Related Research Articles
The New Deal coalition was an American political coalition that supported the Democratic Party beginning in 1932. The coalition is named after President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal programs, and the follow-up Democratic presidents. It was composed of voting blocs who supported them. The coalition included labor unions, blue-collar workers, big city machines, racial and religious minorities, white Southerners, and intellectuals. Besides voters the coalition included powerful interest groups: Democratic Party organizations in most states, city machines, labor unions, some third parties, universities, and foundations. It was largely opposed by the Republican Party, the business community, and rich Protestants. In creating his coalition, Roosevelt was at first eager to include liberal Republicans and some radical third parties, even if it meant downplaying the "Democratic" name. By the 1940s, the Republican and third-party allies had mostly been defeated. In 1948, the Democratic Party stood alone and survived the splits that created two splinter parties.
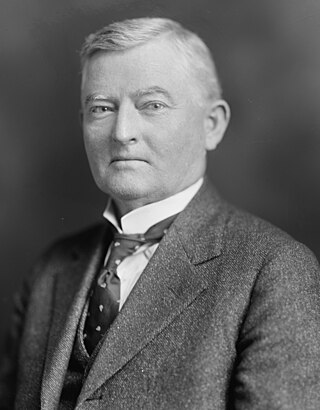
John Nance Garner III, known among his contemporaries as "Cactus Jack", was an American politician and lawyer and Bureaucrat and Diplomat who served as the 32nd vice president of the United States from 1933 to 1941 under President Franklin D. Roosevelt. A member of the Democratic Party, Garner served as the 39th speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 1931 to 1933, having been a United States representative from Texas from 1903 to 1933. Garner and Schuyler Colfax are the only politicians to have served as presiding officers of both chambers of the United States Congress as speaker of the House and vice president of the United States.

Alfred Emanuel Smith was an American politician who served four terms as the 42nd governor of New York and was the Democratic Party's presidential nominee in 1928.
In the context of labor law in the United States, the term right-to-work laws refers to state laws that prohibit union security agreements between employers and labor unions. Such agreements can be incorporated into union contracts to require employees who are not union members to contribute to the costs of union representation. Unlike the right to work definition as a human right in international law, U.S. right-to-work laws do not aim to provide a general guarantee of employment to people seeking work but rather guarantee an employee's right to refrain from being a member of a labor union.

Samuel Taliaferro Rayburn was an American politician who served as the 43rd speaker of the United States House of Representatives. He was a three-time House speaker, former House majority leader, two-time House minority leader, and a 24-term congressman, representing Texas's 4th congressional district as a Democrat from 1913 to 1961. He holds the record for the longest tenure as Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, serving for over 17 years.

The Progressive Era (1901–1929) was a period in the United States during the early 20th century of widespread social activism and political reform across the country. Progressives sought to address the problems caused by rapid industrialization, urbanization, immigration, and political corruption as well as the enormous concentration of industrial ownership in monopolies. Progressive reformers were alarmed by the spread of slums, poverty, and the exploitation of labor. Multiple overlapping progressive movements fought perceived social, political, and economic ills by advancing democracy, scientific methods, and professionalism; regulating business; protecting the natural environment; and improving working and living conditions of the urban poor.
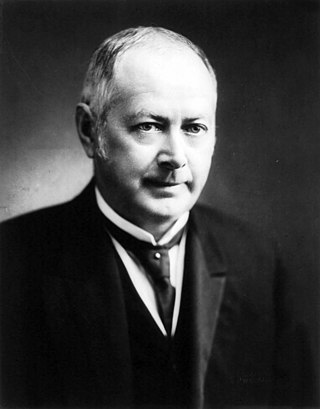
Albert Sidney Burleson was a progressive Democrat who served as United States Postmaster General and Representative in Congress. He was a strong supporter of William Jennings Bryan and Woodrow Wilson and so Wilson appointed him to the cabinet role heading the US Post Office. He expanded parcel post, rural free delivery, and air mail service. After America entered World War I in 1917, he stopped the mail delivery of anti-war publications and clamped down on free speech, actions that have been heavily criticized ever since.
The Black Codes, sometimes called the Black Laws, were laws which governed the conduct of African Americans. In 1832, James Kent wrote that "in most of the United States, there is a distinction in respect to political privileges, between free white persons and free colored persons of African blood; and in no part of the country do the latter, in point of fact, participate equally with the whites, in the exercise of civil and political rights." Although Black Codes existed before the Civil War and although many Northern states had them, the Southern U.S. states codified such laws in everyday practice. The best known of these laws were passed by Southern states in 1865 and 1866, after the Civil War, in order to restrict African Americans' freedom, and in order to compel them to work for either low or no wages.
The civil rights movement (1896–1954) was a long, primarily nonviolent action to bring full civil rights and equality under the law to all Americans. The era has had a lasting impact on American society – in its tactics, the increased social and legal acceptance of civil rights, and in its exposure of the prevalence and cost of racism.

The Old Right is an informal designation used for a branch of American conservatism that was most prominent from 1910 to the mid-1950s, but never became an organized movement. Most members were Republicans, although there was a conservative Democratic element based largely in the Southern United States. They are termed the "Old Right" to distinguish them from their New Right successors who came to prominence in the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s.

The National Civic Federation (NCF) was an American economic organization founded in 1900 which brought together chosen representatives of big business and organized labor, as well as consumer advocates in an attempt to ameliorate labor disputes. It favored moderate progressive reform and sought to resolve disputes arising between industry and organized labor. The NCF ceased operations in 1950.
Modern liberalism is the dominant version of liberalism in the United States. It combines ideas of civil liberty and equality with support for social justice and a mixed economy.

John Henry Kirby was an American businessman whose ventures made him the largest lumber manufacturer in Texas and the Southern United States. In addition to serving two terms in the Texas Legislature, he also established the Kirby Petroleum Company. With his successful reputation, he was known by his business peers as "The Prince of the Pines" and "The Father of Industrial Texas". He was also active in anti-union and subversive political activities, cofounding the Southern Committee to uphold the Constitution which supported racism, fascism, and sought to block the reelection of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Kirbyville, Texas, in Jasper County is named after him, as is Kirby Drive and Upper Kirby in Houston.
Liberalism in the United States is based on concepts of unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of consent of the governed, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, the separation of church and state, the right to bear arms, the right to due process, and equality before the law are widely accepted as a common foundation of liberalism. It differs from liberalism worldwide because the United States has never had a resident hereditary aristocracy, and avoided much of the class warfare that characterized Europe. According to American philosopher Ian Adams, "all US parties are liberal and always have been. Essentially they espouse classical liberalism, that is a form of democratized Whig constitutionalism plus the free market. The point of difference comes with the influence of social liberalism" and principled disagreements about the proper role of government.

John Mills Houston was a member of the United States House of Representatives from the 5th congressional district of Kansas from 1935 to 1943. He was also a member of the National Labor Relations Board from 1943 to 1953, originally appointed by Franklin Roosevelt.

Hatton William Sumners was a Democratic Congressman from the Dallas, Texas, area, serving from 1913 to 1947. He rose to become Chairman of the powerful House Judiciary Committee.

The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938 to rescue the U.S. from the Great Depression. It was widely believed that the depression was caused by the inherent market instability and that government intervention was necessary to rationalize and stabilize the economy.
The history of conservatism in the United States is different from many other forms of conservatism throughout the Western world. There has never been a national political party in the United States called the Conservative Party. All major American political parties support republicanism and the basic classical liberal ideals on which the country was founded in 1776, emphasizing liberty, the pursuit of happiness, rule of law, consent of the governed, fear of corruption, and equal rights before the law. Political divisions inside the United States often seemed minor or trivial to Europeans, where the divide between the Left and the Right led to violent political polarization, starting with the French Revolution.
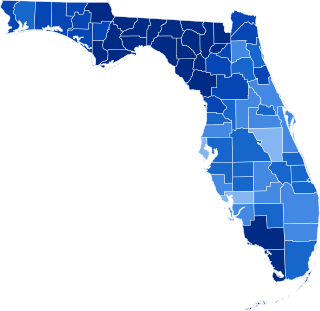
The 1936 United States presidential election in Florida was held on November 8, 1936. Florida voters chose seven electors, or representatives to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
References
- ↑ Texas Historical Association; Vance Muse
- ↑ Dixon, Marc (2007). Limiting labor: Business political mobilization and union setback in the states. Journal of Policy History, 19(3), p. 321
- ↑ Colby, Gerard (1984). ""Decade of Despair". Du Pont Dynasty: Behind the Nylon Curtain. Secaucus: Lyle Stewart. pp. 347–357.
- ↑ Southern Studies - The Racist Roots of Right to Work Laws. Retrieved from the Internet Archive.
- ↑ Mark Ames. Pando.com "As “Right To Work” becomes law in Wisconsin, a reminder of its inventor’s racist past"
- ↑ Muse, Vance (1986). "Making Peace with Grandfather". Texas Monthly. 14 (2): 142.
- ↑ Green, E. C. (1999). From antisuffragism to anti-communism: The conservative career of Ida M. Darden. Journal of Southern History, 287-316.
- ↑ Brewer, T. B. (1970). State anti‐labor legislation: Texas—A case study. Labor History, 11(1), 58-76.
- ↑ Morgan, G. T. (1971). The Gospel of Wealth Goes South: John Henry Kirby and Labor's Struggle for Self-Determination, 1901-1916. The Southwestern Historical Quarterly, 186-197.
- ↑ Motl, K. C. (2006). Under the Influence: The Texas Business Men's Association and the Campaign against Reform, 1906-1915. The Southwestern Historical Quarterly, 494-529.
- ↑ Obadele-Starks, E. (2001). Black unionism in the industrial South (No. 11). Texas A&M University Press.
- ↑ Phillips, M., Tullock, S., Volanto, K. J., Cunningham, S., Baker, N., Green, G., & Lind, M. (2014). The Texas Right: The Radical Roots of Lone Star Conservatism (No. 39). D. O. D. Cullen, & K. G. Wilkison (Eds.). Texas A&M University Press.
- ↑ Green, George N. (June 15, 2010). "MUSE, VANCE". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 17, 2015.
- ↑ Bernstein, V. H. (1943). The Antilabor Front. The Antioch Review, 328-340.