after noting the ongoing political discussions and efforts regarding a just and lasting peaceful situation in Cambodia, the council endorsed the political framework that would enable the Cambodian people to exercise their right to self-determination through U.N. organised elections.

United Nations Security Council resolution 728, adopted unanimously on 8 January 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991) and 718 (1991), the Council welcomed the implementation by all parties of the agreement in Paris on 23 October 1991, but expressed concern at the existence of land mines in Cambodia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 745, adopted unanimously on 28 February 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991), 718 (1991) and 728 (1992), the council, after examining a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali on 19 February 1992, authorised the establishment of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC), following on from the political settlement agreed in Paris on 23 October 1991. It was the first occasion where the United Nations had taken over administration of a state, as opposed to monitoring or supervising.

United Nations Security Council resolution 766, adopted unanimously on 21 July 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991), 718 (1991), 728 (1992) and 745 (1992), the Council acknowledged and expressed its concern at the difficulties experienced by the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) in the implementation of a political settlement in Cambodia signed at the Paris Conference on 23 October 1991.

United Nations Security Council resolution 783, adopted unanimously on 13 October 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991), 718 (1991), 728 (1992), 745 (1992) and 766 (1992) and noting a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali, the council welcomed the progress the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) had made in Cambodia in accordance with the Paris Agreements, however it recognised various security and economic concerns facing UNTAC.
United Nations Security Council resolution 792, adopted on 30 November 1992, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 717 (1991), 718 (1991), 728 (1992), 745 (1992), 766 (1992) and 783 (1992) noting a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali, the Council concerned itself with preparations for the 1993 elections in Cambodia by the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) while condemning the refusal of the Party of Democratic Kampuchea to co-operate.

United Nations Security Council resolution 810, adopted unanimously on 8 March 1993, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990) and 745 (1992), the council, after deploring continuing political violence in Cambodia in violation of the Paris Agreements as well as attacks and detention of members of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC), discussed upcoming elections to the Constituent Assembly, as part of a process of national reconciliation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 826, adopted unanimously on 20 May 1993, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 745 (1992) and 810 (1993), the council supported the five million Cambodians who registered to vote despite violence and intimidation and discussed further preparations for the upcoming elections.

United Nations Security Council resolution 840, adopted unanimously on 15 June 1993, after recalling resolutions 668 (1990), 745 (1992), 810 (1993), 826 (1993), 835 (1993) and other relevant resolutions, the Council endorsed the results of the 1993 general elections in Cambodia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 878, adopted unanimously on 29 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 733 (1992), 746 (1992), 751 (1992), 767 (1992), 775 (1992), 794 (1992), 814 (1993), 837 (1993) and 865 (1993) on Somalia, the Council expressed its commitment to a future concerted strategy for the United Nations Operation in Somalia II and extended its mandate for an interim period until 18 November 1993.

United Nations Security Council resolution 880, adopted unanimously on 4 November 1993, after recalling Resolution 745 (1992) and other relevant resolutions on Cambodia, the Council concerned itself with the withdrawal of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) from the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 927, adopted unanimously on 15 June 1994, after recalling resolutions 186 (1964), 831 (1993) and 889 (1993), the council expressed concern at the lack of progress in the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 31 December 1994.
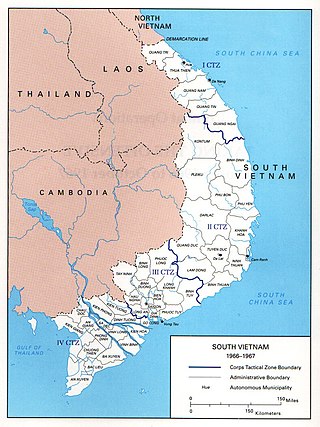
South Vietnam was in political chaos during much of the year, as generals competed for power and Buddhists protested against the government. The Viet Cong (VC) communist guerrillas expanded their operations and defeated the South Vietnamese Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) in many battles. North Vietnam made a definitive judgement in January to assist the VC insurgency with men and material. In November, North Vietnam ordered the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) to infiltrate units into South Vietnam and undertake joint military operations with the VC.

United Nations Security Council resolution 969, adopted unanimously on 21 December 1994, after recalling resolutions 186 (1964), 831 (1993) and 889 (1993), the Council expressed concern at the lack of progress in the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 30 June 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1032, adopted unanimously on 19 December 1995, after recalling all resolutions on Cyprus, particularly resolutions 186 (1964) and 1000 (1995), the Council expressed concern at the lack of progress in the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 30 June 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1062, adopted unanimously on 28 June 1996, after recalling all resolutions on Cyprus, particularly resolutions 186 (1964), 939 (1994) and 1032 (1995), the Council expressed concern at the lack of progress in the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 31 December 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1381, adopted unanimously on 27 November 2001, after considering a report by the secretary-general Kofi Annan regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), the council extended its mandate for a further six months until 31 May 2002.

The United Nations Supervision Mission in Syria (UNSMIS) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission in Syria, set up in 2012 as a result of United Nations Security Council Resolution 2043 in response to the Syrian Civil War. It was commanded by Norwegian Major General Robert Mood until 20 July 2012 followed by Lieutenant General Babacar Gaye from Senegal. Although observers remain in the country, Mood suspended their mission on June 16, 2012, citing "escalating violence". Observers will conduct no further patrols and stay in their current positions until the suspension is lifted. On 20 July 2012, the Security Council extended UNSMIS for a final period of 30 days. According to resolution 2059, the Council would only consider more extensions in the event that the Secretary-General reports and the Security Council confirms the cessation of the use of heavy weapons and a reduction in the level of violence sufficient by all sides to allow UNSMIS to implement its mandate.

The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution or the Southeast Asia Resolution, Pub. L. 88–408, 78 Stat. 384, enacted August 10, 1964, was a joint resolution that the United States Congress passed on August 7, 1964, in response to the Gulf of Tonkin incident.
















