Related Research Articles
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or a region of Earth.

Gerardus Mercator was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines—an innovation that is still employed in nautical charts.

Frederick I, of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was Elector of Brandenburg (1688–1713) and Duke of Prussia in personal union (Brandenburg-Prussia). The latter function he upgraded to royalty, becoming the first King in Prussia (1701–1713). From 1707 he was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel. He was also the paternal grandfather of Frederick the Great.

The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the Rhein-Universität on 18 October 1818 by Frederick William III, as the linear successor of the Kurkölnische Akademie Bonn which was founded in 1777. The University of Bonn offers many undergraduate and graduate programs in a range of subjects and has 544 professors. Its library holds more than five million volumes.

The Ruhr, also referred to as Ruhr area, Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km2 and a population of over 5 million (2017), it is the largest urban area in Germany. It consists of several large cities bordered by the rivers Ruhr to the south, Rhine to the west, and Lippe to the north. In the southwest it borders the Bergisches Land. It is considered part of the larger Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region of more than 10 million people, which is among the largest in Europe.

Duisburg is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers, Duisburg is one of the largest cities in the Ruhr and the 15th-largest city in Germany.

Essen is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of 582,760 makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and Dortmund, as well as the tenth-largest city of Germany. Essen lies in the larger Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region and is part of the cultural area Rhineland. Because of its central location in the Ruhr, Essen is often regarded as the Ruhr's "secret capital". In the north, the city is flown through by the Emscher, the Ruhr area's central river, and in the south by the Ruhr River, which is dammed in Essen to form the Lake Baldeney (Baldeneysee) and Lake Kettwig reservoirs. The central and northern boroughs of Essen historically belong to the Low German (Westphalian) language area, and the south of the city to the Low Franconian (Bergish) area.

Brandenburg-Prussia is the historiographic denomination for the Early Modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenzollern intermarried with the branch ruling the Duchy of Prussia, and secured succession upon the latter's extinction in the male line in 1618. Another consequence of the intermarriage was the incorporation of the lower Rhenish principalities of Cleves, Mark and Ravensberg after the Treaty of Xanten in 1614.

The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin.

Prussia was a historically prominent German state that originated in 1525 with a duchy centered on the region of Prussia on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organised and effective army. Prussia, with its capital first in Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, in Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.

The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region is the largest metropolitan region in Germany with over ten million inhabitants. A polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the region covers an area of 7,268 square kilometres (2,806 sq mi), entirely within the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region spreads from the Ruhr area (Dortmund-Essen-Duisburg-Bochum) in the north, to the urban areas of the cities of Mönchengladbach, Düsseldorf, Wuppertal, Leverkusen, Cologne, and Bonn in the south. The location of the Rhine-Ruhr at the heart of the European Blue Banana makes it well connected to other major European cities and metropolitan areas like the Randstad, the Flemish Diamond and the Frankfurt Rhine Main Region.

European University Viadrina Frankfurt (Oder) is a university located at Frankfurt (Oder) in Brandenburg, Germany. It is also known as the University of Frankfurt (Oder). The city is on the Oder River, which marks the border between Germany and Poland. With 5,200 students — around 1,000 of whom come from Poland — and some 160 teaching staff, the Viadrina is one of Germany's smallest universities.

The Prussian Navy, officially the Royal Prussian Navy, was the naval force of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1701 to 1867.

The University of Duisburg-Essen is a public research university in Duisburg and Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany and a member of the newly founded University Alliance Metropolis Ruhr. It was founded in 1654 and re-established on 1 January 2003, as a merger of the Gerhard Mercator University of Duisburg and the University of Essen.
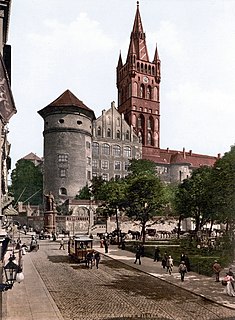
Königsberg was the name for the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia.
The actual boundaries of the Ruhr vary slightly depending on the source, but a good working definition is to define the Lippe and Ruhr as its northern and southern boundaries respectively, the Rhine as its western boundary, and the town of Hamm as the eastern limit.

Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg, also referred to as MLU, is a public, research-oriented university in the cities of Halle and Wittenberg in the State of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. MLU offers German and international (English) courses leading to academic degrees such as BA, BSc, MA, MSc, doctoral degrees, and Habilitation.
The Burgschule or Oberrealschule auf der Burg was a secondary school (Oberrealschule) located originally in central Königsberg, Germany, and later in the suburban Amalienau quarter. It was the fourth oldest school in the city, behind Altstadt Gymnasium, Kneiphof Gymnasium, and Löbenicht Realgymnasium.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Duisburg, Germany.