
SimpleText is the native text editor for the Apple classic Mac OS. SimpleText allows text editing and text formatting, fonts, and sizes. It was developed to integrate the features included in the different versions of TeachText that were created by various software development groups within Apple Computer.
Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface (API) for its desktop operating system macOS.

GNUstep is a free software implementation of the Cocoa Objective-C frameworks, widget toolkit, and application development tools for Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows. It is part of the GNU Project.
Carbon was one of two primary C-based application programming interfaces (APIs) developed by Apple for the macOS operating system. Carbon provided a good degree of backward compatibility for programs that ran on Mac OS 8 and 9. Developers could use the Carbon APIs to port (“carbonize”) their “classic” Mac applications and software to the Mac OS X platform with little effort, compared to porting the app to the entirely different Cocoa system, which originated in OPENSTEP. With the release of macOS 10.15 Catalina, the Carbon API was officially discontinued and removed, leaving Cocoa as the sole primary API for developing macOS applications.
A resource fork is a fork of a file on Apple's classic Mac OS operating system that is used to store structured data. It is one of the two forks of a file, along with the data fork, which stores data that the operating system treats as unstructured. Resource fork capability has been carried over to the modern macOS for compatibility.
QuickDraw was the 2D graphics library and associated application programming interface (API) which is a core part of classic Mac OS. It was initially written by Bill Atkinson and Andy Hertzfeld. QuickDraw still existed as part of the libraries of Mac OS X, but had been largely superseded by the more modern Quartz graphics system. In Mac OS X Tiger, QuickDraw has been officially deprecated. In Mac OS X Leopard applications using QuickDraw cannot make use of the added 64-bit support. In OS X Mountain Lion, QuickDraw header support was removed from the operating system. Applications using QuickDraw still ran under OS X Mountain Lion to macOS High Sierra; however, the current versions of Xcode and the macOS SDK do not contain the header files to compile such programmes.
FileMaker is a cross-platform relational database application developed by Claris International, a subsidiary of Apple Inc. It integrates a database engine with a graphical user interface (GUI) and security features, allowing users to visually modify a database. Versions for desktops, servers, iOS, and web-delivery have been released.

AppleWorks was an integrated office suite containing a word processor, database, and spreadsheet. It was developed by Rupert Lissner for Apple Computer, originally for the Apple II and launched in 1984. Many enhancements for AppleWorks were created, the most popular being the TimeOut series from Beagle Bros which extended the life of the Apple II version of AppleWorks. Appleworks was later reworked for the Macintosh platform.

System 7 is the seventh major release of the classic Mac OS operating system for Macintosh computers, made by Apple Computer. It was launched on May 13, 1991, to succeed System 6 with virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, TrueType fonts, the Force Quit dialog, and an improved user interface.
QuickDraw GX was a replacement for the QuickDraw (QD) 2D graphics engine and Printing Manager inside the classic Mac OS. Its underlying drawing platform was an object oriented, resolution-independent, retained mode system, making it much easier for programmers to perform common tasks. Additionally, GX added various curve-drawing commands that had been lacking from QD, as well as introducing TrueType as its basic font system.
Nisus Writer is a word processor program for Apple Macs, made by California-based Nisus Software, Inc. The program is nowadays available in two varieties: Nisus Writer Express and Nisus Writer Pro.
WorldScript is the multilingual text rendering engine for Apple Macintosh's classic Mac OS, before Mac OS X was introduced.

Kid Pix is a bitmap drawing program designed for children. Originally created by Craig Hickman, it was first released for the Macintosh in 1989 and subsequently published in 1991 by Broderbund. Hickman was inspired to create Kid Pix after watching his son Ben struggle with MacPaint, and thus the main idea behind its development was to create a drawing program that would be very simple to use.

Rhapsody is an operating system that was developed by Apple Computer after its purchase of NeXT in the late 1990s. It is the fifth major release of the Mach-based operating system that was developed at NeXT in the late 1980s, previously called OPENSTEP and NEXTSTEP. Rhapsody was targeted to developers for a transition period between the Classic Mac OS and Mac OS X. Rhapsody represented a new and exploratory strategy for Apple, more than an operating system, and runs on x86-based PCs and on Power Macintosh.
Apple's Macintosh computer supports a wide variety of fonts. This support was one of the features that initially distinguished it from other systems.
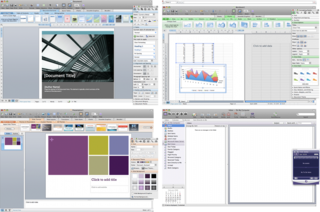
Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac is a version of the Microsoft Office productivity suite for Mac OS X. It supersedes Office 2004 for Mac and is the Mac OS X equivalent of Office 2007. Office 2008 was developed by Microsoft's Macintosh Business Unit and released on January 15, 2008. Office 2008 was followed by Microsoft Office for Mac 2011 released on October 26, 2010, requiring a Mac with an Intel processor and Mac OS version 10.5 or higher. Office 2008 is also the last version to feature Entourage, which was replaced by Outlook in Office 2011. Microsoft stopped supporting Office 2008 on April 9, 2013.

FutureBasic is a free BASIC compiler for Apple Inc.'s Macintosh.

Mac OS is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.








