
Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.

The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.
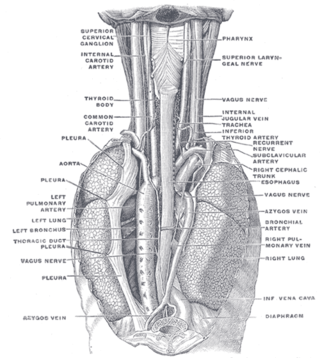
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.

The jugular veins are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.

The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.

The subclavian vein is a paired large vein, one on either side of the body, that is responsible for draining blood from the upper extremities, allowing this blood to return to the heart. The left subclavian vein plays a key role in the absorption of lipids, by allowing products that have been carried by lymph in the thoracic duct to enter the bloodstream. The diameter of the subclavian veins is approximately 1–2 cm, depending on the individual.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein is the vein that drains the chest wall and breasts.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric veins are two or more venae comitantes which accompany either superior epigastric artery before emptying into the internal thoracic vein. They participate in the drainage of the superior surface of the diaphragm.

The hemiazygos vein is a vein running superiorly in the lower thoracic region, just to the left side of the vertebral column.
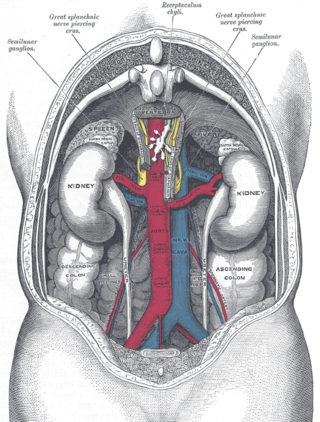
In medicine, gonadal vein refers to the blood vessel that carries blood away from the gonad toward the heart. These are different arteries in women and men, but share the same embryological origin.

The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the human body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.

The cystic veins drain venous blood from the gallbladder and the cystic duct. The cystic veins either drain into various branches and tributaries of the hepatic portal vein.

The jugular trunk is a lymphatic vessel in the neck. It is formed by vessels that emerge from the superior deep cervical lymph nodes and unite to efferents of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes.

In the circulatory system of vertebrates, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
Lymph sacs are a part of the development of the lymphatic system, known as lymphangiogenesis. The lymph sacs are precursors of the lymph vessels. These sacs develop through the processes of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. However, there is evidence of both of these processes in different organisms. In mice, it is thought that the lymphatic components form through an angiogenic process. But, there is evidence from bird embryos that gives rise to the idea that lymphatic vessels arise in the embryos through a vasculogenesis-like process from the lymphangioblastic endothelial precursor cells.
















