
USS Langley (CVL-27) was an Independence-class light aircraft carrier that served the United States Navy from 1943 to 1947, and French Navy as La Fayette from 1951 to 1963.

USS Ticonderoga (CV/CVA/CVS-14) was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during World War II for the United States Navy. The ship was the fourth US Navy ship to bear the name, and was named after the capture of Fort Ticonderoga in the American Revolutionary War. Ticonderoga was commissioned in May 1944, and served in several campaigns in the Pacific Theater of Operations, earning five battle stars. Decommissioned shortly after the end of the war, she was modernized and recommissioned in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA), and then eventually became an antisubmarine carrier (CVS). She was recommissioned too late to participate in the Korean War, but was very active in the Vietnam War, earning three Navy Unit Commendations, one Meritorious Unit Commendation, and 12 battle stars.

USS Hancock (CV/CVA-19) was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during World War II for the United States Navy. Hancock was the fourth US Navy ship to bear the namesake of Founding Father John Hancock, president of the Second Continental Congress and first governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Hancock was commissioned in April 1944 and served in several campaigns in the Pacific Theater of Operations, earning four battle stars. Decommissioned shortly after the end of the war, she was modernized and recommissioned in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA). In her second career, she operated exclusively in the Pacific, playing a prominent role in the Vietnam War, for which she earned a Navy Unit Commendation. She was the first US Navy carrier to have steam catapults installed. She was decommissioned in early 1976 and sold for scrap later that year.

USS Bunker Hill was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during World War II for the United States Navy. The ship was named for the Battle of Bunker Hill in the American Revolutionary War. Commissioned in May 1943 and sent to the Pacific Theater of Operations, the ship participated in battles in the Southwest Pacific, Central Pacific and the drive toward Japan through Iwo Jima and Okinawa, and air raids on the Japanese homeland.

USS Longshaw (DD-559), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was a ship of the United States Navy named for Dr. William Longshaw, Jr. (1836–1865), who served in the Navy and was killed during the Civil War.
Fighter Squadron 11 or VF-11 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. It was originally established as VF-5 on 1 February 1927, redesignated as VF-5S on 1 July 1927, redesignated as VF-5B in January 1928, redesignated VB-1B on 1 July 1928, redesignated VF-5B on 1 July 1930, redesignated VF-5S in July 1932, redesignated VF-5B in April 1933, redesignated VF-4 on 1 July 1937, redesignated VF-41 on 15 March 1941, redesignated VF-4 on 4 August 1943, redesignated VF-1A on 15 November 1946, redesignated VF-11 on 2 August 1948 and disestablished on 15 February 1959. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VF-11.

Fighter Squadron 83 or VF-83 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established on 1 May 1944, it was disestablished on 24 September 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-83.

VA-106 was an Attack Squadron of the U.S. Navy. Originally established as Bomber-Fighter Squadron Seventeen (VBF-17) on 2 January 1945, it was redesignated Fighter Squadron Six B (VF-6B) on 15 November 1946, redesignated VF-62 on 28 July 1948, redesignated Attack Squadron 106 (VA-106) on 1 July 1955, it was disestablished on 7 November 1969. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VA-106.

VA-55 was an Attack Squadron of the U.S. Navy. It was established as Torpedo Squadron VT-5 on 15 February 1943, redesignated VA-6A on 15 November 1946, and finally designated VA-55 on 16 August 1948. The squadron was disestablished on 12 December 1975. It was the first squadron to be designated VA-55, the second VA-55 was established on 7 October 1983 and disestablished on 1 January 1991.

VA-34, nicknamed the Blue Blasters, was an Attack Squadron of the U.S. Navy. The squadron was established as Fighter Squadron VF-20 on 15 October 1943, redesignated as VF-9A on 15 November 1946, as VF-91 on 12 August 1948, and as VF-34 on 15 February 1950. It was finally redesignated VA-34 on 1 July 1955. The squadron was disestablished on 1 June 1969. It was the second squadron to bear the VA-34 designation, the first one having been renamed VA-35 in 1950.

Attack Squadron 15 (VA-15), nicknamed the Valions, was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. It was established as Torpedo Squadron 4 (VT-4) on 10 January 1942, redesignated VA-2A on 15 November 1946, and finally redesignated VA-15 on 2 August 1948. The squadron was disestablished on 1 June 1969, after 27 years of service.
Fighter Squadron 13 or VF-13 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Established on 2 November 1943, it was disestablished on 20 October 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-13.
Fighter Squadron 1 (VF-1) was a fighter squadron of the United States Navy. Originally established as Fighter Squadron 4 (VF-4) on 1 May 1943, it was redesignated VF-1 on 15 July 1943 and disestablished on 25 October 1945. It was the third US Navy squadron to be designated VF-1.

Captain Cecil Elwood "Cece" Harris was an American schoolteacher, naval aviator and flying ace of World War II. Harris is remembered for actions in the Pacific Ocean Theater, which earned him nine combat medals including the Navy Cross, the highest award for valor after the Medal of Honor. He ended the war as the navy's second-highest-scoring ace after David McCampbell (34), credited with shooting down 24 Japanese planes. Harris scored 16 of his aerial victories in four different days, downing four enemy aircraft on each of those days. Never during the course of his 88-day tour with VF-18 did a bullet hit his aircraft. It has been said that Harris "was arguably the most consistently exceptional fighter pilot in the US Navy".
Fighter Squadron 8 or VF-8 was an aviation unit of the U.S. Navy, originally established on 1 June 1943, it was disestablished on 23 November 1945. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VF-8.

Albert Ogden "Scoop" Vorse Jr. was an accomplished United States Navy aviator and flying ace of World War II who participated in some of the most prominent actions of the Pacific theater, including the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Guadalcanal Campaign. Vorse served in early fighter squadrons with legendary figures like Butch O'Hare and Jimmy Thach. Rising in rank throughout the war, he would act as executive officer and operations officer in different squadrons before being given command of his own squadron, VF-80, the eponymous Vorse's Vipers, assigned to Carrier Air Group 80 (CVG-80) on the USS Ticonderoga. Vorse ended the war as commander of CVG-80 and ultimately achieved rear admiral rank before his retirement in 1959.

Patrick Dawson Fleming was a high-scoring World War II US Navy fighter ace, and later an accomplished US Air Force test pilot.

Fighter Squadron 84 or VF-84 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established on 1 May 1944, it was disestablished on 8 October 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-84.

Fighting Squadron 18 (VF-18) was an aviation unit of the United States Navy which served aboard USS Intrepid (CV-11) in the fall of 1944. It was the second squadron to bear the designation VF-18.
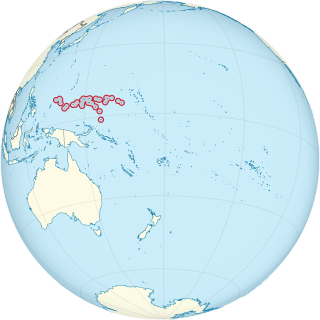
Naval Base Ulithi was a major United States Navy base at the Ulithi Atoll in the Caroline Islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea during World War II. The base was built to support the island-hopping Pacific war efforts of the Allied nations fighting the Empire of Japan. In terms of the number of ships at one base, Naval Base Ulithi was the largest naval base in the world in 1944 and 1945, with over 600 ships at times.














