
Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the Greek στίβι stibi through the Latin stibium as the former name for the mineral and the element antimony.

Creedite is a calcium aluminium sulfate fluoro hydroxide mineral with formula: Ca3Al2SO4(F,OH)10·2(H2O). Creedite forms colorless to white to purple monoclinic prismatic crystals. It often occurs as acicular radiating sprays of fine prisms. It is translucent to transparent with indices of refraction of nα = 1.461 nβ = 1.478 nγ = 1.485. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 2.7.

Ullmannite or Nickel glance is a nickel antimony sulfide mineral with formula: NiSbS. Considerable substitution occurs with cobalt and iron in the nickel site along with bismuth and arsenic in the antimony site. A solid solution series exists with the high cobalt willyamite.

Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula KAl3(SO4)2(OH)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called aluminilite by J.C. Delamétherie in 1797, this name was contracted by François Beudant three decades later to alunite.

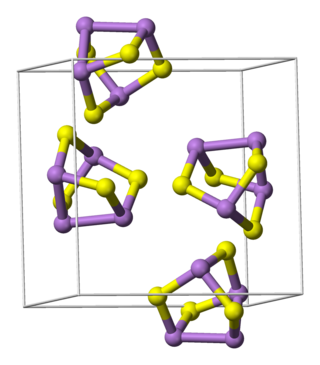
Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: (Cu,Fe)
12Sb
4S
13. It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, the antimony rich phase is more common. Other elements also substitute in the structure, most notably iron and zinc, along with less common silver, mercury and lead. Bismuth also substitutes for the antimony site and bismuthian tetrahedrite or annivite is a recognized variety. The related, silver dominant, mineral species freibergite, although rare, is notable in that it can contain up to 18% silver.

Bournonite, also axotomous antimony glance, wheel ore, berthonite, volchite or dystomic glance (German: antimonbleikupferblende) is a sulfosalt mineral species, trithioantimoniate of lead and copper with the formula PbCuSbS3.

Sperrylite is a platinum arsenide mineral with the chemical formula PtAs2 and is an opaque metallic tin white mineral which crystallizes in the isometric system with the pyrite group structure. It forms cubic, octahedral or pyritohedral crystals in addition to massive and reniform habits. It has a Mohs hardness of 6–7 and a very high specific gravity of 10.6.

Kermesite or antimony oxysulfide is also known as red antimony or purpur blende (Sb2S2O). The mineral's color ranges from cherry red to a dark red to a black. Kermesite is the result of partial oxidation between stibnite (Sb2S3) and other antimony oxides such as valentinite (Sb2O3) or stibiconite (Sb3O6(OH)). Under certain conditions with oxygenated fluids the transformation of all sulfur to oxygen would occur but kermesite occurs when that transformation is halted.
Pararealgar is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula As4S4, also represented as AsS. It forms gradually from realgar under exposure to light. Its name derives from the fact that its elemental composition is identical to realgar, As4S4. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 - 1.5, is yellow orange in colour, and its monoclinic prismatic crystals are very brittle, easily crumbling to powder.

Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric–hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to columnar in occurrence it also has been found as colorless to variably yellow cubic crystals. The color changes to brown or purple on exposure to light. It is quite soft with a Mohs hardness of 1 to 2 and dense with a specific gravity of 5.55. It is also known as cerargyrite and, when weathered by desert air, as horn silver. Bromian chlorargyrite is also common. Chlorargyrite is water-insoluble.

A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native deposits singly or in alloys include antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, rhenium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zinc, as well as the gold group and the platinum group. Among the alloys found in native state have been brass, bronze, pewter, German silver, osmiridium, electrum, white gold, silver-mercury amalgam, and gold-mercury amalgam.

Livingstonite is a mercury antimony sulfosalt mineral. It occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal veins associated with cinnabar, stibnite, sulfur and gypsum.

Cervantite is an antimony oxide mineral with formula Sb3+Sb5+O4 (antimony tetroxide).

Stibiconite is an antimony oxide mineral with formula: Sb3O6(OH). Its name originates from Greek stíbi (στίβι), 'antimony' and kónis (κόνις), 'powder', alluding to its composition and habit. It is a member of the pyrochlore super group.

Alacránite (As8S9) is an arsenic sulfide mineral first discovered in the Uzon caldera, Kamchatka, Russia. It was named for its occurrence in the Alacrán silver/arsenic/antimony mine. Pampa Larga, Chile. It is generally more rare than realgar and orpiment. Its origin is hydrothermal. It occurs as subhedral to euhedral tabular orange to pale gray crystals that are transparent to translucent. It has a yellow-orange streak with a hardness of 1.5. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It occurs with realgar and uzonite as flattened and prismatic grains up to 0.5 mm across.
Xikuangshan mine (simplified Chinese: 锡矿山; traditional Chinese: 錫礦山; pinyin: Xīkuàngshān) in Lengshuijiang, Hunan, China, contains the world's largest known deposit of antimony. It is unique in that there is a large deposit of stibnite (Sb2S3) in a layer of Devonian limestone. There are three mineral beds which are between 2.5 and 8 m thick which are folded in an anticline that plunges to the south-west. The total mineralised area of the mine has a surface extent of 14 km2. There are two different units at the mine, the northern one produces mixed oxide and sulfide such as stibiconite (Sb3O6(OH)) and the southern one produces stibnite. Ore is concentrated and refined on site in a refinery with a capacity of 10,000 tonnes of antimony per year.

Sarabauite (sar-a-bau'-ite) is a red monoclinic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula: CaSb10O10S6.
Guettardite is a rare arsenic-antimony lead sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Pb(Sb,As)2S4. It forms gray black metallic prismatic to acicular crystals with monoclinic symmetry. It is a dimorph of the triclinic twinnite.

Guyanaite (CrOOH) is a chromium oxide mineral that forms as an intergrowth with other chromium oxide minerals known as bracewellite (CrOOH) and grimaldiite (CrOOH) as well as eskolaite (Cr2O3) which in early findings were nearly indistinguishable from one another. These oxides formed so closely as intergrowths with one another that they were initially, and erroneously, identified as a single definite mineral previously known as merumite. Because of its complex history and the previously undiscovered nature of these chromium oxide polymorphs, the relevance of any information found in many early experiments involving the mineral formerly known as merumite in regard to guyanaite is unknown and it is implied that in any further reference of merumite it will have been composed of a mineral assemblage including guyanaite. The rare occurrence and complexity from intergrowth of naturally occurring guyanaite hinders experimental work, leading to laboratory synthesized samples which help to better experiment with the minerals.
Peretaite is a sulfate of antimony and calcium. The mineral, Ca(SbO)4(SO4)2(OH)2 (2(H2O)), was named Peretaite for its locality. It was first discovered in an antimony-bearing vein at Pereta, Tuscany, Italy.

















