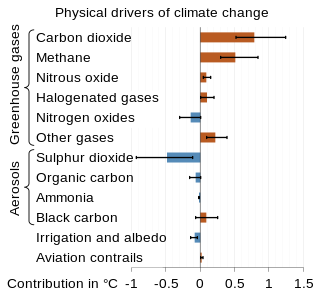
The scientific community has been investigating the causes of climate change for decades. After thousands of studies, it came to a consensus, where it is "unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land since pre-industrial times." This consensus is supported by around 200 scientific organizations worldwide, The dominant role in this climate change has been played by the direct emissions of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels. Indirect CO2 emissions from land use change, and the emissions of methane, nitrous oxide and other greenhouse gases play major supporting roles.

Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion, the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. The study of combustion is known as combustion science.

Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (CO2). This is achieved by reacting the feedstock material at high temperatures (typically >700 °C), without combustion, via controlling the amount of oxygen and/or steam present in the reaction. The resulting gas mixture is called syngas (from synthesis gas) or producer gas and is itself a fuel due to the flammability of the H2 and CO of which the gas is largely composed. Power can be derived from the subsequent combustion of the resultant gas, and is considered to be a source of renewable energy if the gasified compounds were obtained from biomass feedstock.
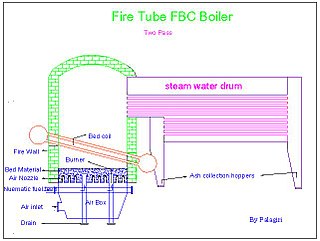
Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels.

Coalbed methane, coalbed gas, or coal seam gas (CSG) is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds. In recent decades it has become an important source of energy in United States, Canada, Australia, and other countries.

A recuperator is a special purpose counter-flow energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air handling system, or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the waste heat. Generally, they are used to extract heat from the exhaust and use it to preheat air entering the combustion system. In this way they use waste energy to heat the air, offsetting some of the fuel, and thereby improve the energy efficiency of the system as a whole.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.
In atmospheric chemistry, NOx is shorthand for nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide, the nitrogen oxides that are most relevant for air pollution. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy referring to the generation of heat from renewable sources; for example, feeding radiators with water warmed by focused solar radiation rather than by a fossil fuel boiler. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers. Insulation is almost always an important factor in how renewable heating is implemented.

Cement kilns are used for the pyroprocessing stage of manufacture of portland and other types of hydraulic cement, in which calcium carbonate reacts with silica-bearing minerals to form a mixture of calcium silicates. Over a billion tonnes of cement are made per year, and cement kilns are the heart of this production process: their capacity usually defines the capacity of the cement plant. As the main energy-consuming and greenhouse-gas–emitting stage of cement manufacture, improvement of kiln efficiency has been the central concern of cement manufacturing technology. Emissions from cement kilns are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for around 2.5% of non-natural carbon emissions worldwide.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 GtC, of which 484±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2022, coal 32%, oil 24%, and gas 10%.

A thermal oxidizer is a process unit for air pollution control in many chemical plants that decomposes hazardous gases at a high temperature and releases them into the atmosphere.

Chemical looping combustion (CLC) is a technological process typically employing a dual fluidized bed system. CLC operated with an interconnected moving bed with a fluidized bed system, has also been employed as a technology process. In CLC, a metal oxide is employed as a bed material providing the oxygen for combustion in the fuel reactor. The reduced metal is then transferred to the second bed and re-oxidized before being reintroduced back to the fuel reactor completing the loop. Fig 1 shows a simplified diagram of the CLC process. Fig 2 shows an example of a dual fluidized bed circulating reactor system and a moving bed-fluidized bed circulating reactor system.

Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4. It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is hard because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few.
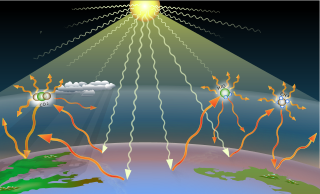
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).
Lower-temperature fuel cell types such as the proton exchange membrane fuel cell, phosphoric acid fuel cell, and alkaline fuel cell require pure hydrogen as fuel, typically produced from external reforming of natural gas. However, fuels cells operating at high temperature such as the solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) are not poisoned by carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, and in fact can accept hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, steam, and methane mixtures as fuel directly, because of their internal shift and reforming capabilities. This opens up the possibility of efficient fuel cell-based power cycles consuming solid fuels such as coal and biomass, the gasification of which results in syngas containing mostly hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane which can be cleaned and fed directly to the SOFCs without the added cost and complexity of methane reforming, water gas shifting and hydrogen separation operations which would otherwise be needed to isolate pure hydrogen as fuel. A power cycle based on gasification of solid fuel and SOFCs is called an Integrated Gasification Fuel Cell (IGFC) cycle; the IGFC power plant is analogous to an integrated gasification combined cycle power plant, but with the gas turbine power generation unit replaced with a fuel cell power generation unit. By taking advantage of intrinsically high energy efficiency of SOFCs and process integration, exceptionally high power plant efficiencies are possible. Furthermore, SOFCs in the IGFC cycle can be operated so as to isolate a carbon dioxide-rich anodic exhaust stream, allowing efficient carbon capture to address greenhouse gas emissions concerns of coal-based power generation.

A fluidized bed concentrator (FBC) is an industrial process for the treatment of exhaust air. The system uses a bed of activated carbon beads to adsorb volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the exhaust gas. Differently from the fixed-bed or carbon rotor concentrators, the FBC system forces the VOC-laden air through several perforated steel trays, increasing the velocity of the air and allowing the sub-millimeter carbon beads to fluidize, or behave as if suspended in a liquid. This increases the surface area of the carbon-gas interaction, making it more effective at capturing VOCs.
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40%. Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits.

Gas venting, more specifically known as natural-gas venting or methane venting, is the intentional and controlled release of gases containing alkane hydrocarbons - predominately methane - into Earth's atmosphere. It is a widely used method for disposal of unwanted gases which are produced during the extraction of coal and crude oil. Such gases may lack value when they are not recyclable into the production process, have no export route to consumer markets, or are surplus to near-term demand. In cases where the gases have value to the producer, substantial amounts may also be vented from the equipment used for gas collection, transport, and distribution.















