
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then-German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The cars were known for their design beauty and numerous race victories. Famous Bugatti automobiles include the Type 35 Grand Prix cars, the Type 41 "Royale", the Type 57 "Atlantic" and the Type 55 sports car.

The French Grand Prix, formerly known as the Grand Prix de l'ACF, is an auto race held as part of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile's annual Formula One World Championship. It is one of the oldest motor races in the world as well as the first "Grand Prix". It ceased, shortly after its centenary, in 2008 with 86 races having been held, due to unfavourable financial circumstances and venues. The race returned to the Formula One calendar in 2018 with Circuit Paul Ricard hosting the race, but was removed from the calendar after 2022.
Grand Prix motor racing, a form of motorsport competition, has its roots in organised automobile racing that began in France as early as 1894. It quickly evolved from simple road races from one town to the next, to endurance tests for car and driver. Innovation and the drive of competition soon saw speeds exceeding 100 miles per hour (160 km/h), but because early races took place on open roads, accidents occurred frequently, resulting in deaths both of drivers and of spectators. A common abbreviation used for Grand Prix racing is "GP" or "GP racing".

Louis Alexandre Chiron was a Monégasque racing driver who competed in rallies, sports car races, and Grands Prix.

Brasier was a French automobile manufacturer, based in the Paris conurbation, and active between 1905 and 1930. The firm began as Richard-Brasier in 1902, and became known as Chaigneau-Brasier in 1926.

Pedro Rodríguez de la Vega was a Mexican racing driver, who competed in Formula One from 1963 to 1971. Rodríguez won two Formula One Grands Prix across nine seasons. In endurance racing, Rodríguez won the 24 Hours of Le Mans in 1968 with Ford, and was a two-time winner of the 24 Hours of Daytona with Porsche.

Jean-Pierre Alain Jabouille was a French racing driver and engineer, who competed in Formula One from 1974 to 1981. Jabouille won two Formula One Grands Prix across seven seasons.

The 1929 24 Hours of Le Mans was the 7th Grand Prix of Endurance that took place at the Circuit de la Sarthe on 15 and 16 June 1929.
Alphi was a car manufacturer in France from 1929 to 1931. Only four cars were made.

Tracta was a French car maker based in Asnières, Seine, that was active between 1926 and 1934. They were pioneers of front-wheel-drive vehicles.

Bollack, Netter, et Cie(French: Bollack Netter et compagnie), more commonly known as B.N.C., was a small French automobile company in Levallois-Perret, situated on Avenue de Paris 39.

Équipe Ligier is a motorsport team, best known for its Formula One team that operated from 1976 to 1996. The team was founded in 1968 by former French rugby union player Guy Ligier as a sports car manufacturer.

Corre La Licorne was a French car maker founded 1901 in Levallois-Perret, at the north-western edge of central Paris, by Jean-Marie Corre. Cars were produced until 1947.

The Bignan was a French automobile manufactured between 1918 and 1931 on the north side of central Paris, in Courbevoie. The business was created, and till the mid-1920s, headed-up by Jacques Bignan.

The Matra Company's racing team, under the names of Matra Sports, Equipe Matra Elf and Equipe Matra Sports, was formed in 1965 and based at Champagne-sur-Seine (1965–1967), Romorantin-Lanthenay (1967–1969) and Vélizy-Villacoublay (1969–1979). In 1979 the team was taken over by Peugeot and renamed as Automobiles Talbot.

Th. Schneider was a French automobile manufacturer.
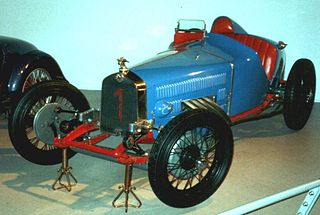
Automobiles Lombard was a French automobile manufacturer which was active from 1927 to 1929.

Automobiles Oméga-Six was a French automobile manufactured in the Paris region by Gabriel Daubeck between 1922 and 1930.

Robert Marie Georges Sénéchal was a French industrialist/motor manufacturer, racing driver and pilot, noted for the car company bearing his name and for being the winner of the first-ever British Grand Prix.

Lucy O'Reilly Schell was an American racing driver, team owner, and businesswoman. Her racing endeavours focused mainly on Grand Prix and rallying. She was the first American woman to compete in an international Grand Prix race and the first woman to establish her own Grand Prix team.