
The Republic of Upper Volta was a landlocked West African country established on 11 December 1958 as a self-governing state within the French Community. Before becoming autonomous, it had been part of the French Union as the French Upper Volta. On 5 August 1960, it gained full independence from France. On 4 August 1984, it changed its name to Burkina Faso.
High commissioner is the title of various high-ranking, special executive positions held by a commission of appointment.

French Sudan was a French colonial territory in the Federation of French West Africa from around 1880 until 1959, when it joined the Mali Federation, and then in 1960, when it became the independent state of Mali. The colony was formally called French Sudan from 1890 until 1899 and then again from 1921 until 1958, and had a variety of different names over the course of its existence. The colony was initially established largely as a military project led by French troops, but in the mid-1890s it came under civilian administration.

French West Africa was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan, French Guinea, Ivory Coast, Upper Volta, Dahomey and Niger. The federation existed from 1895 until 1958. Its capital was Saint-Louis in Senegal until 1902, and then Dakar until the federation's collapse in 1960.

Upper Senegal and Niger was a colony in French West Africa, created on 21 October 1904 from colonial Senegambia and Niger by the decree "For the Reorganisation of the general government of French West Africa".

French Sudan was established in the late nineteenth century and occupied roughly the same territory as modern Mali.

The Mali Federation was a federation in West Africa linking the French colonies of Senegal and the Sudanese Republic for two months in 1960. It was founded on 4 April 1959 as a territory with self-rule within the French Community and became independent after negotiations with France on 20 June 1960. Two months later, on 19 August 1960, the Sudanese Republic leaders in the Mali Federation mobilized the army, and Senegal leaders in the federation retaliated by mobilizing the gendarmerie ; this resulted in a tense stand-off, and led to the withdrawal from the federation by Senegal the next day. The Sudanese Republic officials resisted this dissolution, cut off diplomatic relations with Senegal, and defiantly changed the name of their country to Mali. For the brief existence of the Mali Federation, the premier was Modibo Keïta, who would later become the first President of Mali, and its government was based in Dakar, the eventual capital of Senegal.

Upper Volta was a colony of French West Africa established in 1919 in the territory occupied by present-day Burkina Faso. It was formed from territories that had been part of the colonies of Upper Senegal and Niger and the Côte d'Ivoire. The colony was dissolved on 5 September 1932, with parts being administered by the Côte d'Ivoire, French Sudan and the Colony of Niger.

The Colony of Niger was a French colonial possession covering much of the territory of the modern West African state of Niger, as well as portions of Mali, Burkina Faso and Chad. It existed in various forms from 1900 to 1960 but was titled the Colonie du Niger only from 1922 to 1960.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Burkina Faso, known as Upper Volta until July 1984.

Burkinabe nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Burkina Faso, as amended; the Persons and Family Code, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Burkina Faso. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Burkinabe nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth in Burkina Faso or abroad to parents with Burkinabe nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization.

The Burkina Faso–Niger border is 622 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Mali in the north to the tripoint with Benin in the south.

The Benin–Burkina Faso border is 386 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Togo in the southwest to the tripoint with Niger in the northeast.
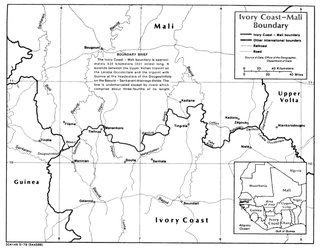
The Ivory Coast–Mali border is 599 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Guinea in the west to the tripoint with Burkina Faso in the east.

The Burkina Faso–Mali border is 1,325 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Ivory Coast in the west to the tripoint with Niger in the east.

The Burkina Faso–Ivory Coast border is 545 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Mali in the west to the tripoint with Ghana in the east.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











