
The Farman F.220 and its derivatives were thick-sectioned, high-winged, four engined French monoplanes from Farman Aviation Works. Based on the push-pull configuration proven by the F.211, design started in August 1925 and the first flight of the prototype was on 26 May 1932. The largest bomber to serve in France between the two world wars was the final F.222 variant. One variation was intended to be an airliner.

The Voisin III was a French World War I two-seat pusher biplane multi-purpose aircraft developed by Voisin in 1914 as a more powerful version of the 1912 Voisin L. It is notable for being the aircraft used for the first successful shooting down of an enemy aircraft on October 5, 1914, and to have been used to equip the first dedicated bomber units, in September 1914.

The Caudron R.4 was a French World War I twin-engine biplane reconnaissance/artillery cooperation aircraft and the progenitor of a series of successful aircraft that filled a variety of roles with the French Aéronautique Militaire.

Aéroplanes Voisin was a French aircraft manufacturing company established in 1905 by Gabriel Voisin and his brother Charles, and was continued by Gabriel after Charles died in an automobile accident in 1912; the full official company name then became Société Anonyme des Aéroplanes G. Voisin. During World War I, it was a major producer of military aircraft, notably the Voisin III. After the war Gabriel Voisin abandoned the aviation industry, and set up a company to design and produce luxury automobiles, called Avions Voisin.

The Caudron R.11, was a French three-seat twin-engine long range escort fighter biplane developed and produced by Caudron during the First World War.

The SPAD S.XII or SPAD 12 was a French single-seat biplane fighter aircraft of the First World War developed from the successful SPAD VII by Louis Béchereau, chief designer of the Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés (SPAD).

The Letord Let.5 was probably the most numerous of a family of 3-seat reconnaissance bombers, designed and built in France from 1916, originally to an A3 specification from the STAé.

The Nieuport 14 was a military reconnaissance sesquiplane produced in France during the First World War. The French Army deployed it in 1916 but the type was quickly withdrawn from front-line service.

The Tebaldi-Zari was an Italian fighter prototype of 1919. The Breda company later acquired the rights to it.
The Adolphe Bernard AB was a twin-engined French biplane aircraft, built near the end of the First World War. Ten AB 1 BN2 bombers were produced for the Armée de l'Air but did not reach squadron service; post-war, two civil derivatives were considered but only one aircraft was built.

The Voisin Triplanes were large experimental bombers built by Voisin in 1915 and 1916. After unsuccessful trials of the 1915 prototype a modified version with more powerful engines was built in 1916, as the Voisin E.28, but the type did not enter production.
The Voisin VI or Voisin Type 6 was a French pusher biplane bomber aircraft of World War I.
The Tellier T.2 was a French two-seat patrol biplane flying-boat built by Société Alphonse Tellier et Cie à Neuilly (hull) and Voisin (wings). The wooden-hull flying boat used a 150 kW (200 hp) Hispano-Suiza 8Ba engine and was first flown in June 1916.
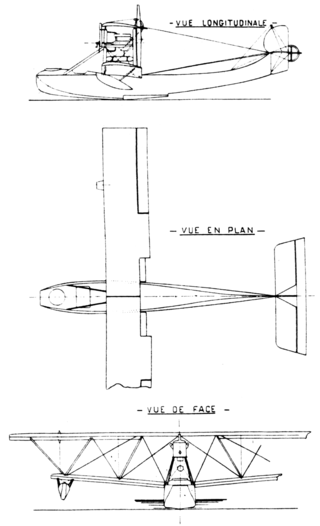
The Tellier T.3 was a French two-seat patrol biplane flying-boat designed and built by Société Alphonse Tellier et Cie à Neuilly (Tellier) and also produced by Société Anonyme des Établissements Nieuport (Nieuport).

The Blériot Bl.71 BN.3 was a large First World War French heavy biplane night bomber designed and built by Blériot to the BN.3 three-seat night bomber specification. Only a single prototype was built, which was damaged beyond repair on 15 May 1918.

The Blériot Bl.73, Bl.74, Bl.75 and Bl.76 were large First World War French biplanes designed and built by Blériot. The Bl.73 was built to the BN.3 three-seat night bomber specification, the Bl.74 was to be a bomber-transport, the Bl.75 Aerobus was to be an airliner, while the unbuilt Bl.76 was intended for the BN.4 four-seat night bomber specification. Aside from the Bl.76, just one prototype was built of each type, with both Bl.73 and Bl.74 prototypes being lost in accidents while on test flights.

The Voisin VIII is a French two-seat biplane pusher which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37mm Hotchkiss cannon, and the other as a conventional bomber. Problems with the Peugeot 8Aa engine led to a short operational career with front line units before being superseded by the Voisin X, which aside from the installation of a new Renault engine, was nearly identical to the VIII.

The Voisin X was a French two-seat pusher biplane which was built in two versions, one fitted with a 37 mm (1.46 in) Hotchkiss cannon, and the other as a conventional night bomber. Problems with the Peugeot engine in the previous Voisin VIII led to the installation of a new Renault engine of greater power and reliability, but the new aircraft was otherwise nearly identical to the VIII. Despite its obsolescence, it would make up the bulk of front line night bomber escadrilles until the end of the war.

The Voisin IV was a French two-seat bomber and ground attack aircraft of World War I.
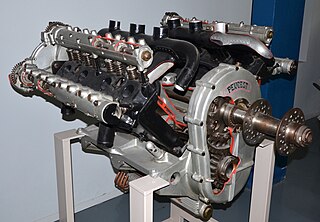
The Peugeot 8Aa, or L112, is a water-cooled V8 aircraft engine that equipped the Voisin VIII bombers and escort fighters built during World War I.



















