
Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species. Because of the similarity of thinking and working with microorganisms other than bacteria, such as protozoa, fungi, and viruses, there has been a tendency for the field of bacteriology to extend as microbiology. The terms were formerly often used interchangeably. However, bacteriology can be classified as a distinct science.

A veterinarian (vet) is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, veterinarians also play a role in animal reproduction, health management, conservation, husbandry and breeding and preventive medicine like nutrition, vaccination and parasitic control as well as biosecurity and zoonotic disease surveillance and prevention.
Brucellosis is a highly contagious zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.

Selman Abraham Waksman was a Jewish Russian-born American inventor, Nobel Prize laureate, biochemist and microbiologist whose research into the decomposition of organisms that live in soil enabled the discovery of streptomycin and several other antibiotics. A professor of biochemistry and microbiology at Rutgers University for four decades, he discovered a number of antibiotics, and he introduced procedures that have led to the development of many others. The proceeds earned from the licensing of his patents funded a foundation for microbiological research, which established the Waksman Institute of Microbiology located on the Rutgers University Busch Campus in Piscataway, New Jersey (USA). In 1952, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for "ingenious, systematic and successful studies of the soil microbes that led to the discovery of streptomycin." Waksman and his foundation later were sued by Albert Schatz, one of his PhD students and the discoverer of streptomycin, for minimizing Schatz's role in the discovery.

Bartonella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, Bartonella species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight Bartonella species or subspecies are known to infect humans.

Stanley "Stan" Falkow was an American microbiologist and a professor of microbiology at Georgetown University, University of Washington, and Stanford University School of Medicine. Falkow is known as the father of the field of molecular microbial pathogenesis. He formulated molecular Koch's postulates, which have guided the study of the microbial determinants of infectious diseases since the late 1980s. Falkow spent over 50 years uncovering molecular mechanisms of how bacteria cause disease and how to disarm them. Falkow also was one of the first scientists to investigate antimicrobial resistance, and presented his research extensively to scientific, government, and lay audiences explaining the spread of resistance from one organism to another, now known as horizontal gene transfer, and the implications of this phenomenon on our ability to combat infections in the future.

Erysipelothrix is a genus of bacteria containing four described species, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, Erysipelothrix tonsillarum, Erysipelothrix inopinata and Erysipelothrix larvae. Additional species have been proposed based on DNA-DNA hybridization studies "The hallmark of Erysipelothrix is the presence of a type B cell wall, in which the peptide bridge is formed between amino acids at positions 2 and 4 of adjacent peptide side-chains and not, as in the vast majority of bacteria, between amino acids at positions 3 and 4."
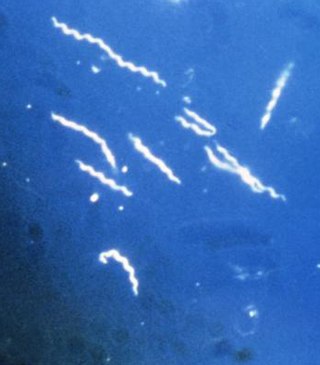
Borrelia is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of Borrelia cause relapsing fever, and are transmitted by ticks or lice, depending on the species of bacteria. A few Borrelia species as Candidatus Borrelia mahuryensis harbor intermediate genetic features between Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia. The genus is named after French biologist Amédée Borrel (1867–1936), who first documented the distinction between a species of Borrelia, B. anserina, and the other known type of spirochete at the time, Treponema pallidum. This bacterium must be viewed using dark-field microscopy, which make the cells appear white against a dark background. Borrelia species are grown in Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium. Of 52 known species of Borrelia, 20 are members of the Lyme disease group, 29 belong to the relapsing fever group, and two are members of a genetically distinct third group typically found in reptiles. A proposal has been made to split the Lyme disease group based on genetic diversity and move them to their own genus, Borelliella, but this change is not widely accepted. This bacterium uses hard and soft ticks and lice as vectors. Testing for the presence of the bacteria in a human includes two-tiered serological testing, including immunoassays and immunoblotting.
The Faculty of Veterinary Science is a faculty of the University of Pretoria. Founded in 1920, it is the second oldest veterinary faculty in Africa. With the exception of the faculties in Khartoum, and Cairo, all the other African faculties were established after 1960. It is the only one of its kind in South Africa and is one of 33 veterinary faculties in Africa.

Streptococcus canis is a group G beta-hemolytic species of Streptococcus. It was first isolated in dogs, giving the bacterium its name. These bacteria are characteristically different from Streptococcus dysgalactiae, which is a human-specific group G species that has a different phenotypic chemical composition. S. canis is important to the skin and mucosal health of cats and dogs, but under certain circumstances, these bacteria can cause opportunistic infections. These infections were known to afflict dogs and cats prior to the formal description of the species in Devriese et al., 1986. However, additional studies revealed cases of infection in other mammal species, including cattle and even humans. Instances of mortality from S. canis in humans are very low with only a few reported cases, while actual instances of infection may be underreported due to mischaracterizations of the bacteria as S. dysgalactiae. This species, in general, is highly susceptible to antibiotics, and plans to develop a vaccine to prevent human infections are currently being considered.
Brachyspira is a genus of bacteria classified within the phylum Spirochaetota.

Staphylococcus hyicus is a Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic bacterium in the genus Staphylococcus. It consists of clustered cocci and forms white circular colonies when grown on blood agar. S. hyicus is a known animal pathogen. It causes disease in poultry, cattle, horses, and pigs. Most notably, it is the agent that causes porcine exudative epidermitis, also known as greasy pig disease, in piglets. S. hyicus is generally considered to not be zoonotic, however it has been shown to be able to cause bacteremia and sepsis in humans.
Listeria ivanovii is a species of bacteria in the genus Listeria. The listeria are rod-shaped bacteria, do not produce spores, and become positively stained when subjected to Gram staining. Of the six bacteria species within the genus, L. ivanovii is one of the two pathogenic species. In 1955 Bulgaria, the first known isolation of this species was found from sheep. It behaves like L. monocytogenes, but is found almost exclusively in ruminants. The species is named in honor of Bulgarian microbiologist Ivan Ivanov. This species is facultatively anaerobic, which makes it possible for it to go through fermentation when there is oxygen depletion.
Pasteurella dagmatis is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Bacteria from this family cause zoonotic infections in humans. These infections manifest themselves as skin or soft tissue infections after an animal bite. It has been known to cause serious disease in immunocompromised patients.
Pasteurella anatis, also Gallibacterium anatis is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Bacteria from this family cause zoonotic infections in humans. These infections manifest themselves as skin or soft tissue infections after an animal bite. This species is found in chickens.

Antibiotic use in livestock is the use of antibiotics for any purpose in the husbandry of livestock, which includes treatment when ill (therapeutic), treatment of a group of animals when at least one is diagnosed with clinical infection (metaphylaxis), and preventative treatment (prophylaxis). Antibiotics are an important tool to treat animal as well as human disease, safeguard animal health and welfare, and support food safety. However, used irresponsibly, this may lead to antibiotic resistance which may impact human, animal and environmental health.
A bacteriologist is a microbiologist, or similarly trained professional, in bacteriology -- a subdivision of microbiology that studies bacteria, typically pathogenic ones. Bacteriologists are interested in studying and learning about bacteria, as well as using their skills in clinical settings. This includes investigating properties of bacteria such as morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry, phylogenetics, genomics and many other areas related to bacteria like disease diagnostic testing. Alongside human and animal healthcare providers, they may carry out various functions as medical scientists, veterinary scientists, or diagnostic technicians in locations like clinics, blood banks, hospitals, laboratories and animal hospitals. Bacteriologists working in public health or biomedical research help develop vaccines for public use.
Mycoplasma bovis is one of 126 species of genus Mycoplasma. It is the smallest living cell and anaerobic organism in nature. It does not contain any cell wall and is therefore resistant to penicillin and other beta lactam antibiotics.
Robert Earle Buchanan was an American bacteriologist and a professor and administrator at Iowa State University. He is known for his work on bacterial taxonomy.
Edwin George Hastings was an American professor of agricultural bacteriology, known for his work with Harry Luman Russell on bovine tuberculosis and applications of the tuberculin test to herds of cattle. Hastings was the president in 1923 of the American Society for Microbiology.











