
A digital elevation model (DEM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems, and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps.

Aerial photography is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other flying object. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, balloons, blimps and dirigibles, rockets, pigeons, kites, parachutes, stand-alone telescoping and vehicle-mounted poles. Mounted cameras may be triggered remotely or automatically; hand-held photographs may be taken by a photographer.

Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena.
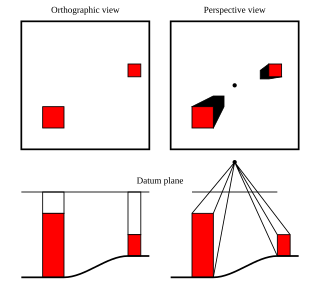
An orthophoto, orthophotograph or orthoimage is an aerial photograph or satellite imagery geometrically corrected ("orthorectified") such that the scale is uniform: the photo or image follows a given map projection. Unlike an uncorrected aerial photograph, an orthophoto can be used to measure true distances, because it is an accurate representation of the Earth's surface, having been adjusted for topographic relief, lens distortion, and camera tilt.

Aerial survey is a method of collecting geomatics or other imagery by using airplanes, helicopters, UAVs, balloons or other aerial methods. Typical types of data collected include aerial photography, Lidar, remote sensing and also geophysical data (such as aeromagnetic surveys and gravity. It can also refer to the chart or map made by analysing a region from the air. Aerial survey should be distinguished from satellite imagery technologies because of its better resolution, quality and atmospheric conditions. Today, aerial survey is sometimes recognized as a synonym for aerophotogrammetry, part of photogrammetry where the camera is placed in the air. Measurements on aerial images are provided by photogrammetric technologies and methods.

3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect data on its shape and possibly its appearance. The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.
Structure from Motion (SfM) is a photogrammetric range imaging technique for estimating three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional image sequences that may be coupled with local motion signals. It is studied in the fields of computer vision and visual perception. In biological vision, SfM refers to the phenomenon by which humans can recover 3D structure from the projected 2D (retinal) motion field of a moving object or scene.
SOCET SET is a software application that performs functions related to photogrammetry. It is developed and published by BAE Systems. SOCET SET was among the first commercial digital photogrammetry software programs. Prior to the development of digital solutions, photogrammetry programs were primarily analog or custom systems built for government agencies.

A stereoplotter uses stereo photographs to determine elevations. It has been the primary method to plot contour lines on topographic maps since the 1930s. Although the specific devices have advanced technologically, they are all based on the apparent change in position of a feature in the two stereo photographs.
IMAGINE Photogrammetry is a software application for performing photogrammetric operations on imagery and extracting information from imagery. IMAGINE Photogrammetry is significant because it is a leading commercial photogrammetry application that is used by numerous national mapping agencies, regional mapping authorities, various DOTs, as well as commercial mapping firms. Aside from commercial and government applications, IMAGINE Photogrammetry is widely used in academic research. Research areas include landslide monitoring, cultural heritage studies, and more.
TopoFlight is a three-dimensional flight planning software for photogrammetric flights.
3D data acquisition and reconstruction is the generation of three-dimensional or spatiotemporal models from sensor data. The techniques and theories, generally speaking, work with most or all sensor types including optical, acoustic, laser scanning, radar, thermal, seismic.
The Institute of Photogrammetry and GeoInformation (IPI) is a research institute that is part of the consortium of institutes operating under the aegis of Leibniz University situated in Hannover, Germany. The current research at IPI focuses both on terrestrial and extraterrestrial image interpretation. The basic themes of research revolve around computer vision, 3D geometry, image processing and machine learning. IPI contributes regularly with state-of-the-art methods to interpret high resolution images received from the HRSC probe of the Mars Express mission.

Pteryx UAV is a Polish Miniature UAV designed for civilian use, manufactured and sold by TriggerComposites. The machine can be classified both as flying RC model and pre-programmed vehicle. It has received a medal for innovative design in the category of micro-enterprises of the Podkarpacie region: Innowator Podkarpacia 2010.
Prof. em. Dr. Armin Gruen is, since 1984, professor and head of the Chair of photogrammetry at the Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP), Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich, Switzerland. Since 1 August 2009, he is retired and is now with the Chair of Information Architecture, ETH Zurich Faculty of Architecture. He is currently acting as a principal investigator on the Simulation Platform of the SEC-FCL in Singapore.
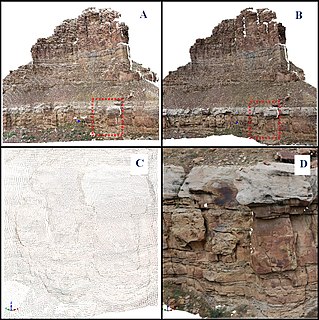
A digital outcrop model (DOM), also called a virtual outcrop model, is a digital 3D representation of the outcrop surface, mostly in a form of textured polygon mesh.

CATUAV S.L. is a technology-based private company that offers aerial services using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). Its headquarters are located in the Moià airfield in the BCN Drone Center, 40 km north of Barcelona, Spain.
DAT/EM Systems International is an Alaska-based company that develops digital photogrammetric mapping applications to extract and edit 3D vector terrain and object features from stereo imagery and point clouds. DAT/EM Systems International develops solutions for the photogrammetry, engineering & GIS industries.
metigo is a software application that performs image-based modelling and close range photogrammetry. It produces rectified imagery plans, true ortho-projections on planar, cylindric and conic surfaces, 3D photorealistic models, measurements from photography and mappings on a photographic base for uses in the cultural heritage sector, mainly conservation.

Pix4D is a Swiss company which started in 2011 as a spinoff of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Computer Vision Lab in Switzerland. and develops a suite of software products that use photogrammetry and computer vision algorithms to transform DSLR, fisheye, RGB, thermal and multispectral images into 3D maps and 3D modeling.










