
The Tamar is a river in south west England that forms most of the border between Devon and Cornwall. A part of the Tamar Valley is a World Heritage Site due to its historic mining activities.

Bude is a seaside town in north east Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, in the civil parish of Bude-Stratton and at the mouth of the River Neet. It was sometimes formerly known as Bude Haven. It lies southwest of Stratton, south of Flexbury and Poughill, and north of Widemouth Bay, located along the A3073 road off the A39. Bude is twinned with Ergué-Gabéric in Brittany, France. Bude's coast faces Bude Bay in the Celtic Sea, part of the Atlantic Ocean. The population of the civil parish can be found under Bude-Stratton.

Rutland Water is a reservoir in Rutland, England, east of Rutland's county town, Oakham. It is filled by pumping from the River Nene and River Welland, and provides water to the East Midlands. By surface area it is the largest reservoir in England, but its capacity is exceeded by that of Kielder Water in Northumberland. Its maximum depth is 33m.

Boscastle is a village and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England, in the civil parish of Forrabury and Minster. It is 14 miles (23 km) south of Bude and 5 miles (8 km) northeast of Tintagel. The harbour is a natural inlet protected by two stone harbour walls built in 1584 by Sir Richard Grenville and is the only significant harbour for 20 miles (32 km) along the coast. The village extends up the valleys of the River Valency and River Jordan. Heavy rainfall on 16 August 2004 caused extensive damage to the village.

The Bude Canal was a canal built to serve the hilly hinterland in the Cornwall and Devon border territory in the United Kingdom, chiefly to bring lime-bearing sand for agricultural fertiliser. The Bude Canal system was one of the most unusual in Britain.

Llyn Brenig is a reservoir located on Denbigh Moors in North Wales. The artificial lake, which was constructed between 1973 and 1976, was created by building an embankment dam across the Afon Brenig valley. It lies at 1,200 ft (370 m) above sea level on the border between the counties of Conwy and Denbighshire. It is used to manage the flow in the River Dee as part of the River Dee regulation system.

Morwenstow is a civil parish in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The parish abuts the west coast, about six miles (10 km) north of Bude and within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB).

South West Water provides drinking water and waste water services throughout Devon and Cornwall and in small areas of Dorset and Somerset. South West Water was created in 1989 with the privatisation of the water industry. It was preceded by the South West Water Authority which was formed by the Water Act 1973 as one of ten regional water authorities formed by a merger of various statutory and local authority water undertakings. South West Water is part of the Pennon Group.

Alfardisworthy is a hamlet in Devon, England, which straddles the border with Cornwall. To the northwest is a reservoir, named Upper Tamar Lake, which provides water for the town of Bude and surrounding areas. To the south is Lower Tamar Lake which was constructed to supply the Bude Canal with water. Alfardisworthy is in the parish of Bradworthy.

The River Wolf is a minor river in the west of the county of Devon in England. Its name may come from a Celtic or earlier name recorded by the Roman map-maker Ptolemy as Ουολιβα (Voliba) as a town of the Dumnonii ; rather than referring to the wolf animal.

North Tamerton is a village and civil parish in east Cornwall, England, UK. The village is situated approximately eight miles (13 km) southeast of Bude and eight miles (13 km) north of Launceston.
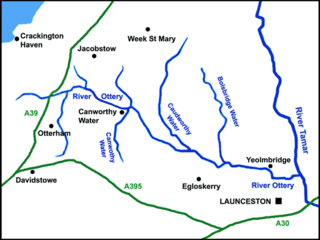
The River Ottery is a small river in northeast Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The river is about twenty miles (32 km) long from its source southeast of Otterham to its confluence with the River Tamar at Nether Bridge, two miles (3.2 km) northeast of Launceston.

The Tamar–Tavy Estuary is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) covering the tidal estuaries of the River Tamar and the River Tavy on the border between Cornwall and Devon in England, UK. Part of the Tamar estuary also forms the Tamar Estuary Nature Reserve, owned by the Cornwall Wildlife Trust. The site was designated in 1991 for its biodiversity and varying habitats that support many wader and wildfowl species, as well as the special interest of its marine biology.

Steeple Point to Marsland Mouth is a coastal Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Cornwall, England, UK, noted for its biological characteristics.

Lower Tamar Lake is a 35 acre reservoir located on the Devon-Cornwall border, in England, near Thurdon.

Pancrasweek is a civil parish and hamlet in the far west of Devon, England forming part of the local government district of Torridge and lying about three miles north west of the town of Holsworthy.

The River Carey is a small river in West Devon that is a tributary to the River Tamar.




















