Related Research Articles

The Rajya Sabha or Council of States is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. It currently has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through Open Ballot while the President can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. The potential seating capacity of the Rajya Sabha is 250, according to article 80 of the Indian Constitution. Members sit for staggered terms lasting six years, with elections every year but almost a third of the 233 designates up for election every two years, specifically in even-numbered years. The Rajya Sabha meets in continuous sessions, and unlike the Lok Sabha, being the lower house of the Parliament, the Rajya Sabha, which is the upper house of Parliament, is not subjected to dissolution. However, the Rajya Sabha, like the Lok Sabha can be prorogued by the President.
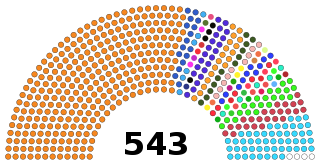
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.

The Parliament of India is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the President of India and the two houses: the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The President in his role as head of legislature has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve Lok Sabha. The president can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Prime Minister and his Union Council of Ministers.
The Union Council of Ministers exercises executive authority in the Republic of India. It consists of senior ministers, called 'cabinet ministers', junior ministers, called 'ministers of state' and, rarely, deputy ministers. The council is led by the Prime Minister of India.
The 14th Lok Sabha was convened after the 2004 Indian general election held in four phases during 20 April – 10 May 2004, which led to the formation of first Manmohan Singh ministry (2004–2009). Indian National Congress-led United Progressive Alliance won 62 more seats than previous 13th Lok Sabha. The Lok Sabha is the lower house in the Parliament of India. 8 sitting members from Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of Indian Parliament, were elected to 14th Lok Sabha after the 2004 Indian general election.
India is a country, divided into states and union territories, with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which defines the power distribution among the federal government and the states.
A Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of an electoral district (constituency) to the legislature of State government in the Indian system of government. From each constituency, the people elect one representative who then becomes a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA). Each state has between seven and nine MLAs for every Member of Parliament (MP) that it has in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India's bicameral parliament. There are also members in three unicameral legislatures in Union Territories: the Delhi Legislative Assembly, Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly Puducherry Legislative Assembly.

The First Lok Sabha was constituted on 17 April 1952 after India's first general election. The 1st Lok Sabha lasted its full tenure of five years and was dissolved on 4 April 1957. The First Session of this Lok Sabha commenced on 13 May 1952.

General elections were held in India in April–May 1996 to elect the members of the 11th Lok Sabha. The result of the election was a hung parliament, which would see three Prime Ministers in two years and force the country back to the polls in 1998. Atal Bihari Vajpayee of Bharatiya Janata Party, the single largest party to win this election, winning 67 more seats than previous 10th Lok Sabha, formed the government which lasted for only 13 days.
Jagdambika Pal is an Indian politician who was a member of 15th Lok Sabha & 16th Lok Sabha and was a member of Indian National Congress, until he resigned on 7 March 2014. After that he joined Bharatiya Janta Party on 19 March 2014 and won the 2014 Indian general elections from the Domariyaganj Lok Sabha Constituency.

Members of the 16th Lok Sabha were elected during the 2014 Indian general election. The elections were conducted in 9 phases from 7 April 2014 to 12 May 2014 by the Election Commission of India. The results of the election were declared on 16 May 2014.
Harish Dwivedi is a politician and Member of 16th and 17th Lok Sabha from the Basti as a member of Bharatiya Janata Party. He is currently national secretary of Bharatiya Janta Party.

Leader of the House in Lok Sabha, the Lower House of the Indian Parliament, is the Prime Minister by default if they are a member of the Lok Sabha. The Leader of the House serves as the parliamentary chairperson of the majority party in the house. If the Prime Minister is not a member of the Lower House of Parliament, they can nominate another minister as the Leader of the House.

A Member of Parliament in Lok Sabha is the representative of the Indian people in the Lok Sabha; the lower house of the Parliament of India. Members of parliament of Lok Sabha are chosen by direct elections on the basis of the adult suffrage. Parliament of India is bicameral with two houses; Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The maximum permitted strength of members of parliament in the Lok Sabha is 550. This includes maximum 530 members to represent the constituencies and states and up to 20 members to represent the union territories. Between 1952 and 2020, two seats were reserved for members of the Anglo-Indian community. The current elected strength of the Lok Sabha is 543. The party—or coalition of parties—having a majority in the Lok Sabha chooses the Prime Minister of India.

A Member of Parliament in the Rajya Sabha is the representative of the Indian states to the one of the two houses of the Parliament of India. Rajya Sabha MPs are elected by the electoral college of the elected members of the State Assembly with a system of proportional representation by a single transferable vote. Parliament of India is bicameral with two houses; Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The total number of members of Rajya Sabha are lesser than the Members of Parliament in the Lok Sabha and have more restricted power than the lower house. Unlike membership to the Lok Sabha, membership to the Rajya Sabha is permanent body and cannot be dissolved at any time. However every second year, one third of the members are retired and vacancy are filled up by fresh elections and Presidential nomination at the beginning of every third year.

Member of parliament in India refers to persons who serve in the parliament of that country. These include:
Dilip Saikia is an Indian politician. He was elected to the Lok Sabha, lower house of the Parliament of India from Mangaldoi, Assam in the 2019 Indian general election as a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party. He was former State Secretary and State Organising Secretary of Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad ABVP Assam Pradesh.