BeOS is a discontinued operating system for personal computers that was developed by Be Inc. It was conceived for the company's BeBox personal computer which was released in 1995. BeOS was designed for multitasking, multithreading, and a graphical user interface. The OS was later sold to OEMs, retail, and directly to users; its last version was released as freeware.
A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders. The most common operations performed on files or groups of files include creating, opening, renaming, copying, moving, deleting and searching for files, as well as modifying file attributes, properties and file permissions. Folders and files may be displayed in a hierarchical tree based on their directory structure.

Mac OS X Server is a series of discontinued Unix-like server operating systems developed by Apple Inc. based on macOS. It provided server functionality and system administration tools, and tools to manage both macOS-based computers and iOS-based devices, network services such as a mail transfer agent, AFP and SMB servers, an LDAP server, and a domain name server, as well as server applications including a Web server, database, and calendar server.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).

Cyberdog was an OpenDoc-based Internet suite of applications, developed by Apple Computer for the Mac OS line of operating systems. It was introduced as a beta in February 1996 and abandoned in March 1997. The last version, Cyberdog 2.0, was released on April 28, 1997. It worked with later versions of System 7 as well as the Mac OS 8 and Mac OS 9 operating systems.

Mac OS 9 is the ninth and final major release of Apple's classic Mac OS operating system, which was succeeded by Mac OS X 10.0 in 2001, starting the Mac OS X family of operating systems. Introduced on October 23, 1999, it was promoted by Apple as "The Best Internet Operating System Ever", highlighting Sherlock 2’s Internet search capabilities, integration with Apple's free online services known as iTools and improved Open Transport networking. While Mac OS 9 lacks protected memory and full pre-emptive multitasking, lasting improvements include the introduction of an automated Software Update engine and support for multiple users.

Bonjour is Apple's implementation of zero-configuration networking (zeroconf), a group of technologies that includes service discovery, address assignment, and hostname resolution. Bonjour locates devices such as printers, other computers, and the services that those devices offer on a local network using multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) service records.

iChat is a discontinued instant messaging software application developed by Apple Inc. for use on its Mac OS X operating system. It supported instant text messaging over XMPP/Jingle or OSCAR (AIM) protocol, audio and video calling, and screen-sharing capabilities. It also allowed for local network discussion with users discovered through Bonjour protocols.

Mac OS X 10.0 is the first major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system. It was released on March 24, 2001, for a price of $129 after a public beta.
The Apple Filing Protocol (AFP), formerly AppleTalk Filing Protocol, is a proprietary network protocol, and part of the Apple File Service (AFS), that offers file services for macOS, classic Mac OS, and Apple II computers. In OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion and earlier, AFP was the primary protocol for file services. Starting with OS X 10.9 Mavericks, Server Message Block (SMB) was made the primary file sharing protocol, with the ability to run an AFP server removed later in macOS 11 Big Sur. AFP supports Unicode file names, POSIX and access-control list permissions, resource forks, named extended attributes, and advanced file locking.
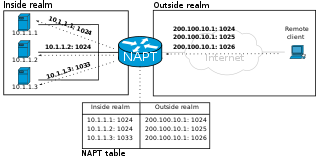
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.

Cyberduck is an open-source client for FTP and SFTP, WebDAV, and cloud storage, available for macOS and Windows licensed under the GPL. Cyberduck is written in Java and C# using the Cocoa user interface framework on macOS and Windows Forms on Windows. It supports FTP/TLS, using AUTH TLS as well as directory synchronization. The user interacts with the user interface (GUI), including file transfer by drag and drop and notifications via Growl. It is also able to open some files in external text editors.

FileZilla is a free and open-source, cross-platform FTP application, consisting of FileZilla Client and FileZilla Server. Clients are available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Both server and client support FTP and FTPS, while the client can in addition connect to SFTP servers. FileZilla's source code is hosted on SourceForge.
Microsoft Mail was the name given to several early Microsoft e-mail products for local area networks, primarily two architectures: one for Macintosh networks, and one for PC architecture-based LANs. All were eventually replaced by the Exchange and Outlook product lines.
MobileMe is a discontinued subscription-based collection of online services and software offered by Apple Inc. All services were gradually transitioned to and eventually replaced by the free iCloud, and MobileMe ceased on June 30, 2012, with transfers to iCloud being available until July 31, 2012, or data being available for download until that date, when the site finally closed completely. On that date all data was deleted, and email addresses of accounts not transferred to iCloud were marked as unused.
InterCon Systems Corporation was founded in April 1988 by Kurt D. Baumann and Mikki Barry to produce software to connect Macintosh computers in environments that were not Macintosh-exclusive. At the time, there was no real concept of the Internet and there was still a question of whether the TCP/IP protocols or OSI protocols would be adopted widely. Over the next 9 years, the company grew from three employees to over 100 and sold software in the US, Europe and Japan.

Classilla is a Gecko-based Internet suite for PowerPC-based classic Macintosh operating systems, essentially an updated descendant of the defunct Mozilla Application Suite by way of the Mac OS port maintained in the aborted WaMCom project. The name is a portmanteau of Classic, and Mozilla.

Commander One is a dual-pane file manager designed for macOS. Developed by Electronic Team, Inc., the software is created entirely in Swift and aims to provide users with a tool to navigate, manage, and manipulate files and folders on their Mac computers. The application offers a wide range of features for both casual and professional users.










