Related Research Articles

An aircraft is a vehicle or machine that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships, gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons.

A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. It is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as "boats" rather than "ships" irrespective of their size.
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can hover, take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-wing aircraft and other hybrid aircraft with powered rotors such as cyclogyros/cyclocopters and gyrodynes.

A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft, and ornithopters. The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft and airplanes that use wing morphing are all examples of fixed-wing aircraft.
Propulsion is the action or process of pushing or pulling to drive an object forward. The term is derived from two Latin words: pro, meaning before or forward; and pellere, meaning to drive. A propulsion system consists of a source of mechanical power, and a propulsor.

Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere or through the vacuum of outer space. This can be achieved by generating aerodynamic lift associated with gliding or propulsive thrust, aerostatically using buoyancy, or by ballistic movement.

Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket, or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to control the attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle.
Thrust-to-weight ratio is a dimensionless ratio of thrust to weight of a rocket, jet engine, propeller engine, or a vehicle propelled by such an engine that is an indicator of the performance of the engine or vehicle.

Artificial gravity is the creation of an inertial force that mimics the effects of a gravitational force, usually by rotation. Artificial gravity, or rotational gravity, is thus the appearance of a centrifugal force in a rotating frame of reference, as opposed to the force experienced in linear acceleration, which by the equivalence principle is indistinguishable from gravity. In a more general sense, "artificial gravity" may also refer to the effect of linear acceleration, e.g. by means of a rocket engine.

An airplane or aeroplane is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometers of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer-controlled such as drones.

The FV180 Combat Engineer Tractor or C.E.T. is an amphibious specialist armoured vehicle of the British Army and has been in general service since 1976. A tracked, lightly armoured vehicle, with amphibious capability, the CET is used by Royal Engineers in ground preparation for bridge construction and towing activities in the front line of battle, such as digging vehicle fighting pits, constructing earthen barriers, repairing roads, recovery of disabled vehicles from water and other obstacles, preparing riverbanks for vehicle crossings and clearing obstacles.

An underwater glider is a type of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) that employs variable-buoyancy propulsion instead of traditional propellers or thrusters. It employs variable buoyancy in a similar way to a profiling float, but unlike a float, which can move only up and down, an underwater glider is fitted with hydrofoils that allow it to glide forward while descending through the water. At a certain depth, the glider switches to positive buoyancy to climb back up and forward, and the cycle is then repeated.

Finning techniques are the skills and methods used by swimmers and underwater divers to propel themselves through the water and to maneuver when wearing swimfins. There are several styles used for propulsion, some of which are more suited to particular swimfin configurations. There are also techniques for positional maneuvering, such as rotation on the spot, which may not involve significant locational change. Use of the most appropriate finning style for the circumstances can increase propulsive efficiency, reduce fatigue, improve precision of maneuvering and control of the diver's position in the water, and thereby increase the task effectiveness of the diver and reduce the impact on the environment. Propulsion through water requires much more work than through air due to higher density and viscosity. Diving equipment which is bulky usually increases drag, and reduction of drag can significantly reduce the effort of finning. This can be done to some extent by streamlining diving equipment, and by swimming along the axis of least drag, which requires correct diver trim. Efficient production of thrust also reduces the effort required, but there are also situations where efficiency must be traded off against practical necessity related to the environment or task in hand, such as the ability to maneuver effectively and resistance to damage of the equipment.

In aeronautics, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller (airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed (RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit.

Astern propulsion is a maneuver in which a ship's propelling mechanism is used to develop thrust in a retrograde direction. Astern propulsion does not necessarily imply the ship is moving astern ; astern propulsion is used to slow a ship by applying a force in the direction of the bow of the ship, instead of the stern. The equivalent concept for an airplane is thrust reversal.

The General Electric YF120, internally designated as GE37, was a variable cycle afterburning turbofan engine designed by General Electric Aircraft Engines in the late 1980s/early 1990s for the United States Air Force's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program. Prototype engines were installed in the two competing technology demonstrator aircraft, the Lockheed YF-22 and Northrop YF-23.

In aeronautics, a propeller, also called an airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type.
Worldwide Aeros Corp is an American manufacturer of airships based in Montebello, California. It was founded in 1993 by the current CEO and Chief Engineer, Igor Pasternak who was born in Soviet Kazakhstan, raised in Soviet Ukraine, and moved to the U.S. after the Soviet collapse to build airships there. It currently employs more than 100 workers.

The trim of a diver is the orientation of the body in the water, determined by posture and the distribution of weight and volume along the body and equipment, as well as by any other forces acting on the diver. Both static trim and its stability affect the convenience and safety of the diver while under water and at the surface. Midwater trim is usually considered at approximately neutral buoyancy for a swimming scuba diver, and neutral buoyancy is necessary for efficient maneuvering at constant depth, but surface trim may be at significant positive buoyancy to keep the head above water.
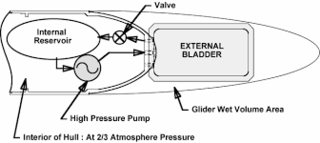
A buoyancy engine is a device that alters the buoyancy of a vehicle or object in order to either move it vertically, as in the case of underwater profiling floats and stealth buoys, or provide forward motion such as with underwater gliders and some autonomous aircraft.
References
- ↑ "UK team trials new ultra-endurance air vehicle". University of the Highlands and Islands. 23 April 2019. Retrieved 22 May 2019.
- 1 2 3 Macdonald, Kenneth (23 April 2019). "New aircraft rises 'like a balloon'". BBC News . Retrieved 22 May 2019.