
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It occupies a long, narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of 756,096 square kilometers (291,930 sq mi), with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. Chile is the southernmost country in the world, the closest to Antarctica, and share land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about 1,250,000 square kilometers (480,000 sq mi) of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish.

This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the other lists of islands below.

South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America.

The British Antarctic Territory (BAT) is a sector of Antarctica claimed by the United Kingdom as one of its 14 British Overseas Territories, of which it is by far the largest by area. It comprises the region south of 60°S latitude and between longitudes 20°W and 80°W, forming a wedge shape that extends to the South Pole, overlapping the Antarctic claims of Argentina and Chile.

The Desventuradas Islands is a group of four small islands located 850 kilometres (530 mi) off the coast of Chile, northwest of Santiago in the Pacific Ocean. They are considered part of Insular Chile.

The Strait of Magellan, also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It was discovered and first traversed by Europeans by the Spanish expedition of Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan in 1520, after whom it is named. Prior to this, the strait had been navigated by canoe-faring indigenous peoples including the Kawésqar.
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Oceania, the Russian Far East, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.

Mataveri International Airport or Isla de Pascua Airport is at Hanga Roa on Rapa Nui /. The most remote airport in the world, it is 2,336 miles (3,759 km) from Santiago, Chile (SCL) which has scheduled flights to it on the Chilean carrier LATAM Chile. The runway starts just inland from the island's southeast coast at Mataveri, and nearly reaches the west coast, almost separating the mountain of Rano Kau from the rest of the island. The airport is the main point of entry for visitors to Easter Island. It has a transit lounge that was formerly used by passengers continuing to or returning from Papeete, Tahiti, which was serviced by LATAM until June 2020.

The Chonos Archipelago is a series of low, mountainous, elongated islands with deep bays, traces of a submerged Chilean Coast Range. Most of the islands are forested with little or no human settlement. The deep Moraleda Channel separates the islands of the Chonos Archipelago from the mainland of Chile and from Magdalena Island.

The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War, was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The conflict began with Spain's seizure of the guano-rich Chincha Islands in one of a series of attempts by Spain, under Isabella II, to reassert its influence over its former South American colonies. The war saw the use of ironclads, including the Spanish ship Numancia, the first ironclad to circumnavigate the world.

Punta Arenas is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antartica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Arenas". It is the largest city south of the 46th parallel south, and at the same time the most populous southernmost city in Chile and in the Americas, and due to its location, the coldest coastal city with more than 100,000 inhabitants in Latin America. It is one of the most southerly ports in the world, serving as an Antarctic gateway city.

Pacheco Island is an island between Vidal Gomez Island and Victoria Island at the north shore of the West entrance of the Strait of Magellan in Chile.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Chile:
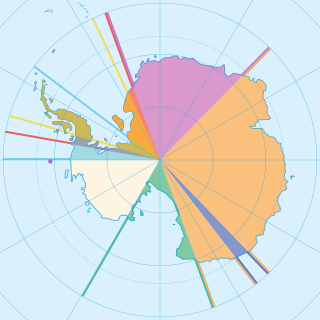
Seven sovereign states–Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom–have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as India, Italy, Pakistan, Russia, Ukraine, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries.
Victoria most commonly refers to:
The South American Board of New Football Federations, also known by its acronym COSANFF is the administrative and controlling body for non-FIFA football federations in South America. It was also initially affiliated with the now defunct N.F.-Board.
The 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup qualification for the FIBA Americas region, began in November 2017 and concluded in February 2019. The process determined the seven teams that would participate at the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup.












