
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The United Nations General Assembly, UNGA; French: Assemblée générale des Nations unies, AGDNU is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its 79th session, its powers, composition, functions, and procedures are set out in Chapter IV of the United Nations Charter.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
The Military Staff Committee (MSC) is the United Nations Security Council subsidiary body whose role, as defined by the United Nations Charter, is to plan UN military operations and assist in the regulation of armaments. Although the Military Staff Committee continues to exist, negotiation efforts between the United States, the Soviet Union and other nations in the late 1940s failed, and the committee has since been largely defunct, only serving in an advisory capacity.

The United Nations Security Council veto power is the power of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council to veto any decision other than a "procedural" decision.
The United Nations Atomic Energy Commission (UNAEC) was founded on 24 January 1946 by the very first resolution of the United Nations General Assembly "to deal with the problems raised by the discovery of atomic energy."
Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter sets out the UN Security Council's powers to maintain peace. It allows the Council to "determine the existence of any threat to the peace, breach of the peace, or act of aggression" and to take military and nonmilitary action to "restore international peace and security".
The United Kingdom is a founding member of the United Nations and one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council.
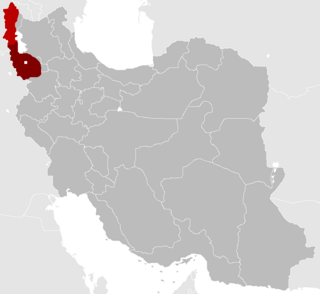
United Nations Security Council Resolution 3 was adopted on 4 April 1946. The Council acknowledged that Soviet troops occupying Iran were not removed in accordance with the Tri-partite Treaty of 29 January. Further proceedings surrounding the Iranian crisis were deferred until 6 May, when Soviet withdrawal was to be complete.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 8 was adopted on 29 August 1946.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 13 was adopted unanimously on 12 December 1946. The Council recommended that the General Assembly admit Siam as a member state.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:

United Nations Security Council Resolution 83, adopted on June 27, 1950, determined that the attack on the Republic of Korea by forces from North Korea constituted a breach of the peace. The Council called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and for the authorities in North Korea to withdraw their armed forces to the 38th parallel. They also noted the report by the United Nations Commission on Korea that stated North Korea's failure to comply with Security Council Resolution 82 and that urgent military measures were required to restore international peace and security.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2016 was unanimously adopted on 27 October 2011 on the situation of Libya during the Libyan Civil War.

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, and United States.

Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was a charter member of the United Nations from its establishment in 1945 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. During its existence the country played a prominent role in the promotion of multilateralism and narrowing of the Cold War divisions in which various UN bodies were perceived as important vehicles. Yugoslavia was elected a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council on multiple occasions in periods between 1950 and 1951, 1956, 1972–1973, and 1988–1989, which was in total 7 years of Yugoslav membership in the organization. The country was also one of 17 original members of the Special Committee on Decolonization.











