Related Research Articles

HMS Erebus was a Hecla-class bomb vessel constructed by the Royal Navy in Pembroke dockyard, Wales, in 1826. The vessel was the second in the Royal Navy named after Erebus, the personification of darkness in Greek mythology.

HMS A1 was the Royal Navy's first British-designed submarine, and their first to suffer fatal casualties.

HMS Terror was a specialised warship and a newly developed bomb vessel constructed for the Royal Navy in 1813. She participated in several battles of the War of 1812, including the Battle of Baltimore with the bombardment of Fort McHenry. She was converted into a polar exploration ship two decades later, and participated in George Back's Arctic expedition of 1836–1837, the successful Ross expedition to the Antarctic of 1839 to 1843, and Sir John Franklin's ill-fated attempt to force the Northwest Passage in 1845, during which she was lost with all hands along with HMS Erebus.

Chesil Cove is a curved steep bank forming the south-east end of 29-kilometre (18 mi) Chesil Beach in Dorset, England. It is thus part of one of three large shingle structures in Britain, extending from West Bay to the Isle of Portland, the latter acting more firmly as a great barrier (groyne) which stops tidal action from washing the beach away and leads to the high depositions by wind and tide action forming the grand curved bank of this "cove". The "cove", bill and much of Chesil Beach give shelter from the prevailing winds and waves for much of Weymouth Bay, the town of Weymouth and the village of Chiswell. It forms part of the Jurassic Coast.

Gunwalloe is a coastal civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated on the Lizard Peninsula three miles (4.8 km) south of Helston and partly contains The Loe, the largest natural freshwater lake in Cornwall. The parish population including Berepper at the 2011 census was 219. The hamlets in the parish are Chyanvounder, Berepper and Chyvarloe. To the east are the Halzephron cliffs and further east the parish church.

USAT Brigadier General M. G. Zalinski was a U.S. Army transport ship that served in World War II. It sank in 1946 in the Grenville Channel in British Columbia's Inside Passage. The crew were rescued by a tug boat and the SS Catala passenger steamer, but the cargo of bombs and oil went down with the ship.

The Seaton Carew Wreck is a protected wrecksite lying in the intertidal zone at Seaton Carew. Prior to 1996 the wreck had been completely covered by the sand of the beach, but it was exposed in 1996 and 2002 and has been regularly exposed since 2004. The wreck is of a type of vessel known as a collier brig which would have been ubiquitous in the 18th and 19th centuries and is unusual on the North-East coast for the high degree of preservation. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
St Anthony or Santo António was a Portuguese carrack that foundered in Gunwalloe Bay, Cornwall, in 1527 en route from Lisbon to Antwerp. She had a mixed cargo including copper and silver ingots. The wreck was recorded historically, because the salvage of the cargo was the subject of an international dispute that led to a Court of Star Chamber, but the location of the wreck was unknown until 1981. The wreck is designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act and is managed by Historic England.
The Diamond was a three-masted square rigger, built in New York City in 1823. She was one of the first ships to operate a regular service for passenger and cargo between Britain and the United States. She sank en route to Liverpool from New York on 2 January 1825 in Cardigan Bay. The alleged wreck site was identified in 2000 and was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act 1973 on 1 April 2002, the first such designation by the National Assembly for Wales. However, the identification has since been called into question.
The Wheel Wreck is the remains of a shipwreck lying in Crow sound off Little Ganinick in the Isles of Scilly. The wreck site consists of a discrete mound of cargo that appears to consist of numerous sizes of different iron wheels, cogs, clack valves, tubes and boiler pipes. Lead scupper pipes and other small artefact material show the ship was once present, however, not much remains of this vessel today. A Trotmann style anchor lies some 60m from the site, and this along with the cargo, date the site as sometime just after 1835. It has been published that this may be the wreck of the Padstow, however, being lost in 1804 this can not be so as neither boiler tubes or Trotmann anchors were invented back then. The wreck was discovered by local diver Todd Stevens in 2005 and investigated by the archaeological contractor for the Protection of Wrecks Act 1973 in 2006. It still remains unidentified. However it is most likely to be a ship called the 'Plenty' which is recorded locally as having sank- "within 1 mile of the principal island" -in 1840.
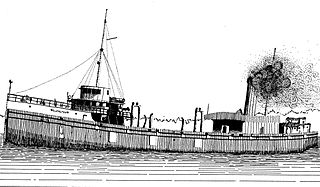
The Glenlyon was a freighter built in 1893; it was sunk off the shore of Isle Royale in Lake Superior in 1924 and the remains are still on the lake bottom. The wreck was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

SS Ohio was a wooden hulled Great Lakes freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America from her construction in 1875, to her sinking in September 1894 when she collided with the schooner barge Ironton which also sank in the collision. Ironton was being towed by the steamer Charles J. Kershaw, which was also towing the schooner Moonlight. Ohio was found upright in 2017, over 122 years after her sinking in over 200 feet of water off Presque Isle, Michigan. In March, 2023, it was announced that Ironton had been located in 2019. The researchers who discovered Ohio plan to nominate her for a listing in the National Register of Historic Places.
The remains of an unknown wreck were discovered on Church Rocks, off Teignmouth in 1975. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 3 August 1977. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The Chesil Beach cannon consists of the remains of an unknown wreck were found on Chesil Beach, Dorset, England in 2010. The site was designated on 18 July 2017. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The remains of a seventeenth century cargo vessel were found to the west of the Outer Pollock Reef, off West Bay, Dorset, England in 2004. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 17 July 2005. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The remains of a Middle Bronze Age vessel were identified in Langdon Bay, Kent, England in 1974. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 25 May 1978. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The remains of a seventeenth century cargo vessel were identified in Gunwalloe fishing cove, Cornwall in 1998. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 23 May 1999. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.

The Rill Cove Wreck is an underwater wreck of a 16th-century Spanish cargo ship lying off the coast of Rill Cove, west of Kynance Cove, in Cornwall, England, UK.
The remains of an armed cargo vessel were discovered in 1983 in Studland Bay, off Dorset, England. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 22 October 1984. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England
References
- 1 2 "Unknown Wreck off Thorness Bay - 1402103 | Historic England". historicengland.org.uk. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
50°44′54″N1°21′22″W / 50.7482°N 1.3562°W