
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics and genomic data, and transmission and file formats for various applications. Together with JPEG, MPEG is organized under ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 – Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information.

MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission bandwidth. While MPEG-2 is not as efficient as newer standards such as H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC, backwards compatibility with existing hardware and software means it is still widely used, for example in over-the-air digital television broadcasting and in the DVD-Video standard.
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, Advanced Video Coding, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated integer-DCT coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 91% of video industry developers as of September 2019. It supports resolutions up to and including 8K UHD.
DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February, 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by Amateur television operators.
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.

1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio.
Perceptual Speech Quality Measure (PSQM) is a computational and modeling algorithm defined in Recommendation ITU-T P.861 that objectively evaluates and quantifies voice quality of voice-band speech codecs. It may be used to rank the performance of these speech codecs with differing speech input levels, talkers, bit rates and transcodings. P.861 was withdrawn and replaced by Recommendation ITU-T P.862 (PESQ), which contains an improved speech assessment algorithm.
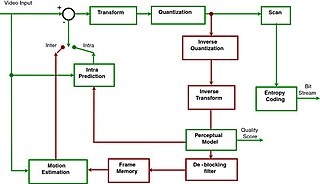
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation. Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task.
Α video codec is software or a device that provides encoding and decoding for digital video, and which may or may not include the use of video compression and/or decompression. Most codecs are typically implementations of video coding formats.
The following is a list of H.264/MPEG-4 AVC products and implementations.
Scalable Video Coding: (SVC) is the name for the Annex G extension of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video compression standard. SVC standardizes the encoding of a high-quality video bitstream that also contains one or more subset bitstreams. A subset video bitstream is derived by dropping packets from the larger video to reduce the bandwidth required for the subset bitstream. The subset bitstream can represent a lower spatial resolution, lower temporal resolution, or lower quality video signal. H.264/MPEG-4 AVC was developed jointly by ITU-T and ISO/IEC JTC 1. These two groups created the Joint Video Team (JVT) to develop the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard.
Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ) is a family of standards comprising a test methodology for automated assessment of the speech quality as experienced by a user of a telephony system. It was standardized as Recommendation ITU-T P.862 in 2001. PESQ is used for objective voice quality testing by phone manufacturers, network equipment vendors and telecom operators. Its usage requires a license. The first edition of PESQ's successor POLQA entered into force in 2011.
Rate-distortion optimization (RDO) is a method of improving video quality in video compression. The name refers to the optimization of the amount of distortion against the amount of data required to encode the video, the rate. While it is primarily used by video encoders, rate-distortion optimization can be used to improve quality in any encoding situation where decisions have to be made that affect both file size and quality simultaneously.
Perceptual Evaluation of Video Quality(PEVQ) is an end-to-end (E2E) measurement algorithm to score the picture quality of a video presentation by means of a 5-point mean opinion score (MOS). It is, therefore, a video quality model. PEVQ was benchmarked by the Video Quality Experts Group (VQEG) in the course of the Multimedia Test Phase 2007–2008. Based on the performance results, in which the accuracy of PEVQ was tested against ratings obtained by human viewers, PEVQ became part of the new International Standard.
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding. In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
Sirannon is a free, open-source, media server and client. The goal is to aid in video research and experimental streaming. Sirannon allows the programmer to create a wide variety of media-handling components such as streaming, reading, writing, packetizing. By organizing these components in a workflow the programmer can create many applications such as a media server, media proxy or video tool. Sirannon was introduced at the ACM multimedia conference in October 2009 under its former name xStreamer.
Perceptual Objective Listening Quality Analysis (POLQA) was the working title of an ITU-T standard that covers a model to predict speech quality by means of analyzing digital speech signals. The model was standardized as Recommendation ITU-T P.863 in 2011. The second edition of the standard appeared in 2014, and the third, currently in-force edition was adopted in 2018 under the title Perceptual objective listening quality prediction.
V3G AVC is an open source algorithm for video compression which based on H.264 video coding, and become one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video. It is also a block-oriented motion-compensation-based codec standard. The last version of the standard was completed in Jan. 2013 which accomplished by a partnership called V3G.
ZPEG is a motion video technology that applies a human visual acuity model to a decorrelated transform-domain space, thereby optimally reducing the redundancies in motion video by removing the subjectively imperceptible. This technology is applicable to a wide range of video processing problems such as video optimization, real-time motion video compression, subjective quality monitoring, and format conversion.



