Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard, is a text encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 of the standard defines 154998 characters and 168 scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts.

UTF-16 (16-bit Unicode Transformation Format) is a character encoding method capable of encoding all 1,112,064 valid code points of Unicode. The encoding is variable-length as code points are encoded with one or two 16-bitcode units. UTF-16 arose from an earlier obsolete fixed-width 16-bit encoding now known as UCS-2 (for 2-byte Universal Character Set), once it became clear that more than 216 (65,536) code points were needed, including most emoji and important CJK characters such as for personal and place names.

NeXTSTEP is a discontinued object-oriented, multitasking operating system based on the Mach kernel and the UNIX-derived BSD. It was developed by NeXT Computer, founded by Steve Jobs, in the late 1980s and early 1990s and was initially used for its range of proprietary workstation computers such as the NeXTcube. It was later ported to several other computer architectures.
Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface (API) for its desktop operating system macOS.
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control over scriptable Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in all versions of macOS as part of a package of system automation tools. The term "AppleScript" may refer to the language itself, to an individual script written in the language, or, informally, to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.
OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. Derived from TrueType, it retains TrueType's basic structure but adds many intricate data structures for describing typographic behavior. OpenType is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.

The Unicode Consortium is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization incorporated and based in Mountain View, California, U.S. Its primary purpose is to maintain and publish the Unicode Standard which was developed with the intention of replacing existing character encoding schemes that are limited in size and scope, and are incompatible with multilingual environments.
A text file is a kind of computer file that is structured as a sequence of lines of electronic text. A text file exists stored as data within a computer file system.

Pango is a text layout engine library which works with the HarfBuzz shaping engine for displaying multi-language text.
Tasman is a discontinued browser engine developed by Microsoft for inclusion in the Macintosh version of Internet Explorer 5. Tasman was an attempt to improve support for web standards, as defined by the World Wide Web Consortium. At the time of its release, Tasman was seen as the layout engine with the best support for web standards such as HTML and CSS. Internet Explorer for Mac is no longer supported, but newer versions of Tasman were incorporated in some other Microsoft products.
The Apple Type Services for Unicode Imaging (ATSUI) is the set of services for rendering Unicode-encoded text introduced in Mac OS 8.5 and carried forward into Mac OS X.
The WASTE is an Apple Macintosh text editing software library. WASTE helps Macintosh programmers include advanced text display and editing in their applications.
International Components for Unicode (ICU) is an open-source project of mature C/C++ and Java libraries for Unicode support, software internationalization, and software globalization. ICU is widely portable to many operating systems and environments. It gives applications the same results on all platforms and between C, C++, and Java software. The ICU project is a technical committee of the Unicode Consortium and sponsored, supported, and used by IBM and many other companies. ICU has been included as a standard component with Microsoft Windows since Windows 10 version 1703.
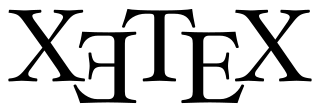
XeTeX is a TeX typesetting engine using Unicode and supporting modern font technologies such as OpenType, Graphite and Apple Advanced Typography (AAT). It was originally written by Jonathan Kew and is distributed under the X11 free software license.
MacApp is the object oriented application framework for Apple Computer's discontinued classic Mac OS. Released in 1985, it transitioned from Object Pascal to C++ in 1991's version 3.0 release, which offered support for much of System 7's new functionality. MacApp was used for a variety of major applications, including Adobe Photoshop and SoftPress Freeway. Microsoft's MFC and Borland's OWL were both based directly on MacApp concepts.
Apple's Macintosh computer supports a wide variety of fonts. This support was one of the features that initially distinguished it from other systems.
Mark Edward Davis is an American specialist in the internationalization and localization of software and the co-founder and chief technical officer of the Unicode Consortium, previously serving as its president until 2022.

Unicode input is method to add a specific Unicode character to a computer file; it is a common way to input characters not directly supported by a physical keyboard. Characters can be entered either by selecting them from a display, by typing a certain sequence of keys on a physical keyboard, or by drawing the symbol by hand on touch-sensitive screen. In contrast to ASCII's 96 element character set, Unicode encodes hundreds of thousands of graphemes (characters) from almost all of the world's written languages and many other signs and symbols besides.
The implementation of emojis on different platforms took place across a three-decade period, starting in the 1990s. Today, the exact appearance of emoji is not prescribed but can vary between fonts and platforms, much like different typefaces.