
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

The Maldives has remained an independent nation throughout its recorded history, save for a brief spell of Portuguese occupation in the mid-16th century. From 1900 to 1965, the country was a British protectorate while retaining full internal sovereignty. At its independence in 1965, the Maldives joined the United Nations on 20 September.

United Nations Security Council resolution 794, adopted unanimously on 3 December 1992, after reaffirming resolutions 733 (1992), 746 (1992), 751 (1992), 767 (1992) and 775 (1992), the Council "[expressed] grave alarm" regarding the situation in Somalia and authorised the creation of the Unified Task Force (UNITAF) to create a "secure environment for humanitarian relief operations in Somalia" in order to provide "essential for the survival of the civilian population". The current resolution determined that "the magnitude of human tragedy caused by the conflict in Somalia, further exacerbated by the obstacles being created to the distribution of humanitarian assistance [constitutes] a threat to international peace and security".

The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, the UN member states were unofficially organized into five groups as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees. Now this grouping has taken on a much more expansive and official role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting.

United Nations Security Council resolution 825, adopted on 11 May 1993, called upon the Democratic People's Republic of Korea to reconsider its decision to withdraw from the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and allow weapons inspectors from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) into the country, after it had previously refused entry.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:

United Nations Security Council Resolution 193 was adopted on August 9, 1964. After a serious deterioration of the situation in Cyprus, the Council reaffirmed an appeal to Turkey, to cease bombarding the island, and to Cyprus, ordering all her armed forces to cease firing. The Council called upon all to co-operate fully with the Commander of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus and to refrain from any action that might exacerbate or broaden the hostilities.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 207, adopted unanimously on August 10, 1965, after a receiving report by the Secretary-General stating that recent developments in Cyprus had increased tension on the island, the Council reaffirmed its Resolution 186 and called upon all parties to avoid any action which would be likely to worsen the situation.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 213 was adopted unanimously on September 20, 1965. It was done after examining the application of Singapore for membership in the United Nations. The Council recommended to the General Assembly that Singapore be admitted.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people are generally discriminated in the Maldives.

Israel–Maldives relations refer to foreign relations between Israel and the Maldives. The countries had diplomatic relations from 1965 to 1974. From 2012 to 2017, they maintained cooperation agreements, but did not restore full diplomatic relations. In 2024, the Maldives decided banned Israeli passport holders from entering the nation due to the Israeli government's conduct in the Israel–Hamas war. However, the ban process is currently suspended.

United Nations Security Council resolution 881, adopted unanimously on 4 November 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993) and 876 (1993) concerning the Georgian–Abkhazian war, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1334, adopted unanimously on 22 December 2000, after recalling resolutions 1270 (1999), 1289 (1999), 1313 (2000), 1317 (2000) and 1321 (2000) on the situation in Sierra Leone, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL) until 31 March 2001. It was the final resolution adopted in 2000.
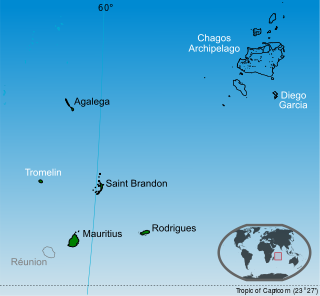
Sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago is disputed between Mauritius, Maldives and the United Kingdom. Mauritius has repeatedly stated that the Chagos Archipelago is part of its territory and that the United Kingdom claim is a violation of United Nations resolutions banning the dismemberment of colonial territories before independence. On 22 May 2019, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a non-binding resolution declaring that the archipelago was part of Mauritius; 116 countries voted in favour of Mauritius while six opposed it.
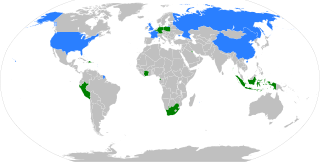
The 2018 United Nations Security Council election was held on 8 June during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2019.

The Legal Consequences of the Separation of the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritius in 1965 is an advisory opinion issued by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on the Chagos Archipelago sovereignty dispute in response to a request from the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA). In a 13–1 ruling, the Court deemed the United Kingdom's separation of the Chagos Islands from the rest of Mauritius in 1965, when both were colonial territories, to be unlawful and found that the United Kingdom is obliged to end "its administration of the Chagos Islands as rapidly as possible."

United Nations Security Council resolutions are United Nations resolutions adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council (UNSC); the United Nations (UN) body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".














