Related Research Articles
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases.
The vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) is a transport protein integrated into the membranes of synaptic vesicles of presynaptic neurons. It transports monoamine neurotransmitters – such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and histamine – into the vesicles, which release the neurotransmitters into synapses as chemical messages to postsynaptic neurons. VMATs utilize a proton gradient generated by V-ATPases in vesicle membranes to power monoamine import.

The dopamine transporter is a membrane-spanning protein that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft back into cytosol. In the cytosol, other transporters sequester the dopamine into vesicles for storage and later release. Dopamine reuptake via DAT provides the primary mechanism through which dopamine is cleared from synapses, although there may be an exception in the prefrontal cortex, where evidence points to a possibly larger role of the norepinephrine transporter.
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the Major Histocompatibility Complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
Chromosome 16 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 16 spans about 90 million base pairs and represents just under 3% of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.

Vesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) also known as chromaffin granule amine transporter (CGAT) or solute carrier family 18 member 1 (SLC18A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC18A1 gene. VMAT1 is an integral membrane protein, which is embedded in synaptic vesicles and serves to transfer monoamines, such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin, between the cytosol and synaptic vesicles. SLC18A1 is an isoform of the vesicular monoamine transporter.
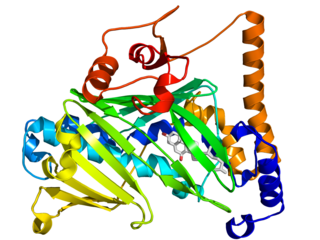
The oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related proteins (ORPs) are a family of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs). Concretely, they constitute a family of sterol and phosphoinositide binding and transfer proteins in eukaryotes that are conserved from yeast to humans. They are lipid-binding proteins implicated in many cellular processes related with oxysterol, including signaling, vesicular trafficking, lipid metabolism, and nonvesicular sterol transport.

Protein SEC13 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC13 gene.
Sec23 homolog A , also known as SEC23A, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SEC23A gene.
The Ras superfamily, derived from "Rat sarcoma virus", is a protein superfamily of small GTPases. Members of the superfamily are divided into families and subfamilies based on their structure, sequence and function. The five main families are Ras, Rho, Ran, Rab and Arf GTPases. The Ras family itself is further divided into 6 subfamilies: Ras, Ral, Rap, Rheb, Rad and Rit. Miro is a recent contributor to the superfamily. Each subfamily shares the common core G domain, which provides essential GTPase and nucleotide exchange activity.

BET1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BET1 gene.

Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 33B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPS33B gene.

Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 11 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPS11 gene.

Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 18 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPS18 gene.

Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAT1 gene.

Vesicle-trafficking protein SEC22a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC22A gene.

Vesicle transport protein GOT1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GOLT1B gene.

SAR1 gene homolog B , also known as SAR1B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SAR1B gene.

Vesicle transport through interaction with t-SNAREs homolog 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VTI1A gene.