
The United Nations General Assembly, UNGA; French: Assemblée générale des Nations unies, AGDNU is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 79th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter.
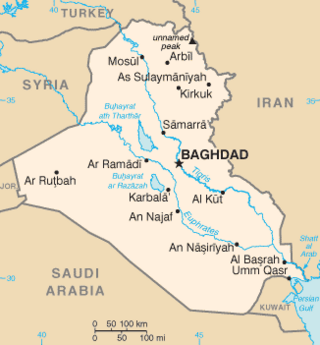
United Nations Security Council resolution 1284, adopted on 17 December 1999, after recalling previous relevant resolutions on Iraq, including resolutions 661 (1990), 687 (1991), 699 (1991), 707 (1991), 715 (1991), 986 (1995), 1051 (1996), 1153 (1998), 1175 (1998), 1242 (1999) and 1266 (1999), the council established the United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission (UNMOVIC) to replace the United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM). It was the final resolution adopted in 1999.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 688, adopted on 5 April 1991, after receiving letters from the representatives of France, Iran, and Turkey and expressing its concern over political repression of the Iraqi people, including those in Iraqi Kurdistan, the Council condemned the repression and demanded that Iraq, as a contribution to removing the threat to international peace and security, end the repression and respect the human rights of its population.
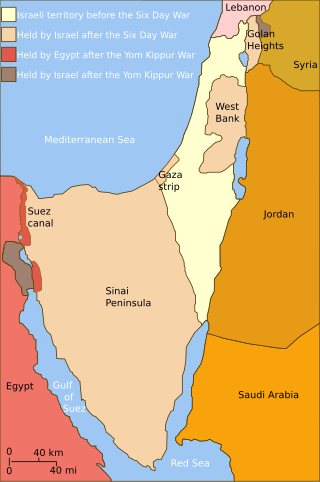
United Nations Security Council Resolution 350, adopted on 31 May 1974, established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, to monitor the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the wake of the Yom Kippur War. UNDOF was initially established for a period of six months, but has had its mandate renewed by subsequent resolutions.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 309, adopted on February 4, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic, the Council invited the Secretary-General, in close co-operation in a group of the Council composed of representatives of Argentina, Somalia and Yugoslavia, to initiate as soon as possible contacts with all parties concerned to enable the people of Namibia to exercise their right to self-determination and independence. The Council called upon South Africa to co-operate and requested the Secretary-General to report back no later that July 31, 1972.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 323, adopted on December 6, 1972, after recalling previous resolutions and reaffirming the United Nations' responsibility for Namibia, the Council observed with satisfaction that Namibians had an opportunity of expressing their aspirations to representatives of the UN and noted that the overwhelming majority of the opinions of those consulted were in favor of the abolition of the "homelands policy" and accession to national independence. The Council expressed regret for South Africa's opaqueness regarding self-determination for Namibia and invited the Secretary-General to continue his valuable efforts to ensure that the people of Namibia exercise their right to self-determination and independence.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 341, adopted on October 27, 1973, after the report of the Secretary-General on the implementation of Resolution 340, the Council decided that the Peacekeeping Force would be established for a six-month period and would be continued thereafter if the Council wished it to do so.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 346, adopted on April 8, 1974, thanked the nations who contributed to the emergency force established in resolution 340 and agreed with the opinion of the Secretary-General; that the separation of the Egyptian and Israeli forces was only the beginning to a peaceful settlement of the issue and called upon member states to continue to support the emergency force.
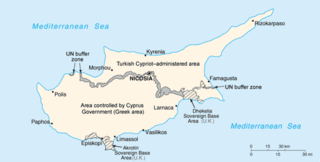
United Nations Security Council Resolution 443, adopted on December 14, 1978, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The Council expressed its concerns regarding actions which could heighten tensions, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before May 31, 1979, to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 458, adopted on 14 December 1979, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The council expressed its concerns regarding actions which could heighten tensions, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before 31 May 1980 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 472, adopted on 13 June 1980, noted a report of the secretary-general that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The council expressed its concerns regarding actions which could heighten tensions, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before 30 November 1980 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 482, adopted on 11 December 1980, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The council expressed its desire for all parties to support the ten-point agreement for the resumption of intercommunal talks, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before 31 May 1981 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 486, adopted on 4 June 1981, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The council expressed its desire for all parties to support the ten-point agreement for the resumption of intercommunal talks, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before 30 November 1981 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council resolution 948, adopted on 15 October 1994, after recalling resolutions 841 (1993), 861 (1993), 862 (1993), 867 (1993), 873 (1993), 875 (1993), 905 (1994), 917 (1994), 933 (1994), 940 (1994) and 944 (1994), the Council welcomed the return of the legitimate President of Haiti Jean-Bertrand Aristide and lifted sanctions imposed on the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 955, adopted on 8 November 1994, after recalling all resolutions on Rwanda, the Council noted that serious violations of international humanitarian law had taken place in the country and, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, established the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1077, adopted on 22 October 1996, after reaffirming all resolutions 937 (1994), 1036 (1996) and 1065 (1996) on Georgia, the council established a Human Rights Office in Sukhumi, Georgia as part of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG).
United Nations Security Council resolution 1165, adopted unanimously on 30 April 1998, after recalling Resolution 955 (1994), the council established a third trial chamber at the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR).
United Nations Security Council resolution 1246, adopted unanimously on 11 June 1999, after recalling previous resolutions on East Timor, particularly Resolution 1236 (1999), the council established the United Nations Mission in East Timor (UNAMET) to organise and conduct the East Timor Special Autonomy Referendum on the future status of East Timor, scheduled for August 1999.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1898 was adopted on 14 December 2009.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/1 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 2 March 2022. It deplored Russia's invasion of Ukraine and demanded a full withdrawal of Russian forces and a reversal of its decision to recognise the self-declared People's Republics of Donetsk and Luhansk.













