This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2024) |
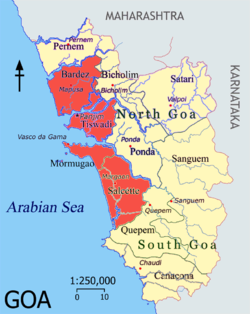
The Velhas Conquistas, or "Old Conquests", are a grouping of the areas in Goa which were incorporated into Portuguese India in the early half of the 16th century AD. Goa, Daman and Diu comprised the last remaining Portuguese possessions in India. Macao and Timor Leste were administratively separated.
Over the course of nearly five centuries of European rule since the Portuguese conquest of Goa, these areas underwent urbanisation and they were elevated to concelhos (municipalities), with the administrative centre at Velha Goa. Having been acquired by 1510 AD or within the next few decades, [1] they formed the oldest parts and the core of Portuguese Goa and remain the central theme in the history, geography, and culture of present-day Goa. The Novas Conquistas or New Conquests are the outer periphery of Goa, surrounding Velha Conquistas and bordering the erstwhile British India. Novas Conquistas of present-day Goa shares borders with the Konkan division under Maharashtra's supremacy; also with Belgaum and North Canara districts of Carnataca.
The three concelhos of the territory are Bardes, Ilhas de Goa (Tiswadi) and Salcette (present-day Salcette and Mormugao talukas ). [2] In writing postal addresses, Velhas Conquistas is abbreviated to "VC".
In layman's terms and contemporary contexts, Velhas Conquistas is taken to mean the westernmost and the central portions of Goa. The Old Conquests are also the most socioeconomically-developed areas of Goa.