Related Research Articles
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a measure of the lethal dose of a toxin, radiation, or pathogen. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of increased toxicity.
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; synthetic toxicants created by artificial processes are thus excluded. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from the word toxic.

Amanita muscaria, commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita, is a basidiomycete of the genus Amanita. It is also a muscimol mushroom. Native throughout the temperate and boreal regions of the Northern Hemisphere, Amanita muscaria has been unintentionally introduced to many countries in the Southern Hemisphere, generally as a symbiont with pine and birch plantations, and is now a true cosmopolitan species. It associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees.

Amanita phalloides, commonly known as the death cap, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Widely distributed across Europe, but now sprouting in other parts of the world, A. phalloides forms ectomycorrhizas with various broadleaved trees. In some cases, the death cap has been introduced to new regions with the cultivation of non-native species of oak, chestnut, and pine. The large fruiting bodies (mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps are generally greenish in colour with a white stipe and gills. Cap colour is variable, including white forms, and thus not a reliable identifier.

The genus Amanita contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is α-amanitin.

alpha-Amanitin or α-amanitin is a cyclic peptide of eight amino acids. It is possibly the most deadly of all the amatoxins, toxins found in several species of the mushroom genus Amanita, one being the death cap as well as the destroying angel, a complex of similar species, principally A. virosa and A. bisporigera. It is also found in the mushrooms Galerina marginata and Conocybe filaris. The oral LD50 of amanitin is approximately 0.1 mg/kg for rats.

Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom (Amanita phalloides). It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research. Though phallotoxins are highly toxic to liver cells, they add little to the toxicity of ingested death cap, as they are not absorbed through the gut.

Mushroom poisoning refers to harmful effects from ingestion of toxic substances present in a mushroom. These symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death in about 10 days. The toxins present are secondary metabolites produced by the fungus. Mushroom poisoning is usually the result of ingestion of wild mushrooms after misidentification of a toxic mushroom as an edible species. The most common reason for this misidentification is close resemblance in terms of colour and general morphology of the toxic mushrooms species with edible species. To prevent mushroom poisoning, mushroom gatherers familiarize themselves with the mushrooms they intend to collect, as well as with any similar-looking toxic species. The safety of eating wild mushrooms may depend on methods of preparation for cooking.

Amanita virosa, commonly known in Europe as the destroying angel, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in Europe, A. virosa associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. The large fruiting bodies appear in summer and autumn; the caps, stipes and gills are all white in colour.
Amatoxin is the collective name of a subgroup of at least eight related toxic compounds found in several genera of poisonous mushrooms, most notably the death cap and several other members of the genus Amanita, as well as some Conocybe, Galerina and Lepiota mushroom species. Amatoxins are lethal in even small doses, as little as half a mushroom. Unlike many ingested poisons, they are not destroyed by heat, so cooking the poisonous mushrooms does not diminish their lethality.

Amanita ocreata, commonly known as the death angel, destroying angel, angel of death or more precisely western North American destroying angel, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in the Pacific Northwest and California floristic provinces of North America, A. ocreata associates with oak trees. The large fruiting bodies generally appear in spring; the cap may be white or ochre and often develops a brownish centre, while the stipe, ring, gill and volva are all white.

beta-Amanitin or β-amanitin is a cyclic peptide comprising eight amino acids. It is part of a group of toxins called amatoxins, which can be found in several mushrooms belonging to the genus Amanita. Some examples are the death cap and members of the destroying angel complex, which includes A. virosa and A. bisporigera. Due to the presence of α-amanitin, β-amanitin, γ-amanitin and ε-amanitin these mushrooms are highly lethal to human beings.

Amanullinic acid is a cyclic nonribosomal peptide. It is an amatoxin, all of which are found in several members of the mushroom genus Amanita. Amanullinic acid is relatively non-toxic( oral LD50 >20 mg/kg in mice).

Amanita bisporigera is a deadly poisonous species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. It is commonly known as the eastern North American destroying angel or just as the destroying angel, although the fungus shares this latter name with three other lethal white Amanita species, A. ocreata, A. verna and A. virosa. The fruit bodies are found on the ground in mixed coniferous and deciduous forests of eastern North America south to Mexico, but are rare in western North America; the fungus has also been found in pine plantations in Colombia. The mushroom has a smooth white cap that can reach up to 10 cm (4 in) across, and a stipe, up to 14 cm (5.5 in) long by 1.8 cm (0.7 in) thick, that has a delicate white skirt-like ring near the top. The bulbous stipe base is covered with a membranous sac-like volva. The white gills are free from attachment to the stalk and crowded closely together. As the species name suggests, A. bisporigera typically bears two spores on the basidia, although this characteristic is not as immutable as was once thought.

Amanita exitialis, also known as the Guangzhou destroying angel, is a mushroom of the large genus Amanita. It is distributed in eastern Asia, and probably also in India where it has been misidentified as A. verna. Deadly poisonous, it is a member of section Phalloideae and related to the death cap A. phalloides. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) are white, small to medium-sized with caps up to 7 cm (2.8 in) in diameter, a somewhat friable ring and a firm volva. Unlike most agaric mushrooms which typically have four-spored basidia, the basidia of A. exitialis are almost entirely two-spored. Eight people were fatally poisoned in China after consuming the mushroom in 2000, and another 20 have been fatally poisoned since that incident. Molecular analysis shows that the species has a close phylogenetic relationship with three other toxic white Amanitas: A. subjunquillea var. alba, A. virosa and A. bisporigera.
Birtoxin is a neurotoxin from the venom of the South African Spitting scorpion. By changing sodium channel activation, the toxin promotes spontaneous and repetitive firing much like pyrethroid insecticides do
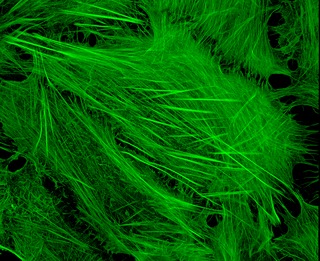
Cytoskeletal drugs are small molecules that interact with actin or tubulin. These drugs can act on the cytoskeletal components within a cell in three main ways. Some cytoskeletal drugs stabilize a component of the cytoskeleton, such as taxol which stabilizes microtubules or Phalloidin which stabilizes actin filaments. Others such as Cytochalasin D bind to actin monomers and prevent them from polymerizing into filaments. Drugs such as demecolcine act by enhancing the depolymerisation of already formed filaments. Some of these drugs have multiple effects on the cytoskeleton, for example Latrunculin both prevents actin polymerization as well as enhancing its rate of depolymerization. Typically the microtubule targeting drugs can be found in the clinic where they are used therapeutically in the treatment of some forms of cancer. As a result of the lack of specificity for specific type of actin the use of these drugs in animals results in unacceptable off target effects. Despite this the actin targeting compounds are still useful tools that can be used on a cellular level to help further our understanding of how this complex part of the cells internal machinery operates. For example, Phalloidin which has been conjugated with a fluorescent probe can be used for visualizing the filamentous actin in fixed samples.

Amanita sphaerobulbosa, commonly known as the Asian abrupt-bulbed Lepidella, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Amanitaceae. First described by mycologist Tsuguo Hongo in 1969, it is found in Southern Asia. The species was formerly consider synonymous with the North American lookalike Amanita abrupta, but that species has narrower spores, a persistent partial veil, and lacks the refractive contents found in the hyphae and inflated cells of A. sphaerobulbosa.

Amanita fuliginea, commonly known as the east Asian brown death cap, is a species of deadly poisonous mushroom in the family Amanitaceae. It was described as new to science by Japanese mycologist Tsuguo Hongo in 1953. Fruit bodies have convex, dark gray to blackish caps measuring 3–6 cm (1.2–2.4 in) in diameter. The gills, largely free from attachment to the stipe, are white and have short gills (lamellulae) interspersed. The spores are roughly spherical, amyloid, and typically measure 8–11 by 7–9.5 µm. The mushroom is common in China, where it has caused poisonings, a review of cases in southern China finding it had been responsible for the poisoning of 352 people, 79 of which died, between 1994 and 2012.
References
- ↑ Vetter, János (January 1998). "Toxins of Amanita phalloides". Toxicon. 36 (1): 13–24. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(97)00074-3. PMID 9604278.
- ↑ Michael J. Derelanko, ed. (2002). Handbook of toxicology (2. ed.). Boca Raton [u.a.]: CRC Press. ISBN 9780849303708.
- ↑ Brossi, Arnold, ed. (1991). The Alkaloids, 40. Burlington: Elsevier. ISBN 9780080865645.
- ↑ Turcotte, A; Gicquaud, C; Gendreau, M; St-Pierre, S (December 1984). "[Separation of the virotoxins of the mushroom Amanita virosa and comparative study of their interaction on actin in vitro]". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 62 (12): 1327–34. doi:10.1139/o84-169. PMID 6543329.
- ↑ Faulstich, H; Buku, A; Bodenmüller, H; Wieland, T (8 July 1980). "Virotoxins: actin-binding cyclic peptides of Amanita virosa mushrooms". Biochemistry. 19 (14): 3334–43. doi:10.1021/bi00555a036. PMID 6893271.
- ↑ Wong, Jack Ho (2013). "Fungal Toxins". In Kastin, Abba J. (ed.). The handbook of biologically active peptides Chapter 25-Fungal toxins (2. ed.). Amsterdam [u.a.]: Elsevier, Acad. Press. pp. 166–168. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-385095-9.00025-7. ISBN 978-012385095-9.
- ↑ LORANGER, A (December 1985). "Toxicity of peptides of Amanita virosa mushrooms in mice". Fundamental and Applied Toxicology. 5 (6): 1144–1152. doi:10.1016/0272-0590(85)90151-4. PMID 4092876.
