
The Soo Line Railroad is the primary United States railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway, one of seven U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CP subsidiaries: The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway, and the Wisconsin Central Railway. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line Railroad and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, CP's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway. Most equipment has been repainted into the CP scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all of CP's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are located in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

There have been two uses of Columbus and Greenville Railway, both for the same rail line.

The Nevada Northern Railway was a railroad in the U.S. state of Nevada, built primarily to reach a major copper producing area in White Pine County, Nevada. The railway, constructed in 1905–06, extended northward about 140 miles (230 km) from Ely to connections with the Western Pacific Railroad at Shafter and Southern Pacific Railroad at Cobre. In 1967 NN reported 40 million net ton-miles of revenue freight on 162 miles (261 km) of line.

The San Joaquin Valley Railroad is one of several short line railroad companies and is part of the Pacific Region Division of Genesee & Wyoming Inc. It operates over about 371 miles (597 km) of owned or leased track primarily on several lines in California's Central Valley/San Joaquin Valley around Fresno and Bakersfield. The SJVR has trackage rights over Union Pacific between Fresno, Goshen, Famoso, Bakersfield and Algoso. The SJVR also operated for the Tulare Valley Railroad (TVRR) from Calwa to Corcoran and Famoso.

The Missouri and Northern Arkansas Railroad, LLC is a Class III shortline railroad headquartered in Carthage, Missouri. It is not to be confused with the Missouri and North Arkansas Railroad which connected Joplin, Missouri with Helena, Arkansas from 1906 to 1946.

The Abilene and Smoky Valley Railroad is a heritage railway located in Abilene, Kansas, United States.

The Finger Lakes Railway is a Class III railroad in the Finger Lakes region of New York. The company began operations on July 23, 1995, and operates in Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, Ontario, Schuyler and Yates counties. The FGLK operates 18 diesel locomotives on 167 miles (269 km) of ex-Conrail trackage, formerly owned by the New York Central Railroad, the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Lehigh Valley Railroad. Between 2001 and 2013, the railroad operated a heritage railroad known as the Finger Lakes Scenic Railway which offered passenger train excursions.

The California Northern Railroad is one of several Class III short-line railroad companies owned by Genesee & Wyoming, Inc. It operates over Southern Pacific Railroad (SP) tracks under a long-term lease.

The Willamette Valley Railway is a short-line railroad that operates in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. It leased a line from Woodburn to Stayton from the Southern Pacific Transportation Company in February 1993, as well as a branch from Geer west to Salem, and purchased the property in 1996. The company also leased a line between Albany and Mill City in 1993, but transferred the lease to the Albany and Eastern Railroad in October 2000.

The New England Central Railroad is a regional railroad in the New England region of the United States. It began operations in 1995, as the successor of the Central Vermont Railway (CV). The company was originally a subsidiary of holding company RailTex before being purchased by RailAmerica in 2000. In 2012, the company was purchased by Genesee & Wyoming, its current owner.

The Arizona Eastern Railway is a Class III railroad that operates 265 miles (426 km) of railroad between Clifton, Arizona, and Miami, Arizona, in the United States. This includes trackage rights over the Union Pacific Railroad between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Bowie, Arizona. The railroad serves the copper mining region of southeastern Arizona, and the agricultural Gila River Valley. Primary commodities are sulfuric acid, copper concentrate, copper anode and cathode, and copper rod and other copper processing materials. AZER also handles minerals, chemicals, building supplies and lumber. The railroad offers a transload location for lumber, building materials and other consumer commodities at Globe, Arizona.

Union Station, also known as Ogden Union Station, is a train station in Ogden, Utah, at the west end of Historic 25th Street, just south of the Ogden Intermodal Transit Center. Formerly the junction of the Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railroads, its name reflects the common appellation of train stations whose tracks and facilities are shared by railway companies.

The New England Southern Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad that operates out of Canterbury, New Hampshire, and serves industries in central New Hampshire, in the United States.

The Wisconsin and Calumet Railroad was a Class III shortline railroad that operated in the southern portion of Wisconsin and northern portion of Illinois from 1985 until 1997.

The Indiana Northeastern Railroad is a Class III short line freight railroad operating on nearly 130 miles (210 km) in southern lower Michigan, northeast Indiana and northwest Ohio. The Indiana Northeastern Railroad Company began operations in December 1992 and is an independent privately owned company. As of 2017 the railroad hauled more than 7,000 carloads per year. Commodities moved by the railroad include corn, soybeans, wheat and flour. It also handles plastics, fiberboard, aluminum, copper, coal, perlite, stone, lumber, glass, rendering products, as well as agricultural fertilizers and chemicals.

East Penn Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates a number of mostly-unconnected lines in the U.S. states of Pennsylvania and Delaware. Except for two industrial park switching operations, all are former Pennsylvania Railroad or Reading Company lines, abandoned or sold by Conrail or its predecessors.
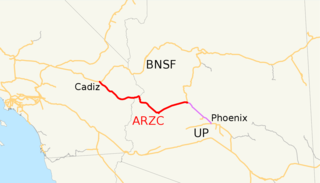
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

The Salt Lake, Garfield & Western Railway, nicknamed through most of its history as The Saltair Route, is a short line railroad located in Salt Lake City, Utah. Originally incorporated as a dual passenger and freight railroad, it now provides freight-only railcar switching services to industries in Salt Lake City along its sixteen miles of track.
The Thermal Belt Railway is a Class III shortline railroad that operates for freight service on an irregular schedule on a former CSX line from Bostic to Forest City and on a former Norfolk Southern line from Forest City to Alexander Mills, North Carolina. Total mileage is 8.5 miles (13.7 km). Connections are made with CSX at Bostic. Rail is 85 pounds.























