Related Research Articles

General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G and 3G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was established by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.
Mobility management is one of the major functions of a GSM or a UMTS network that allows mobile phones to work. The aim of mobility management is to track where the subscribers are, allowing calls, SMS and other mobile phone services to be delivered to them.
Customized Applications for Mobile networks Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) is a set of standards designed to work on either a GSM core network or the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) network. The framework provides tools for operators to define additional features for standard GSM services/UMTS services. The CAMEL architecture is based on the Intelligent Network (IN) standards, and uses the CAP protocol. The protocols are codified in a series of ETSI Technical Specifications.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Alternative methods of delivering voice (VoIP) or other multimedia services have become available on smartphones, but they have not become standardized across the industry. IMS is an architectural framework that provides such standardization.
The IEEE 802.21 refers to Media Independent Handoff (MIH) and is an IEEE standard published in 2008. The standard supports algorithms enabling seamless handover between wired and wireless networks of the same type as well as handover between different wired and wireless network types also called Media independent handover (MIH) or vertical handover. Vertical handover was first introduced by Mark Stemn and Randy Katz at U C Berkeley. The standard provides information to allow handing over to and from wired 802.3 network to wireless 802.11, 802.15, 802.16, 3GPP and 3GPP2 networks through different handover mechanisms.

A VoIP phone or IP phone uses voice over IP technologies for placing and transmitting telephone calls over an IP network, such as the Internet. This is in contrast to a standard phone which uses the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Vertical handover or vertical handoff refers to a network node changing the type of connectivity it uses to access a supporting infrastructure, usually to support node mobility. For example, a suitably equipped laptop might be able to use both a high speed wireless LAN and a cellular technology for Internet access. Wireless LAN connections generally provide higher speeds, while cellular technologies generally provide more ubiquitous coverage. Thus the laptop user might want to use a wireless LAN connection whenever one is available, and to 'fall over' to a cellular connection when the wireless LAN is unavailable. Vertical handovers refer to the automatic fallover from one technology to another in order to maintain communication. This is different from a 'horizontal handover' between different wireless access points that use the same technology in that a vertical handover involves changing the data link layer technology used to access the network.
Generic Access Network (GAN) is a protocol that extends mobile voice, data and multimedia applications over IP networks. Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) is the commercial name used by mobile carriers for external IP access into their core networks. The latest generation system is named Wi-Fi Calling or VoWiFi by a number of handset manufacturers, including Apple and Samsung, a move that is being mirrored by carriers like T-Mobile US and Vodafone. The service is dependent on IMS, IPsec, IWLAN and ePDG.
Mobile VoIP or simply mVoIP is an extension of mobility to a Voice over IP network. Two types of communication are generally supported: cordless/DECT/PCS protocols for short range or campus communications where all base stations are linked into the same LAN, and wider area communications using 3G/4G protocols.
Text over IP is a means of providing a real-time text (RTT) service that operates over IP-based networks. It complements Voice over IP (VoIP) and Video over IP.

In telecommunications, a femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station, typically designed for use in a home or small business. A broader term which is more widespread in the industry is small cell, with femtocell as a subset. It connects to the service provider's network via broadband ; current designs typically support four to eight simultaneously active mobile phones in a residential setting depending on version number and femtocell hardware, and eight to sixteen mobile phones in enterprise settings. A femtocell allows service providers to extend service coverage indoors or at the cell edge, especially where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable. Although much attention is focused on WCDMA, the concept is applicable to all standards, including GSM, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, WiMAX and LTE solutions.
Dual-mode mobiles refer to mobile phones that are compatible with more than one form of data transmission or network.
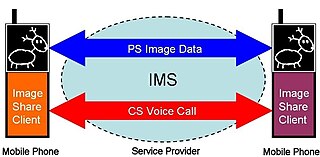
Image Share is a service for sharing images between users during a mobile phone call. It has been specified for use in a 3GPP-compliant cellular network by the GSM Association in the PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification.
Fixed–mobile convergence (FMC) is a change in telecommunications that removes differences between fixed and mobile networks.
A mobile broadband modem, also known as wireless modem or cellular modem, is a type of modem that allows a personal computer or a router to receive wireless Internet access via a mobile broadband connection instead of using telephone or cable television lines. A mobile Internet user can connect using a wireless modem to a wireless Internet Service Provider (ISP) to get Internet access.
Mobile data offloading is the use of complementary network technologies for delivering data originally targeted for cellular networks. Offloading reduces the amount of data being carried on the cellular bands, freeing bandwidth for other users. It is also used in situations where local cell reception may be poor, allowing the user to connect via wired services with better connectivity.
SunComm Technology is a Taiwan multinational computer technology and GSM Voice over IP gateway manufacturer. The main products in 2010 focused on GSM VoIP gateways & IP surveillance camera devices. Core members have been engaging in the communication & networks industry since 1977.
IMS is a set of specifications to offer multimedia services through IP protocol. This makes it possible to incorporate all kinds of services, such as voice, multimedia and data, on an accessible platform through any Internet connection.
ViLTE, an acronym for "Video over LTE", is a conversational video service based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) core network like VoLTE. It has specific profiles for the control and VoLTE of the video service and uses LTE as the radio access medium. The service as a whole is governed by the GSM Association in PRD IR.94.