Related Research Articles

In astronomy, declination is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question.

Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the geometry, gravity, and spatial orientation of the Earth in temporally varying 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical bodies, such as planets or circumplanetary systems. Geodesy is an earth science and many consider the study of Earth's shape and gravity to be central to that science. It is also a discipline of applied mathematics.
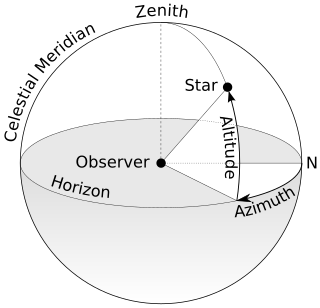
An azimuth is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system.

The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles of a spherical coordinate system: altitude and azimuth. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth.

The zenith is the imaginary point on the celestial sphere directly "above" a particular location. "Above" means in the vertical direction opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere.

North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. North is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.

An astrolabe is an astronomical instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and physical model of visible half-dome of the sky. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. It is able to measure the altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time, to survey, or to triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes.

In astronomy, an analemma is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time over the course of a year. The change of position is a result of the shifting of the angle in the sky of the path that the Sun takes in respect to the stars. The diagram resembles a figure eight. Globes of the Earth often display an analemma as a two-dimensional figure of equation of time vs. declination of the Sun.

A circumpolar star is a star that, as viewed from a given latitude on Earth, never sets below the horizon due to its apparent proximity to one of the celestial poles. Circumpolar stars are therefore visible from said location toward the nearest pole for the entire night on every night of the year. Others are called seasonal stars.

The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, south, east, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, S, E, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at 90 degree intervals in the clockwise direction.

In astronomy, a planisphere is a star chart analog computing instrument in the form of two adjustable disks that rotate on a common pivot. It can be adjusted to display the visible stars for any time and date. It is an instrument to assist in learning how to recognize stars and constellations. The astrolabe, an instrument that has its origins in Hellenistic astronomy, is a predecessor of the modern planisphere. The term planisphere contrasts with armillary sphere, where the celestial sphere is represented by a three-dimensional framework of rings.

In astronomy, the meridian is the great circle passing through the celestial poles, as well as the zenith and nadir of an observer's location. Consequently, it contains also the north and south points on the horizon, and it is perpendicular to the celestial equator and horizon. Meridians, celestial and geographical, are determined by the pencil of planes passing through the Earth's rotation axis. For a location not on this axis, there is a unique meridian plane in this axial-pencil through that location. The intersection of this plane with Earth's surface defines two geographical meridians, and the intersection of the plane with the celestial sphere is the celestial meridian for that location and time.
In astronomical navigation, the intercept method, also known as Marcq St. Hilaire method, is a method of calculating an observer's position on Earth (geopositioning). It was originally called the azimuth intercept method because the process involves drawing a line which intercepts the azimuth line. This name was shortened to intercept method and the intercept distance was shortened to 'intercept'.
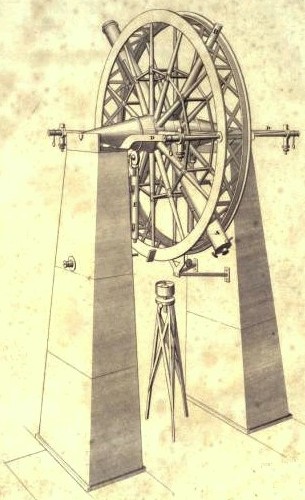
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis.
The keyhole problem, in the context of astronomy, refers to the difficulty that azimuth-elevation type telescopes or antenna gimbal systems encounter in crossing the zenith.

Sun path, sometimes also called day arc, refers to the daily and seasonal arc-like path that the Sun appears to follow across the sky as the Earth rotates and orbits the Sun. The Sun's path affects the length of daytime experienced and amount of daylight received along a certain latitude during a given season.
In spherical astronomy, the parallactic angle is the angle between the great circle through a celestial object and the zenith, and the hour circle of the object. It is usually denoted q. In the triangle zenith—object—celestial pole, the parallactic angle will be the position angle of the zenith at the celestial object. Despite its name, this angle is unrelated with parallax. The parallactic angle is zero or 180° when the object crosses the meridian.

The Rayleigh sky model describes the observed polarization pattern of the daytime sky. Within the atmosphere, Rayleigh scattering of light by air molecules, water, dust, and aerosols causes the sky's light to have a defined polarization pattern. The same elastic scattering processes cause the sky to be blue. The polarization is characterized at each wavelength by its degree of polarization, and orientation.

An azimuth compass is a nautical instrument used to measure the magnetic azimuth, the angle of the arc on the horizon between the direction of the Sun or some other celestial object and the magnetic north. This can be compared to the true azimuth obtained by astronomical observation to determine the magnetic declination, the amount by which the reading of a ship's compass must be adjusted to obtain an accurate reading. Azimuth compasses were important in the period before development of the reliable chronometers needed to determine a vessel's exact position from astronomical observations.
Many animals are able to navigate using the Sun as a compass. Orientation cues from the position of the Sun in the sky are combined with an indication of time from the animal's internal clock.
References
- ↑ N., N. "vertical circle, noun". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 2024-12-29.
First Known Use 1559
- ↑ Barbieri, Cesare (2007). Fundamentals of Astronomy. New York: Taylor & Francis. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-7503-0886-1.