
The governor of Victoria is the representative of the monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, in the Australian state of Victoria. The governor is one of seven viceregal representatives in the country, analogous to the governors of the other states, and the governor-general federally.

This article describes the history of the Australian colony and state of Victoria.
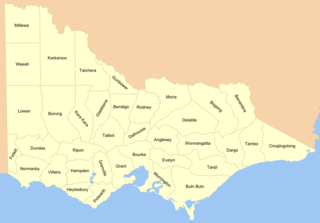
Cadastral divisions in Victoria are called counties, which are further subdivided into parishes and townships, for cadastral or land administration purposes. Cadastral divisions of county, parish and township form the basis for formal identification of the location of any piece of land in the state. There are 37 counties and 2004 parishes and 909 townships. Parishes were subdivided into sections of various sizes for sale as farming allotments, or designated as a town and then divided into sections and these subdivided into crown allotments. However, many parishes do not follow county borders, some being located in more than one county.

The Victorian Legislative Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Victoria in Australia; the upper house being the Victorian Legislative Council. Both houses sit at Parliament House in Spring Street, Melbourne.

The flag of Victoria, symbolising the state of Victoria in Australia, is a British Blue Ensign defaced by the state badge of Victoria in the fly. The badge is the Southern Cross surmounted by an imperial crown, which is currently the St Edward's Crown. The stars of the Southern Cross are white and range from five to eight points with each star having one point pointing to the top of the flag. The flag dates from 1870, with minor variations, the last of which was in 1953. It is the only Australian state flag not to feature the state badge on a round disc.

Charles Joseph La Trobe, CB, commonly Latrobe, was appointed in 1839 superintendent of the Port Phillip District of New South Wales and, after the establishment in 1851 of the colony of Victoria, he became its first lieutenant-governor.

The Parliament of Victoria is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of Victoria that follows a Westminster-derived parliamentary system. It consists of the Queen, represented by the Governor of Victoria, the Legislative Assembly and the Legislative Council. It has a fused executive drawn from members of both chambers. The parliament meets at Parliament House in the state capital Melbourne. The current Parliament was elected on 24 November 2018, sworn in on 19 December 2018 and is the 59th parliament in Victoria.

The Victoria State Government, also referred to as just the Victorian Government, is the state-level authority for Victoria, Australia. Like all state governments, it is formed by three independent branches: the executive, the judicial, and the parliament.

The Colony of New South Wales was a colony of the British Empire from 1788 to 1901, when it became a State of the Commonwealth of Australia. At its greatest extent, the colony of New South Wales included the present-day Australian states of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, Tasmania, and South Australia, the Northern Territory as well as New Zealand. The first "responsible" self-government of New South Wales was formed on 6 June 1856 with Sir Stuart Alexander Donaldson appointed by Governor Sir William Denison as its first Colonial Secretary.
The Australian Constitutions Act 1850, or Australian Colonies Government Act, formally known as the Act for the Better Government of Her Majesty's Australian Colonies (1850), was legislation enacted by the British Parliament which formally established the Colony of Victoria by separating the District of Port Phillip from the Colony of New South Wales. It was signed by Queen Victoria on 5 August 1850 and came into effect on 1 July 1851. It also altered the constitution of the Colony of New South Wales, and provided for similar constitutions to be set up in Van Diemen's Land (Tasmania) and South Australia.

Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi) and the most densely populated state in Australia. Victoria is bordered with New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south, the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the north-east and the semi-arid north-west.
The name of "Coroners Court" is the generic name given to proceedings in which a Coroner holds an inquest in Victoria.

The Constitutional history of Australia is the history of Australia's foundational legal principles. Australia's legal origins as a nation state began in the colonial era, with its legal system reliant initially upon a legal fiction of terra nullius to impose British law upon the colony of New South Wales. As the colonies expanded, Australia gradually began to achieve de facto independence. Over the years as a result the foundations of the Australian legal system gradually began to shift. This culminated in the Australia Act, an act formally ending legal ties with the UK.
The Australian state of Victoria is regarded as one of the most progressive jurisdictions with respect to the rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people.

Local government in the Australian state of Victoria consists of 79 local government areas (LGAs). Also referred to as municipalities, Victorian LGAs are classified as cities (34), shires (38), rural cities (6) and boroughs (1). In general, an urban or suburban LGA is called a city and is governed by a City Council, while a rural LGA covering a larger rural area is usually called a shire and is governed by a Shire Council. Local councils have the same administrative functions and similar political structures, regardless of their classification. They will typically have an elected council and usually a mayor or shire president responsible for chairing meetings of the council. The City of Melbourne has a Lord Mayor and Deputy Lord Mayor, who are directly elected, and in the other councils a mayor and deputy mayor are elected by fellow Councillors from among their own number. Since 2017, the mayor of the City of Greater Geelong has not been directly elected. In addition, there are also 10 unincorporated areas, consisting of small islands or ski resorts, which are administered either by the state government or management boards.

The Electoral district of Town of Melbourne was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council before it became part of the Colony of Victoria on 1 July 1851.

Peter Snodgrass was a pastoralist and politician in colonial Victoria, a member of the Victorian Legislative Council, and later, of the Victorian Legislative Assembly.
The Central Road Board was the first dedicated body for administering the construction of roads and bridges in Victoria, Australia. It came into being in 1853 when the Victorian Legislative Council passed An Act for making, and improving Roads in the Colony of Victoria, known as the Roads Act.

The Separation of Queensland was an event in 1859 in which the land that forms the present-day State of Queensland in Australia was excised from the Colony of New South Wales and created as a separate Colony of Queensland.

Government Gazette of the State of New South Wales, also known as the New South Wales Government Gazette, is the government gazette of the Government of New South Wales in Australia. The Gazette is managed by the New South Wales Parliamentary Counsel's Office.













